
Transgender Survey Harassment, Poverty, and the Intersection
Trangender survey harassment poverty – Transgender survey harassment poverty is a complex issue, highlighting the multifaceted challenges faced by transgender individuals. This exploration delves into the intersection of gender identity and economic hardship, examining how harassment directly impacts financial stability and access to resources. The survey’s role in understanding and addressing these issues is crucial.
This survey investigates the profound link between transgender experiences and poverty. It analyzes how various forms of discrimination, including harassment and lack of access to resources, contribute to financial instability. We will examine the data, explore the systemic factors driving these disparities, and discuss the vital role of support systems and policies in creating a more equitable future for transgender individuals.
Intersection of Gender Identity and Poverty: Trangender Survey Harassment Poverty
Transgender individuals often face significant economic hardship, a complex issue deeply intertwined with systemic discrimination and social stigma. This intersection of gender identity and poverty creates a multifaceted challenge, impacting every aspect of their lives, from housing and employment to access to healthcare and essential resources. Understanding the root causes and consequences of this disparity is crucial to fostering a more equitable and inclusive society.The disparity between transgender individuals and the general population regarding economic stability is substantial.
Numerous studies demonstrate a stark correlation between gender identity and economic hardship. Data consistently shows that transgender people experience disproportionately higher rates of unemployment, poverty, and homelessness compared to cisgender populations. This disparity is not simply a matter of individual choices; it’s a consequence of systemic barriers and societal biases.
Systemic Factors Contributing to Economic Hardship
Transgender individuals face a multitude of systemic barriers that significantly impact their economic well-being. Discrimination in employment, housing, and access to healthcare are key contributors to this economic disparity. Many transgender individuals face significant challenges in securing stable employment due to bias and prejudice. They may be overlooked for promotions, denied opportunities, or outright fired simply for their gender identity.
Similar issues arise in housing, where landlords may refuse to rent to transgender individuals or subject them to unfair terms and conditions. Limited access to healthcare can also exacerbate economic hardship, as medical transitions and related expenses can place a significant strain on an individual’s financial resources.
Impact of Social Stigma and Lack of Resources
Social stigma and lack of access to vital resources significantly compound the economic challenges faced by transgender individuals. The social stigma surrounding gender identity can lead to isolation, discrimination, and even violence, all of which can hinder their ability to secure and maintain employment. Lack of access to resources, such as affordable healthcare, mental health services, and legal assistance, further exacerbates these issues.
The lack of understanding and acceptance from employers, landlords, and the community can make it challenging to navigate daily life, affecting one’s ability to work and to live.
It’s disheartening to see the ongoing harassment and poverty faced by transgender individuals in surveys. While the struggles are real, they don’t define the whole picture. For example, the recent interest in trading Blues player Pavel Buchnevich ( blues pavel buchnevich trade interest ) highlights the complexities of human interest in sports and business. Ultimately, the issues of transgender survey harassment and poverty remain deeply concerning and deserve continued attention and action.
Discrimination Experienced by Transgender Individuals
Discrimination against transgender individuals manifests in various forms, often leading to significant economic hardship. The following table highlights the types of discrimination, their impact on poverty, and illustrative examples.
| Type of Discrimination | Impact on Poverty | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Employment Discrimination | Loss of income, reduced job opportunities, difficulty securing stable employment | Refusal to hire, denial of promotions, unfair termination due to gender identity |
| Housing Discrimination | Increased homelessness risk, higher housing costs, instability | Landlords refusing to rent, unfair lease terms based on gender identity, discrimination in access to affordable housing programs |
| Healthcare Discrimination | Delayed or denied medical care, increased medical costs, health disparities | Discrimination in access to gender-affirming care, denial of coverage for transition-related procedures, lack of understanding from healthcare providers |
| Social Stigma and Discrimination | Reduced social support, isolation, potential for violence, decreased access to resources | Harassment, bullying, discrimination in social settings, denial of community support programs |
Harassment and its Economic Consequences
Transgender individuals face significant economic hardship due to harassment, a pervasive issue that often goes unreported and under-addressed. This harassment manifests in various forms, impacting not only their mental well-being but also their financial stability and opportunities. Understanding the economic consequences is crucial for advocating for policies and support systems that protect and empower transgender individuals.Harassment, in its various forms, creates a climate of fear and instability, directly affecting transgender individuals’ ability to participate fully in society and achieve economic self-sufficiency.
