
Healthy Diet Nutrition Tips Your Guide to Wellness
Healthy diet nutrition tips are crucial for overall well-being. This guide dives deep into the fundamentals of healthy eating, from understanding macronutrients and micronutrients to practical tips for incorporating these principles into your daily life. We’ll explore the essential nutrients, how to create balanced meals, and address dietary needs for various lifestyles and health conditions.
Discover the science behind healthy eating, learn how to make informed food choices, and equip yourself with the knowledge to maintain a healthy diet for a lifetime. We’ll cover everything from the basics to advanced strategies for long-term success. Get ready to embark on a journey towards a healthier, happier you!
Understanding Healthy Diet Fundamentals
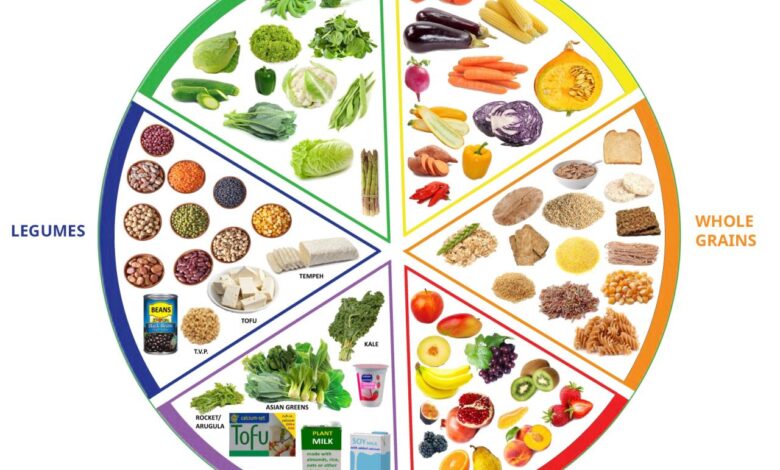
A healthy diet is more than just a collection of foods; it’s a lifestyle choice that fuels your body and mind. It’s about nourishing your body with the right nutrients to support optimal function, energy levels, and overall well-being. Understanding the fundamentals of a healthy diet is key to making informed choices and achieving your nutritional goals.A balanced diet incorporates a variety of foods from different food groups, providing essential nutrients for growth, repair, and energy production.
It’s about mindful eating, understanding portion sizes, and making conscious choices that prioritize your health.
Defining a Healthy Diet
A healthy diet is characterized by a balanced intake of macronutrients and micronutrients. Macronutrients—protein, carbohydrates, and fats—provide the body with energy and building blocks for various functions. Micronutrients, such as vitamins and minerals, are essential for metabolic processes, immune function, and overall health. A diet rich in a diverse range of foods ensures that the body receives the complete spectrum of nutrients it needs.
Balanced Meals and Portion Control
Balanced meals are crucial for optimal nutrition. They combine protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats in appropriate proportions. For example, a balanced lunch might include lean protein (like grilled chicken or fish), complex carbohydrates (brown rice or quinoa), and healthy fats (avocado or nuts). Portion control plays a vital role in achieving nutritional goals. Eating the right amount of food is essential to avoid excess calorie intake, which can lead to weight gain.
By understanding portion sizes, you can effectively manage your calorie intake and achieve your desired nutritional outcomes.
Focusing on a healthy diet is key, especially when the weather changes. With the shift in Oregon’s daylight saving time, it’s easy to get caught up in the schedule changes, but remember to maintain a balanced diet. Keeping up with your nutritional intake is important year-round, especially during the transition to Oregon Daylight Saving Time , and ensuring you get enough vitamins and minerals can help you stay energized and focused throughout the day.
Prioritizing nutrient-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins will help you maintain a healthy lifestyle, regardless of the time change.
The Importance of Hydration
Hydration is fundamental to overall health and plays a significant role in supporting a healthy diet. Water is crucial for numerous bodily functions, including digestion, nutrient absorption, and temperature regulation. Adequate hydration helps maintain energy levels, improves skin health, and supports optimal cognitive function. Aim for 8 glasses of water a day, but individual needs may vary based on activity levels and climate.
