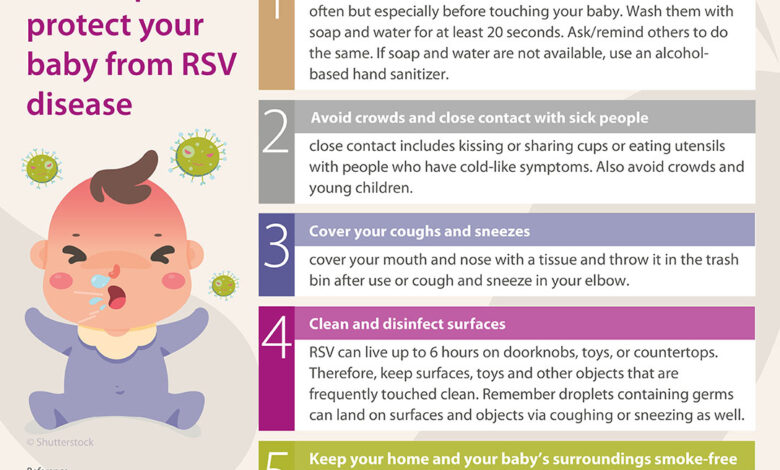
RSV Shots Pregnant Women & Infants
RSV shots pregnant women infants are a critical consideration for expecting mothers and new parents. Understanding the recommendations, potential benefits, and risks associated with these vaccinations is crucial for informed decision-making. This comprehensive guide will explore the nuances of immunization schedules for both pregnant women and infants, highlighting the importance of consulting with healthcare professionals.
This discussion delves into the scientific rationale behind these recommendations, offering a detailed look at the vaccines, schedules, and important considerations. It also explores potential risks and benefits, comparing them to the dangers of contracting RSV. We will address concerns and misconceptions surrounding these vaccinations, providing a wealth of resources for further research and discussion.
Overview of Immunizations for Pregnant Women and Infants
Protecting the health of pregnant women and infants is paramount, and vaccination plays a crucial role in achieving this goal. Immunizations safeguard both the mother and the developing fetus or newborn from potentially harmful diseases. Understanding the recommended schedules and the rationale behind them is essential for informed decision-making.Vaccinations are a cornerstone of public health, preventing the spread of infectious diseases and mitigating their severe consequences.
This is especially important during pregnancy and infancy, when the immune system is still developing and susceptible to infection. The focus here is on the recommended vaccines, their schedules, and the potential benefits and risks.
Recommended Vaccines for Pregnant Women
Pregnant women should receive vaccinations to protect both themselves and their unborn children. Maternal immunity can transfer to the infant, providing temporary protection against certain diseases during the early months of life. Several vaccines are particularly important during pregnancy, and the timing of administration is critical.
Recommended Vaccines for Infants
Infants have a developing immune system and are particularly vulnerable to infectious diseases. Vaccination is crucial to build their immunity and protect them from serious illnesses. The infant immunization schedule is carefully designed to introduce vaccines gradually, allowing the immune system to respond effectively.
Vaccination Schedules and Rationale
Vaccination schedules vary slightly based on geographic location and specific health considerations. However, the overarching goal remains consistent: to provide the necessary protection against infectious diseases. Different regions may have varying recommendations based on local disease prevalence.
Potential Benefits and Risks
Vaccinations offer substantial benefits in preventing severe illness and long-term health complications. However, like any medical procedure, vaccinations carry potential risks, though these are generally minimal compared to the potential risks of contracting the disease. Careful monitoring and consideration of individual health factors are crucial.
Comparison of Vaccination Schedules
Vaccination schedules may differ based on the region’s disease prevalence, vaccine availability, and specific health guidelines. This comparison will highlight the variations and the rationale behind them.
Getting RSV shots for pregnant women and infants is crucial for their health, especially during flu season. While we’re all keeping an eye on the health of our little ones, it’s also interesting to see how professional athletes are navigating their own contracts, like the recent developments in Andy Reid’s Chiefs contract negotiations. Ultimately, prioritizing preventative care, like RSV shots, remains paramount for the well-being of pregnant women and infants.