The direct and indirect costs associated with harassment can range from lost wages to medical expenses and mental health treatments, ultimately creating a cycle of disadvantage. This cycle disproportionately impacts individuals from marginalized socioeconomic backgrounds, exacerbating existing inequalities.
Types of Harassment Faced by Transgender Individuals
Transgender individuals experience a wide range of harassment, including verbal abuse, physical assault, discrimination in housing and employment, and online abuse. These forms of harassment often intersect with other forms of discrimination, creating a compounding effect on the individual’s economic well-being. Discrimination in housing, for example, can lead to homelessness, which in turn creates further financial strain.
Direct Economic Costs of Harassment
The direct economic costs of harassment encompass tangible losses, including lost wages due to time off work for seeking medical attention or avoiding potentially dangerous situations. Medical expenses for physical injuries sustained during assaults or for mental health treatment related to trauma are significant. In cases of job loss due to discrimination or harassment, the individual loses a primary source of income, leading to financial instability and potential homelessness.
For example, a transgender individual who is denied employment due to their gender identity loses potential income and benefits, such as health insurance and retirement savings.
Indirect Economic Costs of Harassment
Indirect economic costs encompass the long-term effects of harassment on an individual’s well-being and ability to participate in the economy. The stress and anxiety caused by harassment can lead to decreased productivity at work, impacting the individual’s ability to maintain employment. Mental health issues stemming from harassment often necessitate expensive treatment, further straining the individual’s finances. Reduced educational opportunities due to harassment can also limit future earning potential.
For instance, a transgender student who faces constant bullying may be discouraged from pursuing higher education, resulting in lower lifetime earning potential.
Comparative Analysis of Economic Burdens Across Socioeconomic Backgrounds
The economic burdens of harassment disproportionately affect transgender individuals from marginalized socioeconomic backgrounds. Those with fewer financial resources are less able to absorb the costs associated with harassment, such as medical expenses and lost wages. They may also lack access to legal resources and support networks, further exacerbating their economic hardship. For example, a transgender individual in poverty who is assaulted may lack the financial means to seek medical attention, leading to long-term health problems and further financial instability.
Impact on Educational Opportunities and Employment Prospects
Harassment significantly impacts transgender individuals’ educational opportunities and employment prospects. Fear of harassment can deter transgender individuals from pursuing higher education or entering certain fields of employment. This can lead to a limited career path and reduced earning potential. For example, a transgender student may avoid applying to certain universities or specific majors due to fear of discrimination or harassment.
Similarly, a transgender individual may be less likely to apply for jobs in certain sectors due to the fear of discrimination or harassment.
Table Illustrating Forms of Harassment and Economic Costs
| Form of Harassment | Frequency (estimated) | Estimated Economic Costs |
|---|---|---|
| Verbal Abuse | High | Lost wages, mental health treatment, reduced productivity |
| Physical Assault | Moderate | Medical expenses, lost wages, mental health treatment, legal fees |
| Discrimination in Housing | Moderate | Moving expenses, lost housing stability, mental health treatment, lost income |
| Discrimination in Employment | Moderate | Lost wages, job search costs, mental health treatment, lost benefits |
| Online Abuse | High | Mental health treatment, time spent dealing with abuse, lost productivity, potential legal fees |
Access to Resources and Support Systems
Navigating the complexities of gender identity often intersects with systemic inequalities, particularly poverty and harassment. This intersection creates significant barriers to accessing essential resources and support systems, impacting transgender individuals’ well-being and perpetuating cycles of disadvantage. Understanding these barriers and the vital role of support systems is crucial to fostering a more equitable environment.The lack of accessible resources for transgender individuals significantly exacerbates the challenges they face in overcoming poverty and harassment.
This lack of access often results in poorer health outcomes, limited educational opportunities, and restricted employment prospects. Effective support systems are critical in mitigating these negative impacts, offering guidance, protection, and empowerment.
