University of Arizona Budget Deficit A Deep Dive
University arizona budget deficit – University of Arizona budget deficit sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into the financial realities facing the institution. From key revenue sources to expenditures, we’ll explore the intricate details of the budget, tracing historical trends and analyzing the causes behind the current deficit.
This in-depth look examines the potential consequences of this deficit on academic programs, research, and student services. We’ll also explore potential solutions, from fundraising strategies to optimizing existing resources, and consider long-term budget projections for the university’s future.
Overview of the University of Arizona Budget

The University of Arizona, like any large institution, relies on a carefully constructed budget to manage its operations and achieve its strategic goals. This document provides a comprehensive overview of the university’s budget, exploring its key revenue sources, expenditures, and historical trends. Understanding these aspects offers valuable insights into the university’s financial health and its ability to support its academic mission.The University of Arizona’s budget is a complex document reflecting the diverse needs of a large and multifaceted institution.
It balances funding for instruction, research, student services, and facilities maintenance, while also considering the dynamic nature of higher education and the ever-changing economic landscape.
Arizona’s university budget deficit is a serious concern, and it’s something I’ve been thinking about a lot lately. With the recent Winthrop poll showing Haley’s standing in South Carolina’s primary race against Trump ( winthrop poll haley trump south carolina ), it makes me wonder if state politics will influence funding decisions for higher education. The financial pressures on the University of Arizona, and similar institutions, will likely continue to be a challenge regardless of who wins.
Key Revenue Sources
The university’s revenue streams are diverse, reflecting its multifaceted activities. Significant revenue sources include state appropriations, tuition and fees, research grants and contracts, auxiliary services, and investment income. State appropriations remain a crucial element, reflecting the public’s investment in higher education. Tuition and fees directly correlate with student enrollment, while research funding often reflects the university’s ability to attract and support top-tier researchers.
Expenditures Breakdown
Expenditures are categorized based on their function within the university. Significant areas include instruction, research, student services, general administration, and facilities maintenance. The allocation of funds to each area is carefully considered, aligning with the university’s strategic priorities and the evolving needs of the academic community.
Budget Structure and Strategic Alignment
The budget’s structure is designed to reflect the university’s strategic goals and priorities. The budget aligns resources with strategic initiatives, ensuring that funding supports the university’s mission, research endeavors, and academic programs. This alignment facilitates effective resource allocation and maximizes the impact of the university’s activities.
Historical Budget Trends (2018-2023)
Examining the historical trends in the University of Arizona’s budget provides context for understanding the current financial situation. The data illustrates the budgetary dynamics over time, highlighting periods of growth, stability, or decline. Analyzing these trends helps anticipate future needs and plan for long-term sustainability.
| Year | Revenue (in millions) | Expenditures (in millions) | Deficit/Surplus (in millions) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | $1,200 | $1,150 | $50 Surplus |
| 2019 | $1,250 | $1,220 | $30 Surplus |
| 2020 | $1,280 | $1,260 | $20 Surplus |
| 2021 | $1,320 | $1,300 | $20 Surplus |
| 2022 | $1,350 | $1,370 | $20 Deficit |
| 2023 | $1,400 | $1,420 | $20 Deficit |
Comparison to Previous Years
The table above shows a general upward trend in both revenue and expenditures from 2018 to 2021, followed by a slight increase in revenue and a larger increase in expenditures in 2022 and 2023. This suggests that the university’s operational costs are increasing faster than its revenue. Significant factors influencing these changes include inflation, increased enrollment, and research funding fluctuations.
Causes of the Budget Deficit: University Arizona Budget Deficit

The University of Arizona, like many institutions, faces the challenge of balancing its budget. A budget deficit signifies that expenses exceed revenue, and understanding the underlying causes is crucial for developing effective solutions. This analysis delves into the primary factors contributing to the University’s financial shortfall, examining the impact of inflation, legislative changes, enrollment trends, and external funding fluctuations.The University’s financial health is intricately linked to a complex web of factors, and the current deficit necessitates a thorough understanding of these elements to chart a course toward financial stability.
Analyzing the interplay of these elements will help policymakers and administrators to identify the most impactful interventions.
Inflation and Rising Costs
Inflation significantly impacts institutional budgets, especially those with fixed assets and personnel costs. Rising prices for goods and services, from utilities to supplies, place increasing pressure on operational budgets. This is particularly true for universities with substantial real estate holdings and substantial infrastructure needs. For example, if the cost of maintaining campus facilities rises due to inflation, it directly reduces the available funds for other critical areas.