Consuming water alongside meals can also aid in digestion and satiety.
Key Components of a Healthy Diet
| Nutrient | Function | Sources | Daily Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protein | Essential for building and repairing tissues, producing enzymes and hormones, and supporting immune function. | Lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, beans, lentils, tofu, nuts, and seeds. | 0.8 grams per kilogram of body weight per day. |
| Carbohydrates | Primary source of energy for the body. Complex carbohydrates provide sustained energy release. | Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and starchy vegetables. | 45-65% of total daily calories. |
| Fats | Essential for hormone production, vitamin absorption, and cell function. Healthy fats are crucial for overall health. | Avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, fatty fish. | 20-35% of total daily calories. Prioritize healthy unsaturated fats. |
| Vitamins and Minerals | Essential for various metabolic processes, immune function, and overall health. | Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein sources. | Varied intake from a wide range of nutrient-rich foods. |
Essential Nutrients and Their Roles
Fueling your body with the right nutrients is crucial for optimal health and well-being. Understanding the essential roles of various nutrients allows you to make informed choices about your diet, promoting vitality and supporting your body’s functions. This section dives deep into the significance of protein, carbohydrates, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals, providing valuable insights for a healthier lifestyle.
Protein: The Body’s Building Block
Protein plays a vital role in building and repairing tissues throughout the body. It’s essential for growth, development, and maintaining a healthy immune system. Amino acids, the building blocks of protein, are crucial for various bodily functions, including hormone production and enzyme activity. A sufficient intake of protein is essential for individuals involved in physical activities, as well as for general health maintenance.
- Protein-rich foods include lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products (milk, yogurt, cheese), legumes (beans, lentils, chickpeas), and tofu.
Carbohydrates: Your Body’s Energy Source
Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for your body. They are broken down into glucose, which cells use for fuel. Carbohydrates are classified as either simple or complex. Understanding the difference between these types is crucial for managing blood sugar levels and overall health.
- Simple carbohydrates are quickly digested and absorbed, leading to a rapid increase in blood sugar. Examples include white bread, sugary drinks, and candy.
- Complex carbohydrates, on the other hand, are digested more slowly, providing a sustained release of energy. These are often found in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
Healthy Fats: Essential for Hormone Production and Brain Function
Healthy fats are crucial for hormone production, brain function, and cell membrane structure. They are essential for overall health and should not be eliminated from the diet. Choosing the right types of fats is key to maintaining a healthy balance.
- Examples of healthy fats include avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish (salmon, tuna).
Vitamins and Minerals: Supporting Body Functions
Vitamins and minerals play a crucial role in numerous bodily functions, from metabolism to immune response. A diverse diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is essential for obtaining a wide range of vitamins and minerals.
- Foods rich in vitamins and minerals include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and lean proteins. For instance, leafy greens like spinach are excellent sources of vitamin K and iron. Citrus fruits provide vitamin C. Dark chocolate and berries contain antioxidants.
Carbohydrate Impact on Blood Sugar
The type of carbohydrate consumed significantly affects blood sugar levels.
| Carbohydrate Type | Impact on Blood Sugar | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Carbohydrates | Rapid increase in blood sugar | Sugary drinks, white bread, candy |
| Complex Carbohydrates | Gradual increase in blood sugar | Whole grains, fruits, vegetables |
Practical Tips for Healthy Eating

Putting healthy eating into practice can feel overwhelming. However, breaking down the process into manageable steps makes it achievable. Small, consistent changes over time lead to significant improvements in your overall well-being. This section will provide practical tips to seamlessly integrate healthy eating into your daily routine.
Incorporating Healthy Foods into Daily Meals
To successfully incorporate healthy foods, start by gradually introducing them into your existing meals. Replace less nutritious options with healthier alternatives. For instance, swap white bread for whole-grain bread, or opt for lean protein sources like chicken breast over processed meats. Focus on increasing the variety of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains in your diet.