The struggles faced by transgender individuals, including harassment and poverty stemming from survey data, are often overlooked. It’s easy to get caught up in the everyday, but issues like these need constant attention. Thankfully, uplifting music like the playlist playlist sza norah jones ag cook can provide a much-needed escape and reminder that we’re all connected.
Ultimately, combating the systemic issues affecting transgender people requires ongoing support and advocacy.
Barriers to Accessing Resources
Transgender individuals encounter numerous obstacles in accessing vital resources, stemming from discrimination, societal stigma, and a lack of culturally competent services. These barriers often include bureaucratic hurdles, financial constraints, and a lack of awareness regarding available support systems. For instance, navigating complex healthcare systems can be daunting, particularly for those lacking the necessary knowledge or financial means to navigate the process effectively.
The Role of Support Systems
Support systems play a critical role in mitigating the negative consequences of poverty and harassment for transgender individuals. These systems provide crucial emotional support, practical assistance, and advocacy. For example, community-based organizations often offer crucial financial aid, legal counsel, and safe spaces for social interaction.
Facing transgender survey harassment and poverty is a serious issue, and unfortunately, it’s often intertwined with health risks. Protecting yourself from those risks is crucial, and understanding things like condon prevencion vih sida is a vital part of overall well-being. Ultimately, tackling the systemic issues that contribute to transgender survey harassment and poverty is key to creating a safer and more equitable environment for everyone.
Healthcare Access and its Impact on Poverty, Trangender survey harassment poverty
Access to gender-affirming healthcare is often limited, particularly in regions with limited resources or restrictive policies. The cost of such care can be prohibitive for individuals living in poverty, further exacerbating their financial struggles. Furthermore, the lack of culturally competent healthcare providers can lead to misdiagnosis, inadequate treatment, and negative health outcomes.
Legal Aid and its Relationship to Poverty
Legal aid plays a vital role in protecting the rights of transgender individuals and ensuring access to justice. However, legal aid services are often insufficient or inaccessible to many, particularly those living in poverty. This lack of access can lead to the denial of essential rights, perpetuation of harassment, and further economic disadvantage.
Financial Assistance and its Impact on Poverty
Financial assistance programs can significantly impact transgender individuals’ lives, providing crucial support for basic needs like housing, food, and transportation. However, many transgender individuals face significant challenges in accessing such programs due to a lack of awareness, bureaucratic obstacles, or discrimination. For example, eligibility criteria for housing assistance may not accommodate the specific needs of transgender individuals.
Comparison of Support Systems Across Regions
Support systems for transgender individuals vary significantly across different regions and communities. In some regions, robust community-based organizations and government initiatives offer comprehensive support, while in others, resources are limited or nonexistent. Cultural factors and societal attitudes also play a significant role in shaping the availability and effectiveness of support systems.
Table: Availability and Effectiveness of Support Services
| Demographic Group | Healthcare Access | Legal Aid Availability | Financial Assistance | Community Support | |---|---|---|---|---| | Rural Communities | Limited options, fewer specialists | Scarce, high barriers | Very limited | Minimal, scattered support groups | | Urban Centers | Better access, some specialized providers | More readily available | Greater availability | Strong networks, diverse support groups | | Low-Income Communities | Limited due to cost and distance | Less accessible due to financial constraints | Fewer opportunities | Community groups often limited by resources | | High-Income Communities | More options, better access to specialists | Easily accessible | More funding available | Often high-quality support | | Immigrant Communities | Potential cultural and language barriers | Varying levels of access | Limited due to immigration status | Support groups often culturally specific |
The table above illustrates a general overview.
Specific circumstances and individual experiences can vary considerably. Factors like location, cultural background, and individual circumstances play a significant role in shaping access to resources and support systems.