Table of Recommended Immunizations
| Vaccine | Target Group | Schedule | Important Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Influenza (Flu) Vaccine | Pregnant women, infants (6 weeks and older) | Annually during pregnancy, 2 months and older for infants | Important for seasonal protection, particularly during pregnancy when complications can be severe. Pregnant women should discuss with their doctor. Infants may need booster doses. |
| Tdap (Tetanus, Diphtheria, Pertussis) | Pregnant women, infants (2 months and older) | During each pregnancy, 2 months, 4 months, 6 months, 12 months, 15-18 months, 4-6 years, 11-12 years | Essential for preventing pertussis (whooping cough) which can be particularly dangerous for infants. Pregnant women receive a Tdap booster dose during each pregnancy to maintain immunity. |
| Hepatitis B Vaccine | Pregnant women, infants | Pregnant women should receive if not previously vaccinated, Infants receive series of doses starting at birth. | Protects against Hepatitis B infection. Important for newborns since they can be infected from the mother. |
| Measles, Mumps, Rubella (MMR) | Pregnant women, infants (12 months and older) | Pregnant women should receive if not previously vaccinated, Infants receive after 12 months. | Protects against measles, mumps, and rubella. Important to avoid congenital rubella syndrome. |
Potential Risks and Benefits of Immunizations
Vaccinations are crucial for protecting pregnant women and infants from preventable diseases. While the benefits often outweigh the risks, it’s essential to understand both sides of the equation to make informed decisions with your healthcare provider. Understanding the potential side effects and the importance of open communication can alleviate anxieties and empower you to make the best choices for your health and your child’s.Immunizations are generally safe and highly effective, offering substantial protection against severe illnesses.
However, like any medical intervention, potential side effects and risks exist. A thoughtful approach to vaccination, involving careful consideration of both risks and benefits in the context of individual health conditions, is key.
Potential Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
Understanding potential side effects is important for managing expectations and ensuring prompt medical attention if necessary. Common side effects from vaccinations can include mild reactions such as soreness, redness, or swelling at the injection site. Fever, fatigue, and headache are also possible, though typically mild and short-lived. In rare cases, more serious adverse reactions can occur, though they are usually uncommon.
The risk of these serious reactions is often significantly lower than the risk of contracting the diseases themselves.
Importance of Discussing Potential Risks with Healthcare Providers
Open communication with your healthcare provider is paramount when considering vaccinations. They can provide personalized information about the potential risks and benefits based on your specific health history and circumstances. This includes any pre-existing conditions, allergies, or other factors that might influence your response to the vaccine. Honest discussion ensures that you are well-informed and can make the best decision for your individual needs.
Getting RSV shots for pregnant women and infants is crucial for their health, especially during flu season. It’s a topic that’s constantly being researched and discussed. Speaking of health, the return of Romeo Gigli to Marrakesh, a highly anticipated event, is definitely making waves in the news. return of romeo gigli marrakesh is creating quite a buzz, but ultimately, the focus should remain on preventative measures like RSV vaccinations for vulnerable populations, particularly pregnant women and infants.
This proactive approach can help mitigate potential risks and address any concerns you may have.
Long-Term Benefits of Vaccination
Vaccinations offer substantial long-term benefits, extending far beyond immediate protection. Immunizations protect individuals from debilitating diseases, preventing hospitalizations, long-term health complications, and even death. The long-term cost savings associated with preventing disease outbreaks and the need for expensive treatments are significant. Reduced healthcare costs for individuals and society as a whole are a direct result of widespread vaccination programs.
Comparing Vaccination Benefits and Risks to Disease Contraction
The benefits of vaccination are often considerably greater than the potential risks. Contracting the diseases themselves carries a substantial risk of serious complications, hospitalization, long-term disability, and even death. For example, measles can lead to pneumonia, encephalitis, and other severe complications. The protection offered by vaccines against these serious outcomes is invaluable.