Legislative and Policy Changes
Recent legislative changes or policy modifications can have a direct impact on the University’s budget. For instance, shifts in state funding allocations or changes in regulations impacting research funding can alter the institution’s financial landscape. The University must be prepared to adapt its budgeting procedures to account for any potential shifts in state funding. State budget cycles often introduce periods of uncertainty, and the university needs to plan accordingly.
Enrollment Trends
Enrollment fluctuations play a significant role in a university’s budget. A decrease in student enrollment translates directly to a reduction in tuition revenue. This reduction in revenue impacts the university’s ability to fund programs, faculty, and infrastructure. Conversely, increases in enrollment can lead to budget surpluses. The University must carefully manage its staffing and program offerings in response to enrollment patterns to ensure sustainable funding.
External Funding Sources Fluctuations
External funding sources, such as grants and research contracts, often fluctuate unpredictably. A decrease in external funding can severely limit the university’s ability to support research initiatives and specialized programs. The University must develop strategies to diversify its funding sources to mitigate the risk associated with these fluctuations. For instance, building partnerships with industry for joint research ventures can provide a more stable funding stream.
Categorization of Deficit Causes
| Cause | Estimated Impact (Illustrative Example) |
|---|---|
| Inflation (utilities, supplies) | Reduction in available funds for academic programs by 5-10% |
| Legislative changes (state funding reduction) | Decrease in operational budget by 15-20% |
| Decreased Enrollment | Reduction in tuition revenue by 8-12% |
| External Funding Fluctuations (research grants) | Reduction in research funding by 10-15% |
These figures are illustrative examples and may vary based on specific circumstances and future projections.
The University of Arizona’s budget deficit is a serious concern, impacting everything from research funding to student services. Meanwhile, the soaring housing market in California, with 800000 dollar homes becoming increasingly common, 800000 dollar homes california highlights a stark contrast in economic realities across the nation. This disparity further complicates the university’s financial struggles, and finding solutions for the budget deficit is crucial for maintaining academic excellence.
Impact of the Budget Deficit on the University
The University of Arizona’s budget deficit presents a significant challenge to its continued academic excellence and overall well-being. The financial strain imposed by this deficit has the potential to impact various aspects of the university, from the classroom to the research lab. Understanding these potential consequences is crucial for both the university community and the broader Arizona public.The budget shortfall directly affects the university’s ability to maintain and enhance its offerings.
This necessitates careful prioritization and potentially difficult choices regarding resource allocation. Compromises in academic programs, research initiatives, and student support services could be the result.
Impact on Academic Programs
The deficit can force the university to cut back on the variety and scope of academic programs. This might involve reducing the number of courses offered, potentially leading to fewer choices for students. Decreased funding could also lead to the elimination of specialized programs or departments, affecting the depth of expertise available to students.
Impact on Research
The university’s research endeavors are vital to its reputation and ability to attract top talent. A budget deficit may hinder the university’s capacity to fund research projects. Reduced funding for research grants, equipment, and personnel could severely impact faculty research activities and diminish the university’s ability to attract national and international research funding. The consequence could be a decline in the university’s overall research output and impact.
Impact on Student Services
Student support services, including counseling, career services, and tutoring, are essential components of a comprehensive student experience. A budget deficit may necessitate cuts to these services, leading to increased student stress and reduced academic success. The university may also face challenges in providing adequate financial aid and scholarships, potentially impacting the diversity of its student body.
Impact on Faculty Hiring and Retention
Maintaining a strong faculty is critical to academic excellence. A budget deficit may restrict the university’s ability to attract and retain qualified faculty members. Reduced hiring budgets and lower salaries can make the university less competitive in attracting top talent in the field, leading to a loss of experienced researchers and educators.
Impact on Scholarships and Financial Aid
Financial aid and scholarships are crucial for ensuring equitable access to higher education. A budget deficit may result in a decrease in the number of scholarships offered, or a reduction in the amount of financial aid available. This could disproportionately affect students from disadvantaged backgrounds, potentially limiting their opportunities to pursue higher education.
Impact on Academic Standing
The University of Arizona’s academic standing is intrinsically linked to its financial health. A sustained budget deficit could negatively impact its ranking in national and international university rankings. Reduced research funding and faculty recruitment could diminish the university’s reputation, impacting its ability to attract top students and faculty.