Benefits of Meal Prepping and Planning
Meal prepping and planning significantly improve the likelihood of adhering to a healthy eating plan. By preparing meals in advance, you reduce the temptation to make unhealthy choices when hunger strikes. This strategy also saves time and reduces stress during the week. Furthermore, planning your meals helps you stay within your budget and ensures you’re consuming a balanced diet.
Strategies for Managing Cravings and Emotional Eating
Understanding the triggers behind cravings and emotional eating is crucial for managing these behaviors. Keep a food journal to identify patterns and associations between emotions and food choices. Practice mindful eating to appreciate the flavors and textures of your meals. Engage in activities that promote emotional well-being, such as exercise, meditation, or spending time with loved ones, as alternatives to emotional eating.
Role of Mindful Eating
Mindful eating involves paying attention to the sensations associated with eating. Savor each bite, notice the taste, texture, and aroma of your food. By focusing on the present moment during meals, you can appreciate your food more fully, eat at a slower pace, and recognize your body’s fullness cues. This approach can help prevent overeating and promote a healthier relationship with food.
Reading Food Labels and Understanding Portion Sizes
Understanding food labels and portion sizes is crucial for making informed choices. Pay close attention to the ingredients list and nutritional information. Compare different options to find the most nutritious choices. Learn to estimate appropriate portion sizes based on recommended daily allowances. This knowledge empowers you to make conscious choices about what you consume.
Creating a Weekly Meal Plan Emphasizing Balanced Nutrition
A well-structured weekly meal plan ensures you consume a balanced diet. Include a variety of foods from all food groups. Prioritize lean proteins, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. Consider your dietary needs and preferences when planning your meals. Adjust the plan based on your activity levels and nutritional goals.
Table of Practical Tips
| Tip | Explanation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Gradual Introduction | Introduce healthy foods gradually into your existing meals. | Replace white bread with whole-wheat bread, or swap sugary drinks for water. |
| Meal Prepping | Preparing meals in advance reduces unhealthy choices and saves time. | Cook extra portions of healthy meals on the weekend and store them for lunches and dinners during the week. |
| Mindful Eating | Focus on the sensations associated with eating to recognize fullness cues. | Pay attention to the taste, texture, and aroma of your food, and eat slowly. |
| Food Journaling | Identify patterns between emotions and food choices. | Keep a log of your meals and emotional state to uncover potential triggers. |
| Portion Control | Learn to estimate appropriate portion sizes to manage calorie intake. | Use measuring cups and spoons to ensure you’re consuming the recommended portion sizes. |
| Reading Labels | Carefully read food labels to understand nutritional content. | Compare different products based on their calorie, fat, and sugar content. |
| Balanced Meal Plan | Plan meals that include a variety of foods from all food groups. | Include protein sources (like fish), whole grains, fruits, and vegetables in your daily meals. |
Healthy Diet for Specific Needs
A healthy diet is crucial for everyone, but specific needs require tailored approaches. Understanding the nuances of different age groups, health conditions, and lifestyles is vital for creating a personalized plan that supports overall well-being. This section delves into dietary adjustments for various circumstances, emphasizing the importance of professional guidance for optimal results.
Dietary Adjustments for Different Age Groups
Meeting the nutritional needs of each age group is paramount for healthy development and maintenance. Children require a balanced intake of nutrients for growth and development, while adults need a diet that supports their active lifestyles and overall health. Seniors, with changing metabolic rates and potential health concerns, require specific dietary considerations.
- Children: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein is essential for children’s growth and development. Focus on nutrient-dense foods, limiting sugary drinks and processed snacks. Portion sizes should be appropriate for their age and activity level.
- Adults: Maintaining a healthy weight and managing chronic diseases are key dietary concerns for adults. A balanced diet with adequate protein, fiber, and healthy fats is recommended, along with portion control and regular physical activity.
- Seniors: Seniors may experience changes in appetite, digestion, and nutrient absorption. A diet rich in calcium, vitamin D, and protein is important for maintaining bone health and muscle mass. Hydration is crucial, and smaller, more frequent meals can be beneficial.
Dietary Considerations for Specific Health Conditions
Certain health conditions necessitate specific dietary modifications to manage symptoms and prevent complications. Understanding the relationship between diet and health conditions is essential for maintaining well-being.