Transgender Surveys and Data Collection
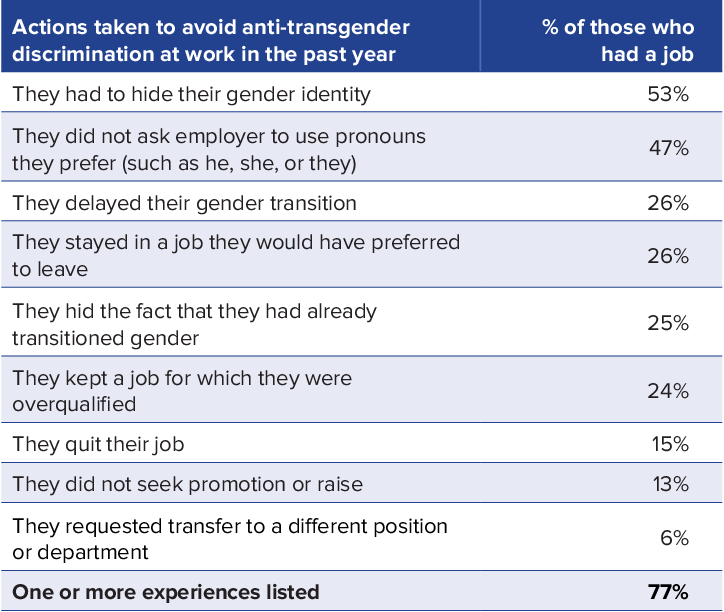
Collecting accurate and inclusive data on transgender experiences is crucial for understanding and addressing the unique challenges faced by this community. Existing data often reflects limited or biased perspectives, leading to a skewed understanding of the realities transgender individuals experience. Reliable data allows for the development of effective policies, programs, and resources that better serve transgender communities. This necessitates careful consideration of methodological factors, participant safety, and the potential for perpetuating harmful stereotypes.
Importance of Inclusive Data Collection
Accurate data on transgender experiences is essential for developing targeted interventions and resources. Without comprehensive data, policies and programs may fail to address the specific needs of transgender individuals, leading to further marginalization and inequality. Understanding the prevalence of various issues, such as harassment, discrimination, and poverty, within the transgender community is crucial for allocating resources effectively and designing interventions that yield meaningful results.
While the glitz and glamour of fashion week, like Saint Laurent Dior Paris Fashion Week saint laurent dior paris fashion week , often overshadows the harsh realities, the struggles of transgender individuals facing harassment and poverty in surveys are a stark reminder of the systemic issues that need addressing. These are serious concerns that deserve far more attention than a runway show, and it’s vital to support those impacted by such discrimination.
This data empowers policymakers and advocates to create more equitable environments for transgender people.
The recent struggles faced by transgender individuals, often facing harassment and poverty due to surveys, are deeply concerning. Sadly, these issues mirror the tragic case of a recent allergy death at Disney World, highlighting the serious need for better safety protocols in public spaces. The disney world allergy death lawsuit serves as a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities of vulnerable groups and the importance of comprehensive safety measures to protect all members of society.
These kinds of situations emphasize the critical need for continued support and advocacy for transgender communities facing discrimination and poverty.
Methodological Considerations for Transgender Surveys
Designing surveys that effectively capture the experiences of transgender individuals requires careful consideration of the unique needs and perspectives of this community. Researchers must prioritize cultural sensitivity and ensure that the language used is inclusive and respectful. Surveys should avoid presumptions or stereotypes, ensuring questions are open-ended and allow for nuanced responses. A crucial element is obtaining informed consent from participants, emphasizing the importance of privacy and confidentiality.
Clear guidelines for reporting and handling sensitive information must be established and adhered to strictly. These measures help ensure the reliability and validity of the data collected.
Avoiding Harmful Stereotypes in Survey Questions
Survey questions should be carefully constructed to avoid perpetuating harmful stereotypes and biases. For example, instead of asking “What is your biological sex?”, a more inclusive approach would be to ask “What is your gender identity?” Questions about gender identity should avoid assumptions about binary gender categories and allow participants to identify with the gender identity they feel most accurately reflects their experience.
Avoid leading questions or those that could potentially create discomfort or stigmatization.
Ensuring Safety and Privacy of Survey Participants
Ensuring the safety and privacy of survey participants is paramount. Providing a safe and confidential environment for participants to share their experiences is critical. Clear protocols for handling sensitive information should be established, ensuring that participant data is protected from unauthorized access and misuse. Anonymization techniques and secure data storage methods should be employed to safeguard personal information.