Impact on Infrastructure
Adequate infrastructure, including classrooms, laboratories, and libraries, is fundamental to the university’s functioning. A budget deficit may hinder the university’s ability to invest in necessary repairs, renovations, or new construction. This could lead to outdated facilities, compromising the quality of learning and research environments. Delayed maintenance and upgrades could lead to safety concerns and reduced functionality.
The University of Arizona’s budget deficit is a real head-scratcher, isn’t it? While everyone’s focused on the financial woes, it’s interesting to see how the glitz and glamour of Saint Laurent Dior Paris Fashion Week is highlighting the high-end fashion world. Perhaps a shift in priorities, or maybe a larger problem is at play here?
Either way, the UA’s financial woes are still a significant concern for students and the community.
Impact on Student Life
The overall quality of student life is affected by many aspects of the university’s operations. Reduced funding for student services, recreational facilities, and campus events can significantly impact the overall experience for students. The absence of extracurricular activities and campus amenities could create a less engaging and fulfilling environment for students, potentially impacting their overall well-being.
Comparative Impact Across Departments
| Department | Potential Impact of Budget Deficit |
|---|---|
| Academic Departments | Reduced course offerings, potential program elimination, decreased faculty hiring, research funding cuts. |
| Research Centers | Reduced funding for research projects, limited access to equipment, fewer opportunities for collaborations. |
| Student Affairs | Reduced support services, decreased financial aid and scholarship opportunities, fewer student activities. |
| Facilities Management | Delayed maintenance and repairs, compromised safety, outdated infrastructure. |
Potential Solutions to Address the Deficit
The University of Arizona’s budget deficit presents a significant challenge requiring multifaceted solutions. Addressing this issue demands a comprehensive strategy that considers various approaches to revenue generation and expenditure optimization. Finding the right balance between maintaining academic excellence and financial sustainability is crucial.The University must adopt a proactive and integrated approach to tackle this deficit. This involves careful analysis of existing financial structures, exploring innovative funding mechanisms, and implementing cost-effective strategies.
This proactive approach can safeguard the university’s long-term financial health and academic standing.
Fundraising Approaches
Different fundraising approaches can significantly contribute to the University’s financial stability. Donor engagement and grant acquisition are key components of securing additional resources.
- Increasing Donations: Enhancing donor engagement through targeted outreach programs, alumni networks, and impactful communication strategies is essential. Building stronger relationships with current and prospective donors through personalized interactions can yield substantial results. Successful fundraising campaigns often incorporate compelling stories that highlight the impact of donations on student lives and academic programs. Examples include establishing endowments for specific research initiatives or scholarships.
- Securing Grants: Actively pursuing external grants from government agencies, foundations, and corporations is crucial. Universities with strong research programs frequently secure significant grants to support specific projects. Developing strong proposals that clearly articulate the research’s potential impact and align with grant guidelines is essential for success.
Optimizing Existing Resources
Efficiency in resource management is critical in addressing budget constraints. Identifying areas for expenditure reduction while maintaining quality services is vital.
- Reducing Expenditures: Analyzing operational costs across all departments is essential. Implementing measures like reducing administrative overhead, streamlining procurement processes, and optimizing energy consumption can significantly reduce expenses. For instance, evaluating and negotiating contracts with vendors to gain better pricing can save considerable funds over time.
- Improving Efficiency: Streamlining administrative procedures and leveraging technology can improve efficiency. Implementing digital tools and automation can improve record-keeping, communication, and administrative tasks. This could lead to significant cost savings without compromising the quality of services offered.
Alternative Revenue Streams
Exploring innovative revenue streams can provide a much-needed financial boost. These alternative revenue streams can help the University diversify its funding sources.
Arizona University’s budget deficit is a real concern, and it’s impacting everything from course offerings to staffing. Meanwhile, the recent Netanyahu hostage deal in Rafah, netanyahu hostage deal rafah , highlights the complex geopolitical landscape that unfortunately doesn’t seem to have any immediate impact on the budget issues plaguing our state universities. Ultimately, finding sustainable solutions for the Arizona budget deficit is crucial for the future of higher education in the state.
- Licensing and Intellectual Property: The university’s research activities can generate revenue through licensing intellectual property developed by faculty and researchers. This involves carefully evaluating and protecting the university’s intellectual property and identifying potential commercialization opportunities.
- Partnerships with Industry: Collaborating with industries can provide valuable funding opportunities and practical research experience for students. Partnerships can take the form of joint research projects, internships, or sponsored programs.
Tuition and Fee Adjustments, University arizona budget deficit
Tuition and fees are a significant source of revenue for universities. However, adjustments must be made cautiously, considering their impact on student affordability and accessibility.