Potential Risks and Benefits for Pregnant Women
| Potential Risks (rare) | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|
| Local reactions (soreness, redness, swelling) | Protection against diseases like rubella, which can cause severe birth defects. |
| Fever, fatigue, headache | Protection from diseases that can be transmitted to the fetus. |
| Rarely, allergic reactions | Reduced risk of complications from contracting the diseases themselves. |
| (Very rare) Severe, systemic reactions | Preservation of health for both the mother and the developing fetus. |
The decision to vaccinate during pregnancy should be made in consultation with a healthcare provider, considering the individual’s health status and the specific risks and benefits of each vaccine. This individualized approach ensures the best possible outcome for both mother and child.
Immunization Considerations During Pregnancy
Pregnancy is a unique time, and it’s important to understand how it affects the immune system and vaccination schedules. While vaccines are generally safe and beneficial for pregnant individuals and their developing babies, specific considerations are crucial to ensure both maternal and fetal well-being. This section dives into those specifics.Understanding the delicate balance between maternal health and fetal development during pregnancy is key when discussing vaccinations.
The changes in the immune system during pregnancy necessitate a thoughtful approach to vaccination decisions, always in consultation with a healthcare professional.
Impact of Pregnancy on the Immune System
Pregnancy significantly alters a woman’s immune system to support the developing fetus. This shift can influence how the body responds to vaccines. The immune system is modulated to prevent rejection of the developing fetus, which can lead to changes in antibody production and immune cell activity. This change in immune response can affect the effectiveness of vaccines.
Vaccination Schedules and Trimester Considerations
Different stages of pregnancy present unique circumstances regarding vaccination. Understanding the trimester-specific impact on the immune system and fetal development is essential.
- First Trimester: The first trimester is characterized by rapid fetal development. Vaccination decisions during this period require careful consideration of potential risks and benefits. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to weigh these factors.
- Second Trimester: The second trimester often involves fewer significant physiological changes compared to the first trimester. This allows for more flexibility in vaccination scheduling, but consultations with a healthcare professional are still crucial to assess individual needs.
- Third Trimester: The third trimester sees continued fetal growth and development, and maternal immune system changes. This trimester might necessitate further discussions with a healthcare professional regarding vaccinations, particularly if any new health concerns arise. Decisions should be tailored to the individual woman’s health status and the specific vaccine in question.
Importance of Healthcare Professional Consultation
Healthcare professionals play a vital role in guiding vaccination decisions during pregnancy. They can assess individual health histories, potential risks, and the specific needs of the pregnant person and the developing fetus.
“A healthcare professional can provide personalized advice on vaccinations based on your specific circumstances.”
This personalized approach is crucial, as each pregnancy and each individual’s health status are unique.
Vaccine Safety Studies Specific to Pregnant Women
Extensive research has been conducted on vaccine safety in pregnant women. Rigorous studies and clinical trials have consistently demonstrated that, in general, vaccines are safe during pregnancy for both the mother and the developing fetus.
Vaccine Modification Considerations During Pregnancy
The following table summarizes potential vaccine modifications that may be considered during different stages of pregnancy. This is not an exhaustive list, and consultations with healthcare professionals are essential.
| Trimester | Vaccine Considerations |
|---|---|
| First Trimester | Prioritize vaccines with well-established safety profiles. Consult with a healthcare provider for specific recommendations. |
| Second Trimester | Consider vaccines that might be beneficial in preventing illnesses, while still carefully considering potential risks. A healthcare provider can weigh the benefits against the risks. |
| Third Trimester | Focus on vaccines to protect against potential infections that could pose risks during delivery or in the postpartum period. Consult with a healthcare professional for the best approach. |
Immunization for Infants
Protecting our little ones from infectious diseases is a top priority for parents. Immunizations play a crucial role in building a strong immune system in infants, safeguarding them against potentially serious illnesses. This comprehensive approach ensures their healthy development and well-being.Early childhood vaccination is vital for preventing infectious diseases and their potential complications. Immunizations train the infant’s immune system to recognize and fight off harmful pathogens, providing long-term protection.