Explicitly informing participants about data security measures builds trust and encourages participation.
Example Survey Questions and Data Collection
| Question | Purpose | Data Type |
|---|---|---|
| What is your gender identity? | To understand the diverse range of gender identities within the community. | Qualitative |
| How often have you experienced harassment in the past year? (e.g., verbal, physical, online) | To measure the prevalence of harassment against transgender individuals. | Quantitative (frequency) |
| What are the biggest challenges you face in accessing healthcare? | To identify specific barriers to healthcare access. | Qualitative |
| What resources or support systems do you utilize? | To identify existing support networks and gaps in access. | Qualitative (types of support) |
| What is your annual income? | To analyze the correlation between gender identity and economic status. | Quantitative (numerical) |
Policy Implications and Solutions
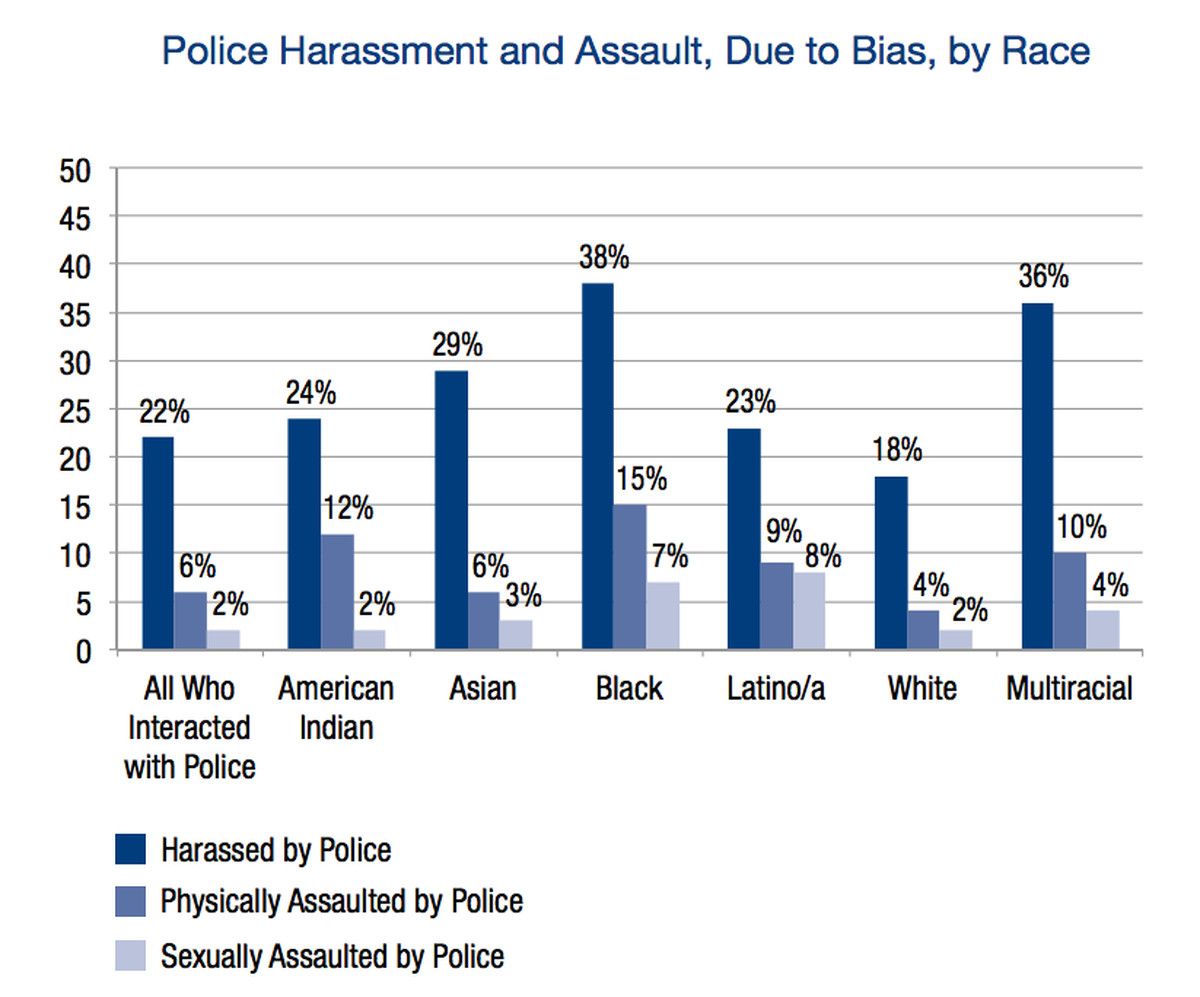
Addressing the complex interplay of gender identity, harassment, and poverty requires multifaceted policy interventions. These interventions must acknowledge the unique vulnerabilities faced by transgender individuals and prioritize their well-being. Effective policies will not only protect them from discrimination and violence but also provide access to essential resources, fostering economic stability and mental health. This necessitates a comprehensive approach that tackles the systemic issues contributing to these disparities.