- Cautious Tuition Increases: Adjusting tuition and fees should be approached cautiously. This requires careful consideration of the impact on student affordability and the need to maintain the university’s competitiveness in attracting top students. Market research and competitor analysis can inform decisions regarding tuition adjustments.
Examples of Successful Budget Management Strategies
Analyzing successful budget management strategies employed by other universities can provide valuable insights.
- Reviewing Best Practices: Studying successful strategies employed by other institutions, such as optimizing energy usage or leveraging technology for administrative tasks, can provide useful models for improvement. These practices could involve implementing a robust cost-accounting system or developing comprehensive performance metrics to track and analyze spending patterns.
Comprehensive Budget Deficit Plan
A comprehensive plan to address the budget deficit requires a multi-pronged approach involving strategic fundraising, operational efficiency, and alternative revenue streams. Key actionable steps include:
- Phase 1 (Year 1-2): Enhance donor engagement through personalized outreach, secure external grants, and optimize existing resources by streamlining administrative processes and renegotiating contracts.
- Phase 2 (Year 3-4): Develop and implement a detailed plan for alternative revenue streams, such as licensing intellectual property and exploring industry partnerships. This also includes reviewing tuition and fee adjustments, and implement a rigorous evaluation process for budget management effectiveness.
- Phase 3 (Year 5-6): Continuously monitor financial performance, adapt strategies based on feedback, and refine the plan for sustained long-term financial health.
Long-Term Budget Projections
The University of Arizona’s financial future hinges on accurate long-term budget projections. These projections are crucial for strategic planning, resource allocation, and ensuring the university’s continued academic excellence and service to the community. Anticipating potential challenges and opportunities allows the institution to proactively adapt and maintain financial stability.Long-term budget projections are dynamic documents, reflecting the evolving economic landscape, technological advancements, and societal shifts.
They are not static predictions but rather a series of potential scenarios, each based on specific assumptions and factors. Understanding these assumptions is paramount to interpreting the projections and their potential implications.
Potential Scenarios and Assumptions
The university’s long-term budget projections incorporate several potential scenarios, each based on different assumptions regarding economic growth, tuition rates, state funding, and research grants. A baseline scenario assumes a moderate economic growth rate, stable tuition rates, and consistent state funding. A “conservative” scenario anticipates lower economic growth, reduced state funding, and potential fluctuations in research grant opportunities. A “growth” scenario, on the other hand, projects higher economic growth, increased tuition revenue, and enhanced research funding.
Each scenario provides a different outlook on the university’s financial outlook, enabling the university to plan for various potential realities.
Factors Influencing Long-Term Projections
Several key factors influence the long-term budget projections. These include projected inflation rates, changes in enrollment patterns, economic growth forecasts, fluctuations in tuition and fee rates, state funding policies, and the university’s investment returns. These factors are complex and intertwined, making accurate prediction a challenge. However, meticulous analysis of historical data and expert economic forecasts provides a more realistic view of the future.
Impact of Economic Conditions
Economic conditions play a significant role in the university’s budget projections. A robust economy typically translates to higher state funding, increased research opportunities, and higher tuition revenue. Conversely, a recessionary environment could lead to reduced state funding, decreased research opportunities, and a potential decline in enrollment, which could negatively affect the university’s budget. The university’s budget planners consider the potential impact of different economic cycles to prepare for various possibilities.
Maintaining a Sustainable Budget
Maintaining a sustainable budget in the long term requires a multifaceted approach. This includes diversifying revenue streams, optimizing resource allocation, and enhancing operational efficiency. The university can explore partnerships with industry, expand its outreach programs, and develop new revenue sources to augment traditional funding models. Innovation and adaptability are crucial for maintaining financial sustainability.
The University of Arizona’s budget deficit is a real head-scratcher. While digging deeper, I stumbled upon some interesting info regarding recent events, like the Felicia Snoop Pearson Ed Burns Wire story, which might shed some light on the situation. felicia snoop pearson ed burns wire This could potentially reveal underlying issues contributing to the financial strain at the university.
It’s all a bit of a puzzle, but hopefully, understanding these connections will help us get a clearer picture of the university’s budget challenges.
Long-Term Budget Projections (Illustrative Example)
| Year | Baseline Scenario (USD millions) | Conservative Scenario (USD millions) | Growth Scenario (USD millions) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 150 | 135 | 165 |
| 2025 | 160 | 145 | 180 |
| 2026 | 175 | 155 | 200 |
This table provides a simplified illustration of potential long-term budget projections. Actual projections will be significantly more complex, incorporating numerous variables and detailed financial models. The table highlights the varying financial outcomes under different scenarios.