Getting RSV shots for pregnant women and infants is crucial for their health, especially during cold and flu season. While those expensive homes in California, like the 800000 dollar homes california I’ve been seeing lately, are a big deal, prioritizing preventative care like these shots is just as important. Protecting vulnerable populations like pregnant women and babies is key to community health.
This proactive measure is far more effective and less risky than relying on treatments after an illness has developed.
Importance of Early Childhood Vaccination
Vaccination is a critical component of preventive healthcare for infants. It creates a shield against potentially devastating diseases. By introducing weakened or inactive forms of the disease-causing agent, vaccines stimulate the immune system to develop antibodies. These antibodies provide immunity, enabling the body to effectively fight off the actual disease should exposure occur. This proactive approach to health is a cornerstone of public health.
Crucial Role of Vaccinations in Preventing Infectious Diseases
Infectious diseases can have devastating consequences for infants. Severe illness can lead to hospitalization, long-term health problems, and even death. Vaccinations dramatically reduce the risk of these diseases. They work by creating a protective barrier against the pathogens that cause these illnesses. This proactive approach to healthcare is crucial for the well-being of infants.
Infant Vaccination Schedule and Reasoning
The infant vaccination schedule is carefully designed to introduce vaccines at specific ages when the infant’s immune system is most receptive and responsive. This phased approach allows the immune system to develop progressively, ensuring optimal protection against various diseases. The specific timing of each vaccine is crucial to maximize its effectiveness.
Getting RSV shots for pregnant women and infants is crucial for their protection. Understanding safe practices like using condoms for preventing the spread of HIV/AIDS, as detailed in this article on condon prevencion vih sida , is also important for overall health. Ultimately, proactive measures like these RSV shots are key to safeguarding the health of pregnant women and infants.
Common Parental Concerns Regarding Infant Vaccinations
Parents often have legitimate concerns about the safety and efficacy of infant vaccinations. It’s understandable to have questions. These concerns can be addressed through open communication with healthcare providers. Detailed information about the vaccines, their composition, and potential side effects can help alleviate parental anxieties. Providers are readily available to address these concerns.
Recommended Vaccines for Infants Under 1 Year of Age
| Vaccine | Disease Prevented | Approximate Age of Administration | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hepatitis B | Hepatitis B | Birth, 1-2 months, 6 months | This virus can cause serious liver problems, and early vaccination is crucial. |
| Rotavirus | Rotavirus diarrhea | 2 months, 4 months, 6 months | Rotavirus is a common cause of severe diarrhea in infants, and vaccination helps prevent it. |
| Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis (DTaP) | Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis | 2 months, 4 months, 6 months, 15 months | These diseases can cause serious illness and complications. Multiple doses are needed for optimal protection. |
| Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) | Haemophilus influenzae type b infections | 2 months, 4 months, 6 months, 12-15 months | This bacterium can cause serious infections, including meningitis. |
| Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV13) | Pneumococcal infections | 2 months, 4 months, 6 months, 12-15 months | This vaccine protects against various pneumococcal infections. |
| Poliovirus | Polio | 2 months, 4 months, 6-18 months | Polio can cause paralysis. Vaccination is vital for preventing this disease. |
| Influenza | Influenza (Flu) | 6 months and onwards | Annual vaccination is recommended to prevent seasonal flu. |
| Measles, Mumps, Rubella (MMR) | Measles, Mumps, Rubella | 12-15 months | These diseases can have severe complications. Vaccination provides long-lasting protection. |
Addressing Concerns and Misconceptions
Navigating the world of vaccinations can be daunting, especially when faced with misinformation and anxieties. This section delves into common concerns surrounding vaccinations, providing evidence-based explanations and strategies for addressing parental anxieties. Understanding the science behind these preventative measures is crucial for informed decision-making.Misconceptions surrounding vaccines often stem from fear and lack of understanding. Many parents harbor anxieties about potential side effects, efficacy, and the overall safety of these life-saving interventions.