Policy solutions must recognize that transgender individuals often experience intersecting forms of discrimination and disadvantage, compounding the challenges of poverty and harassment. A nuanced approach is critical to ensure that these policies are truly impactful and address the root causes of these issues. This includes creating supportive environments, offering resources for economic advancement, and ensuring access to healthcare and mental health services.
Potential Policy Interventions
Addressing the multifaceted issues faced by transgender individuals requires a comprehensive approach encompassing various policy interventions. This approach must acknowledge the complex interplay of gender identity, harassment, and poverty. Effective policies must be tailored to the specific needs of transgender communities, recognizing their diverse experiences and vulnerabilities.
- Anti-discrimination laws and policies are crucial for protecting transgender individuals from harassment and discrimination. These laws must explicitly include gender identity as a protected characteristic, prohibiting discrimination in areas like employment, housing, and public accommodations. Examples include the inclusion of gender identity in existing anti-discrimination laws, such as those already in place in some jurisdictions, or the introduction of specific legislation focused on transgender rights.
This ensures fair treatment in areas of employment, housing, and public services, and prohibits discrimination in the provision of goods and services.
- Social support programs can provide critical resources and assistance to transgender individuals experiencing poverty and harassment. These programs should include financial assistance, job training and placement services, and mental health support. Such programs could include financial assistance initiatives tailored to transgender individuals, vocational training programs focusing on skills in high-demand industries, and access to affordable housing. These programs can offer significant help in building economic stability and overcoming poverty.
For example, some cities have developed job training programs specifically for transgender individuals to address the high unemployment rates within this community.
- Accessible healthcare and mental health services are essential for transgender individuals. This includes access to gender-affirming care, mental health counseling, and preventative healthcare. This access is crucial for physical and mental well-being. Examples of initiatives could include expanding Medicaid coverage for gender-affirming care, creating a network of mental health professionals experienced in working with transgender individuals, and establishing community health centers offering comprehensive care.
Policy Solutions Table
A structured approach to policy development is vital. This table Artikels potential policies, their target populations, and anticipated outcomes.
| Proposed Policy | Target Population | Expected Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Expanding Medicaid coverage for gender-affirming care | Transgender individuals, particularly those experiencing financial hardship | Improved physical and mental health, reduced healthcare disparities, and increased access to essential medical care. |
| Implementing job training programs specifically for transgender individuals | Unemployed or underemployed transgender individuals | Increased employment opportunities, improved economic stability, and empowerment through skill development. |
| Establishing community health centers with specialized services for transgender individuals | Transgender individuals seeking comprehensive healthcare and mental health services | Increased access to preventative healthcare, gender-affirming care, and mental health support, promoting overall well-being and reducing health disparities. |
Impact on Families and Communities

The transgender journey often intersects with profound challenges, significantly impacting not only the individual but also their families and communities. Poverty, harassment, and societal stigma create a complex web of difficulties, affecting the social and emotional well-being of everyone involved. Understanding these interconnected issues is crucial for developing effective support systems and fostering inclusivity.