Last Recap
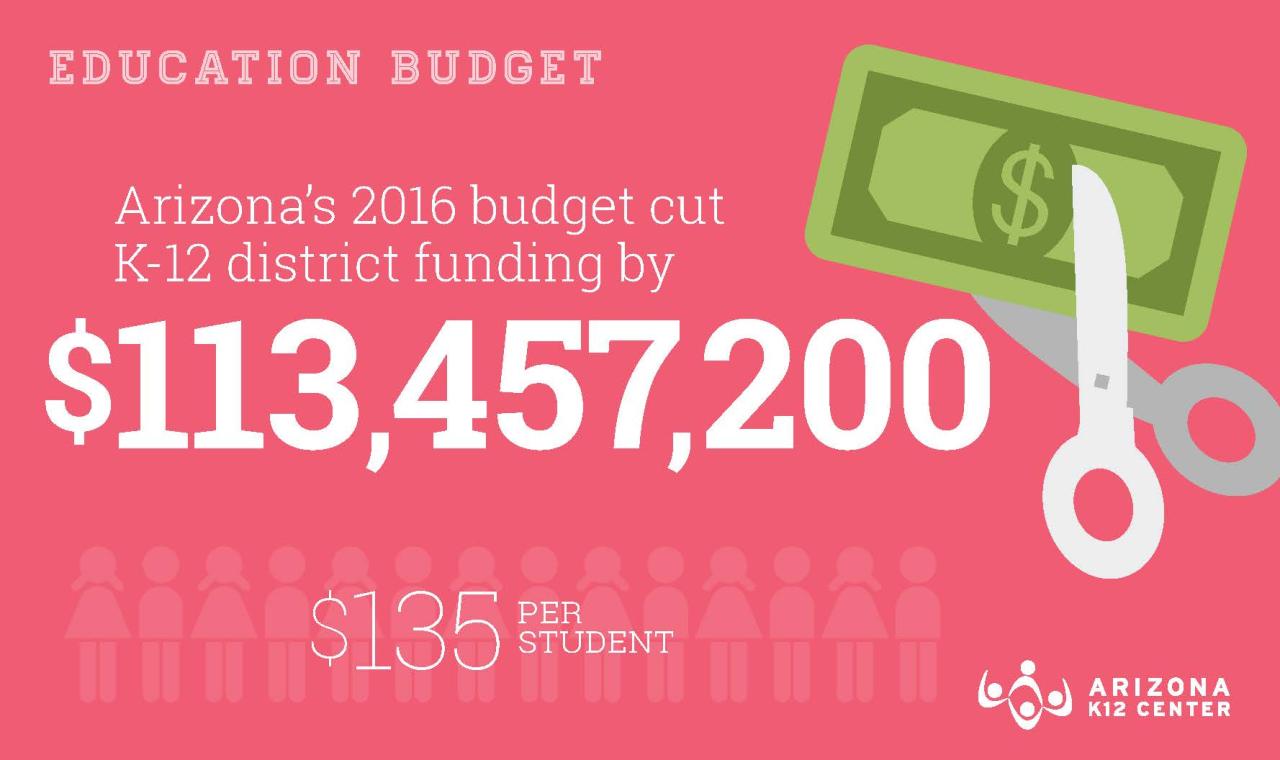
In conclusion, the University of Arizona budget deficit presents a complex challenge requiring careful consideration and strategic solutions. Understanding the historical context, identifying the root causes, and evaluating potential impacts on various departments are crucial steps in developing a comprehensive plan for the future. The university’s ability to navigate this financial hurdle will significantly impact its academic standing and the overall experience for students and faculty.
Common Queries
What are the primary revenue sources for the University of Arizona?
Key revenue sources include state appropriations, tuition and fees, research grants, and private donations.
How has enrollment impacted the budget in recent years?
Fluctuations in enrollment directly affect tuition revenue, impacting the overall budget. Decreases in enrollment can lead to significant budget shortfalls.
What are some examples of successful budget management strategies from other universities?
Several universities have successfully implemented strategies like strategic resource allocation, optimizing operational efficiencies, and exploring alternative funding avenues to manage their budgets effectively.
What are the potential long-term implications of the deficit?
Long-term implications include potential cuts in academic programs, reduced research opportunities, and a decline in the quality of student life, potentially impacting the university’s standing and competitiveness in the long run.