Focusing on a healthy diet is crucial, especially when considering the importance of proper nutrition for overall well-being. Unfortunately, tragic events like the recent armorer Alec Baldwin Rust shooting highlight the need for responsible safety measures in various industries. However, a balanced diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins, can significantly contribute to a healthier lifestyle and help us navigate the complexities of daily life.
- Diabetes: Diabetics need to carefully manage their carbohydrate intake to maintain stable blood sugar levels. Complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, and healthy fats are important components of a diabetic diet. Monitoring blood glucose levels is critical.
- Heart Disease: Individuals with heart disease should focus on a low-sodium, low-saturated fat diet. Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins are beneficial. Reducing cholesterol and controlling blood pressure through diet is essential.
- Allergies: Individuals with food allergies must avoid specific foods to prevent allergic reactions. Identifying and strictly avoiding allergenic foods is paramount to maintaining health.
Importance of Consulting a Healthcare Professional
Personalizing a diet for specific needs is best achieved with professional guidance. Healthcare professionals, including registered dietitians and physicians, can provide personalized dietary advice tailored to individual circumstances. Their expertise ensures the dietary plan aligns with health goals and addresses any potential health concerns.
Dietary Modifications for Different Lifestyles
Dietary adjustments are necessary for various lifestyles. Vegetarian and vegan diets require careful planning to ensure adequate nutrient intake. Athletic lifestyles require a higher intake of protein and specific nutrients for performance and recovery.
Dietary Recommendations for Different Health Conditions
| Health Condition | Dietary Recommendations | Reasons |
|---|---|---|
| Diabetes | Balanced carbohydrate intake, complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, healthy fats | Maintain stable blood sugar levels. |
| High Blood Pressure | Low sodium, low saturated fat, fruits, vegetables, whole grains | Control blood pressure. |
| Heart Disease | Low sodium, low saturated fat, fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins | Manage cholesterol and reduce risk factors. |
| Allergies | Avoid allergenic foods | Prevent allergic reactions. |
Healthy Eating Habits for a Lifetime

Embarking on a healthy eating journey is a marathon, not a sprint. Sustaining positive dietary changes requires more than just a fleeting interest; it demands a long-term commitment to consistency. This journey is not about perfection, but about creating healthy habits that become an integral part of your lifestyle. It’s about understanding that setbacks are inevitable, and how to navigate them with resilience and grace.A healthy diet is not a destination, but a continuous process of learning, adapting, and growing.
Consistency in your approach is key, allowing your body to adapt and reap the benefits of a balanced nutritional intake. This long-term approach is far more effective than short-term, restrictive diets, as it cultivates sustainable habits for lasting well-being.
The Importance of Consistency and Long-Term Commitment
Consistency is the cornerstone of any successful healthy eating plan. Regularity in meal timing and portion control creates a predictable pattern for your body, optimizing its metabolic processes. This predictability aids in better blood sugar management, reducing cravings, and preventing overeating. Long-term commitment means understanding that healthy eating is a lifelong journey, not a fleeting fad. This means embracing the process, acknowledging occasional slip-ups as learning opportunities, and remaining steadfast in your commitment to your overall health.
Strategies for Overcoming Challenges and Maintaining Motivation
Maintaining motivation is crucial for long-term success. Tracking your progress, noting positive changes in energy levels, or celebrating milestones, such as reaching a weight goal, are effective strategies. Building a supportive network of friends or family who understand and encourage your journey can be invaluable. Furthermore, diversifying your meals with various healthy options prevents boredom and maintains excitement for your eating plan.
Finding activities to reward yourself (e.g., a walk in nature, a new book) after achieving dietary goals can further boost motivation.
The Importance of Gradual Changes for Long-Term Success
Making drastic changes all at once is rarely sustainable. Gradual modifications, such as incorporating one new healthy food item each week, or substituting processed foods with whole grains, allow your body and mind to adjust more comfortably. This approach fosters a sense of accomplishment and prevents feelings of deprivation, ultimately increasing the likelihood of long-term adherence to the plan.