The effects of poverty and harassment on transgender individuals ripple outwards, affecting their families and communities in various ways. Financial strain resulting from poverty can lead to stress and conflict within families. Harassment can cause emotional distress, fear, and isolation, not only for the transgender person but also for family members who may witness or experience it. Societal stigma often reinforces these negative impacts, creating a climate of judgment and discrimination that isolates individuals and their loved ones.
This can lead to feelings of shame, guilt, and diminished self-worth within families, especially if the stigma is internalized.
Effects of Societal Stigma
Societal stigma significantly impacts the social and emotional well-being of transgender individuals and their families. The pervasive negativity often creates a hostile environment that isolates and marginalizes transgender people, leading to mental health concerns, such as anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Families may experience similar challenges, including social isolation, strained relationships, and feelings of shame or guilt.
This stigma can also manifest in discriminatory practices, limiting access to essential resources and opportunities for both the transgender individual and their family.
Examples of Support and Solidarity Initiatives
Support and solidarity initiatives are crucial for fostering inclusivity and resilience within families and communities. These initiatives can take various forms, such as educational workshops, community awareness campaigns, and the establishment of support groups. One example is the creation of safe spaces where transgender individuals and their families can connect, share experiences, and build supportive relationships. Another is the development of mentorship programs that connect experienced transgender individuals with younger generations.
Furthermore, community-based initiatives that advocate for policy changes to protect transgender rights can foster a more inclusive and accepting environment.
Comparison of Support Systems
Support systems available to transgender families vary significantly across communities. In some communities, there may be well-established support groups, advocacy organizations, and community centers specifically designed for transgender individuals and their families. However, in other communities, resources may be limited or inaccessible, leading to greater isolation and vulnerability. Factors such as geographical location, socioeconomic status, and the prevalence of cultural and religious norms play a critical role in shaping the availability and accessibility of these support systems.
Table: Supporting Transgender Individuals and Challenging Stigma
| Family/Community Actions | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Education and Awareness | Promoting understanding and dispelling misinformation about transgender identities. | Hosting workshops, organizing community events, sharing educational resources, and supporting media literacy. |
| Creating Safe Spaces | Providing a welcoming and supportive environment for transgender individuals and their families. | Establishing community centers, creating online forums, and organizing social gatherings. |
| Advocacy and Policy Change | Working towards policies that protect transgender rights and promote inclusivity. | Supporting legislation that protects transgender individuals from discrimination, participating in community discussions, and engaging in political advocacy. |
| Financial Support and Resources | Providing financial assistance to transgender individuals and families facing economic hardship. | Offering scholarships, grants, and other forms of financial aid. |
| Mental Health Support | Providing access to mental health resources for transgender individuals and families. | Connecting families with therapists or counselors specializing in gender identity issues, offering workshops on mental wellness, and supporting access to crisis hotlines. |
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, the transgender survey illuminates the significant challenges faced by transgender individuals due to the intersection of harassment, poverty, and systemic discrimination. The data collected will inform crucial policy changes and support initiatives, ultimately striving to create a more inclusive and supportive environment for transgender communities. This ongoing conversation underscores the need for continued advocacy and resources to combat the hardships faced by this population.
Common Queries
What are some common types of harassment faced by transgender individuals?
Transgender individuals experience various forms of harassment, including verbal abuse, physical violence, and discrimination in employment and housing. Bullying and cyberbullying are also significant concerns.
How can surveys be designed to be inclusive of transgender experiences?
Surveys should use inclusive language, avoid perpetuating harmful stereotypes, and prioritize the safety and privacy of participants. Open-ended questions and diverse response options can help gather nuanced perspectives.
What specific policy changes could address the intersection of gender identity, harassment, and poverty?
Anti-discrimination laws, improved access to affordable healthcare and legal aid, and increased funding for support programs are potential policy changes. Additionally, promoting public awareness and education is vital.
What role do support systems play in mitigating the impact of poverty and harassment?
Support systems, such as community centers, family and friend networks, and support groups, can provide essential resources, emotional support, and advocacy for transgender individuals facing these challenges.