Dispelling these myths is paramount to ensuring the health and well-being of both individuals and communities.
Getting RSV shots for pregnant women and infants is crucial for their health, but unfortunately, other pressing issues are also impacting our communities. Recent news about the NYC subway shooting on the D train, as reported in nyc shooting d train , highlights the need for us to prioritize safety and well-being in all aspects of our lives.
While these tragic events are happening, it’s still important to remember the preventative measures like RSV shots that can help protect our vulnerable populations.
Common Vaccine Misconceptions
Numerous misconceptions persist regarding vaccines, often based on unfounded rumors or misinterpreted scientific data. These misconceptions can lead to hesitation or refusal to vaccinate, thereby compromising the collective immunity of the population and increasing the risk of preventable diseases. It is essential to approach these concerns with empathy and accurate information.
- Association with Autism: Extensive research has definitively debunked the link between vaccines and autism. The original study claiming this association was retracted due to fraudulent data, and subsequent large-scale studies have consistently found no correlation.
- Overburdening the Immune System: The human immune system is remarkably resilient. Vaccines stimulate, but do not overwhelm, the immune response. The antigens in vaccines are weakened or inactivated, prompting a targeted and controlled immune reaction. This controlled response prepares the body to fight against the actual pathogens if encountered later.
- Presence of Harmful Additives: Vaccines contain preservatives like thimerosal (ethylmercury) and other trace elements, which are used in very small amounts and are rigorously tested for safety. The amounts are often far below what is considered harmful. Regulatory bodies continuously monitor vaccine safety, ensuring these components are safe for use.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Vaccine Safety and Effectiveness
The safety and effectiveness of vaccines are supported by decades of rigorous scientific research. Large-scale clinical trials and long-term epidemiological studies have consistently demonstrated the safety profile of vaccines and their remarkable ability to prevent the spread of infectious diseases.
“Vaccines are one of the most successful and safest public health interventions in history.”
Strategies for Addressing Parental Concerns
Open communication and transparent information sharing are crucial when addressing parental concerns. Health professionals can play a pivotal role in providing clear and concise explanations, addressing anxieties, and providing access to reliable sources of information. Active listening, empathy, and patience are essential components of this process.
- Facilitate Open Dialogue: Create a safe and supportive environment for parents to voice their concerns and ask questions. Emphasize the importance of vaccination for individual and community health.
- Provide Evidence-Based Information: Present scientific data and statistics demonstrating the safety and efficacy of vaccines in a clear and understandable manner. Direct parents to credible resources like the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) or the World Health Organization (WHO).
- Address Concerns Directly: Actively listen to parental concerns, validate their feelings, and address any misconceptions they might have with accurate information. Provide tailored explanations and reassurance where needed.
Examples of Successful Vaccination Campaigns
Numerous vaccination campaigns have demonstrated the profound impact on public health. The eradication of smallpox is a testament to the power of widespread vaccination. Polio, once a debilitating disease, is now largely controlled in many parts of the world due to vaccination programs.
Table of Common Misconceptions and Evidence-Based Explanations
| Common Misconception | Evidence-Based Explanation | Resources for Further Information |
|---|---|---|
| Vaccines cause autism. | Extensive research has shown no link between vaccines and autism. The original study claiming this association was retracted due to fraudulent data. | CDC, WHO |
| Vaccines overload the immune system. | Vaccines stimulate, but do not overwhelm, the immune system. The antigens in vaccines are weakened or inactivated, triggering a targeted immune response. | Immunology textbooks, scientific journals |
| Vaccines contain harmful additives. | Vaccines contain preservatives and trace elements in very small amounts, which are rigorously tested for safety. These amounts are often far below what is considered harmful. | FDA website, vaccine safety reports |
Resources for Further Information
Navigating the world of vaccinations for pregnant women and infants can feel overwhelming. Knowing where to turn for accurate and reliable information is crucial for making informed decisions about your health and your little one’s. This section provides a curated list of resources to guide you through this important journey.Understanding the importance of reliable sources is key to making sound health choices.