Remember, small, consistent steps pave the way for significant long-term improvements.
Success Stories of Individuals Who Have Successfully Implemented Healthy Eating Habits
Numerous individuals have successfully integrated healthy eating into their daily routines. For example, many have transitioned from processed foods to a more plant-based diet, reporting significant improvements in energy levels and overall well-being. Stories of individuals successfully managing chronic conditions through dietary modifications are also common, highlighting the positive impact of consistent healthy eating.
A healthy diet is crucial for overall well-being, and incorporating nutritious foods can boost your immune system. This is especially important when considering preventative measures like practicing safe sex, including using condoms for protection against STIs like HIV. Learning more about condon prevencion vih sida can empower you to make informed decisions about your health. Ultimately, a balanced diet, combined with responsible choices, contributes to a stronger, healthier you.
Actionable Strategies for Making Healthy Eating a Lifestyle Choice
Making healthy eating a lifestyle involves integrating these choices into your daily routine. It’s not just about what you eat, but when, how, and where you eat. Planning meals ahead of time and prepping ingredients in advance can help maintain healthy choices during busy days. Creating a visually appealing meal environment can also contribute to positive eating habits.
5 Steps to Adopting a Healthy Diet as a Lifestyle
Adopting a healthy diet as a lifestyle involves a structured approach, not just a one-time adjustment. Here are five steps to start your journey:
- Establish Realistic Goals: Begin with small, achievable goals. Focus on gradual changes instead of drastic transformations. This approach builds consistency and prevents feelings of overwhelm. Setting realistic expectations prevents frustration and promotes sustained effort.
- Identify and Address Triggers: Recognizing situations or emotions that lead to unhealthy food choices is essential. This allows for proactive strategies to avoid these triggers. For example, recognizing stress as a trigger can help you choose healthy snacks instead of processed foods when feeling stressed.
- Seek Support: Surround yourself with a supportive network. A friend, family member, or registered dietitian can offer encouragement and guidance. Support systems are crucial for staying motivated and accountable.
- Make Gradual Changes: Instead of radical alterations, incorporate small changes into your diet. This ensures that these changes become ingrained habits. One example could be swapping refined grains for whole grains over time.
- Celebrate Progress: Acknowledge and reward yourself for your achievements. Positive reinforcement strengthens your commitment and builds a positive association with healthy eating.
Healthy Diet and Food Safety
A healthy diet is crucial for overall well-being, but food safety is equally important. Ignoring food safety practices can lead to serious illnesses, disrupting health and potentially causing long-term complications. Proper food handling ensures the safety and quality of the food we consume, enabling us to maximize the nutritional benefits of our dietary choices.Understanding the risks associated with unsafe food handling and implementing preventive measures is essential for maintaining a healthy diet.
This includes recognizing potential hazards, employing safe storage and preparation techniques, and understanding the common signs of spoiled or contaminated food.
Focusing on healthy diet nutrition tips is crucial for overall well-being, but sometimes, even well-intentioned recommendations can be flawed. For example, the recent “read like wind recommendations scandal” highlights how seemingly reputable sources can sometimes fall short of delivering accurate nutritional advice. This recent controversy emphasizes the importance of verifying information and relying on trustworthy sources for your healthy diet nutrition tips, ensuring you’re making informed choices about your diet.
Dig deeper into the details of this news story at read like wind recommendations scandal to better understand the complexities of nutritional guidance.
Importance of Food Safety in Preventing Illness
Safe food handling practices are vital to preventing foodborne illnesses. Contaminated food can harbor harmful bacteria, viruses, and parasites, leading to various infections with symptoms ranging from mild discomfort to severe complications. Preventive measures significantly reduce the risk of these illnesses, safeguarding both individual and public health.
Safe Food Handling Practices
Safe food handling practices are crucial for preventing foodborne illnesses. Proper storage and preparation techniques are key to ensuring food safety. These practices are fundamental to a healthy diet, protecting consumers from potential hazards.
Focusing on a healthy diet is crucial, especially when considering future family planning. For example, ensuring proper nutrition during pregnancy is vital, and understanding the importance of a balanced diet for overall well-being is key. This also connects to the complexities of situations like those surrounding Alabama’s laws regarding frozen embryos and their potential impact on future children, as seen in this article on alabama frozen embryos children.
Ultimately, a healthy lifestyle, encompassing diet and reproductive choices, is a significant factor in a child’s development and future well-being.
- Refrigeration: Store perishable foods, such as meat, poultry, seafood, dairy products, and leftovers, in the refrigerator at or below 40°F (4°C) to slow the growth of harmful bacteria. Proper temperature control is critical for food safety. Ensure that the refrigerator is functioning correctly and that foods are stored at the appropriate temperature.
- Thawing: Never thaw food at room temperature. Thaw food safely in the refrigerator, under cold running water, or in a microwave. Rapid thawing methods help prevent the growth of harmful bacteria.
- Cross-Contamination Prevention: Use separate cutting boards and utensils for raw and cooked foods to avoid cross-contamination. Thoroughly wash your hands and surfaces after handling raw meat, poultry, seafood, or eggs.
- Proper Cooking Temperatures: Cook foods to their recommended internal temperatures to kill harmful bacteria. Use a food thermometer to ensure the food reaches the safe minimum internal temperature. This practice is critical to preventing foodborne illness.
- Safe Storage: Store leftovers in shallow containers and refrigerate them within one hour of cooking. This prevents bacterial growth.
Common Foodborne Illnesses and Their Prevention
Understanding common foodborne illnesses and their prevention is crucial for a healthy diet. Various factors contribute to foodborne illness, and prevention strategies play a significant role in mitigating the risk.
- Salmonella: This bacteria is often found in poultry, eggs, and meat. Cooking poultry to a safe internal temperature and avoiding cross-contamination can prevent Salmonella infection. Proper hand hygiene is also critical.
- E. coli: Raw or undercooked ground beef, contaminated produce, and unpasteurized milk can harbor E. coli. Thorough cooking of ground beef and proper food handling procedures can significantly reduce the risk of E. coli infection.
- Campylobacter: This bacteria is frequently associated with raw or undercooked poultry. Careful handling and cooking of poultry to the proper temperature are essential for preventing Campylobacter infection. Adequate hand hygiene and avoiding cross-contamination are also key.
Recognizing Spoiled or Contaminated Food, Healthy diet nutrition tips
Recognizing spoiled or contaminated food is crucial for maintaining a healthy diet. Spoiled food can lead to foodborne illnesses, and recognizing its signs helps avoid consuming contaminated items.
- Appearance: Look for changes in color, texture, or odor. Mold growth, unusual discoloration, or slimy texture are signs of spoilage.
- Smell: A foul or unusual odor is an indication of potential contamination. This is a clear signal to discard the food.
- Texture: Unusual softness, stickiness, or unusual changes in texture should raise suspicion.
Food Preservation Methods
Different food preservation methods offer various benefits and drawbacks. Selecting the appropriate method depends on the type of food and desired outcome. These methods play a vital role in extending the shelf life of food.