The information presented here is designed to help you find trustworthy organizations and websites dedicated to providing comprehensive vaccination information. This will empower you to discuss your concerns with your healthcare provider and make well-informed decisions.
Reputable Sources for Vaccination Information
Reliable sources provide accurate information about vaccinations. Consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and rely on evidence-based organizations.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): The CDC is a leading authority on public health, offering comprehensive information on vaccinations, including recommendations for pregnant women and infants. They provide detailed schedules, safety data, and answers to frequently asked questions.
- The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP): The AAP is a trusted resource for pediatricians and parents alike. Their website offers guidance on immunization schedules for infants and children, considering developmental stages and potential risks.
- The World Health Organization (WHO): The WHO provides global perspectives on vaccination programs, including recommendations for immunization in different countries and contexts. They offer insights into the broader impact of vaccination on public health.
- The Immunization Action Coalition (IAC): The IAC advocates for improved access to vaccines and promotes vaccination education. They offer a variety of resources, including fact sheets and materials to address common concerns.
Organizations Offering Support for Parents
Seeking support from organizations dedicated to parental well-being is invaluable during the vaccination process.
- La Leche League International: This organization focuses on breastfeeding support, but also provides information on vaccinations and their impact on breastfeeding mothers. They can offer insights into potential challenges and address concerns about vaccine safety during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- National Immunization Network: This network offers a variety of resources and support for parents, healthcare professionals, and communities to improve immunization practices.
- Local Health Departments: Your local health department is a vital resource. They often offer immunization clinics and provide tailored information based on your region’s specific needs.
Importance of Seeking Information from Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers are essential for personalized vaccination advice.
Your doctor is your most valuable resource for understanding the specific risks and benefits of vaccines in your situation. They can assess your individual health history, address concerns, and provide tailored recommendations. Never rely solely on online forums or unverified sources. Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance.
Credible Websites for Comprehensive Information
Comprehensive websites provide detailed information on vaccinations. These sites offer organized summaries and in-depth analyses, making it easier to grasp the subject.
- vaccineinformation.org: This website offers a wealth of information on vaccines, including details on safety, effectiveness, and the scientific evidence supporting their use.
- cdc.gov/vaccines: The CDC’s dedicated vaccine page provides updated information, resources, and tools to stay informed about immunization schedules and safety data.
Table of Resources
A table outlining organizations, contact information, and websites for easy reference.
| Organization | Contact Information | Website |
|---|---|---|
| Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) | (800) 232-4636 | cdc.gov |
| American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) | (800) 428-2742 | healthychildren.org |
| World Health Organization (WHO) | +41 22 791 21 11 | who.int |
| Immunization Action Coalition (IAC) | (202) 662-2100 | immunize.org |
Global Perspectives on Immunization

A global approach to immunization is crucial for protecting populations from preventable diseases. Variations in vaccination rates and policies across countries highlight the complex interplay of factors that influence immunization programs. Understanding these differences is essential for developing effective strategies to improve global health.The success of immunization programs hinges on many variables, including socioeconomic conditions, healthcare infrastructure, cultural beliefs, and political will.
These elements often intertwine to create diverse landscapes of immunization coverage worldwide.
Global Variation in Vaccination Rates and Policies
Vaccination rates vary significantly across the globe. Factors like access to healthcare, economic stability, and public health infrastructure play a vital role in shaping these differences. For instance, countries with robust healthcare systems and accessible facilities generally experience higher vaccination rates. Conversely, countries facing challenges in infrastructure, resource allocation, and healthcare access often encounter lower vaccination coverage.
Factors Contributing to Variations
Several factors contribute to the observed global variation in vaccination rates. These factors include:
- Socioeconomic factors: Poverty, lack of education, and limited access to resources can hinder vaccination uptake. A family’s ability to afford transportation to vaccination centers or the time needed for appointments can be significant barriers.
- Healthcare infrastructure: The availability and quality of healthcare facilities, trained personnel, and cold chain logistics directly impact vaccination access. Inadequate facilities, shortage of healthcare providers, or lack of reliable transportation to health centers can significantly impact vaccination coverage.
- Cultural and religious beliefs: Some communities hold beliefs or practices that may lead to hesitancy or refusal to vaccinate. Addressing these concerns through education and engagement with community leaders can improve vaccination rates.
- Political factors: Government policies and priorities, including resource allocation, influence vaccination programs. The political will to support and implement vaccination campaigns is a critical component of success.
- Information access and dissemination: Misinformation or lack of access to accurate information about vaccination can contribute to hesitancy. Efforts to provide clear, evidence-based information are vital for improving public trust and promoting vaccination.
Implications of These Variations
The disparities in vaccination rates have significant implications for global health. Areas with lower vaccination coverage are more susceptible to outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases, potentially leading to widespread illness and death. These outbreaks can also impact neighboring regions, highlighting the interconnectedness of global health. For example, the resurgence of measles in several countries demonstrates the importance of maintaining high vaccination coverage.
International Efforts to Improve Vaccination Coverage, Rsv shots pregnant women infants
Various international organizations and initiatives work to improve global vaccination coverage. These efforts often focus on strengthening healthcare systems, increasing access to vaccines, and addressing cultural and social barriers.
- The World Health Organization (WHO): The WHO plays a crucial role in coordinating global vaccination efforts, providing technical support, and promoting the use of vaccines.
- Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance: Gavi aims to improve access to vaccines in low- and middle-income countries, particularly for children. Gavi’s programs help build infrastructure and improve vaccine delivery.
- UNICEF: UNICEF focuses on ensuring equitable access to vaccines, particularly in underserved populations, and working with communities to address concerns and misconceptions.
Comparison of Vaccination Policies
Vaccination policies differ across countries, reflecting the unique needs and priorities of each nation. The types of vaccines offered, the age at which they are administered, and the recommended schedules vary.
Global Vaccination Rates by Region
Data on vaccination rates by region are dynamic and can be found in publications from the WHO and UNICEF.
| Region | Estimated Vaccination Rate (Example Data – Needs Updating) |
|---|---|
| North America | High (e.g., >90%) |
| Europe | High (e.g., >90%) |
| South America | Moderate (e.g., 70-90%) |
| Africa | Low to Moderate (e.g., 50-80%) |
| Asia | Variable (e.g., 60-95%) |
Note: These are illustrative examples and actual figures should be obtained from reliable sources.
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, the decision surrounding RSV shots for pregnant women and infants is a personal one, but informed by scientific evidence and professional guidance. By understanding the recommendations, potential benefits, and risks, parents can make empowered decisions about their families’ health. Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and support.
Helpful Answers: Rsv Shots Pregnant Women Infants
Is it safe to get an RSV shot during pregnancy?
Generally, RSV vaccines are considered safe for pregnant women, but it’s essential to discuss potential risks and benefits with your healthcare provider. Your doctor will be able to weigh the benefits of protection against RSV for you and your baby, and consider any existing medical conditions.
What are the common side effects of RSV vaccines?
Common side effects may include soreness, redness, or swelling at the injection site. Some individuals may experience mild fever or fatigue. Serious side effects are rare but possible. Your doctor can provide a more detailed overview.
How soon after birth can my infant receive the RSV vaccine?
The recommended schedule for RSV vaccines in infants varies depending on the specific vaccine and your pediatrician’s recommendations. It is vital to follow the guidelines provided by your child’s healthcare professional.
Are there alternative options to RSV shots?
Alternative options may exist for managing RSV risk, and your healthcare provider can discuss the most appropriate strategy for your specific circumstances.