| Preservation Method | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Refrigeration | Slows bacterial growth, extends shelf life of perishable foods. | Not effective for all foods, some nutrients may be lost. |
| Freezing | Preserves food quality and nutrients, extends shelf life significantly. | Can alter texture of some foods, may require special equipment. |
| Canning | Preserves food for extended periods, allows for preservation of high-nutrient content. | Requires specialized equipment and careful processing. |
| Drying | Reduces moisture content, preventing microbial growth, extends shelf life. | Can alter the texture and flavor of the food, may require specific drying conditions. |
Final Review: Healthy Diet Nutrition Tips
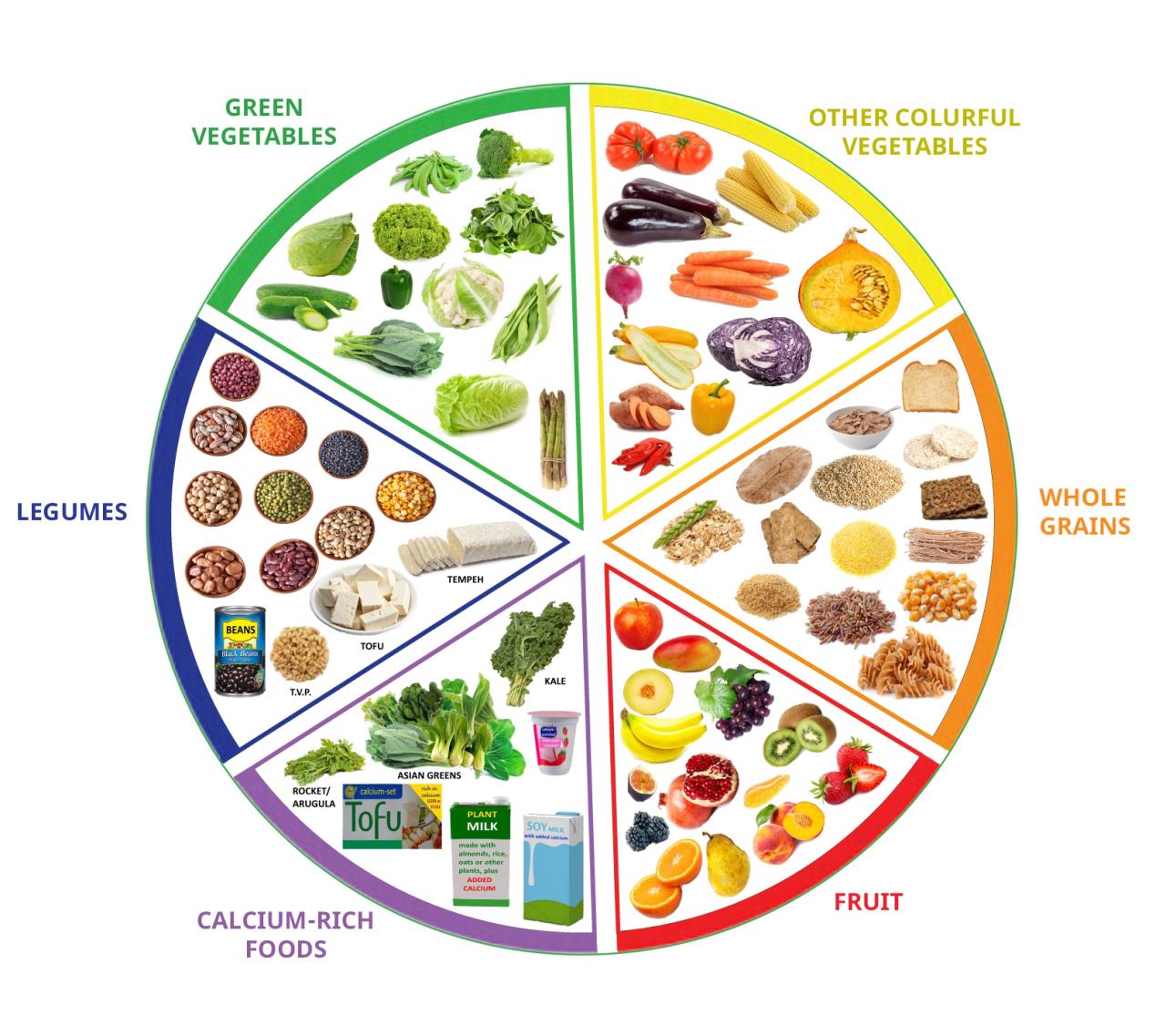
In conclusion, implementing healthy diet nutrition tips isn’t just about following a trend; it’s about nurturing your body and mind. By understanding the fundamentals, incorporating practical strategies, and adapting to your specific needs, you can create a sustainable and fulfilling relationship with food. This guide provides a comprehensive roadmap for achieving optimal health through mindful eating habits. Remember, consistency and a positive mindset are key to long-term success.
Start your journey towards a healthier you today!
Question & Answer Hub
What are some easy ways to incorporate more fruits and vegetables into my diet?
Snack on fruit, add vegetables to smoothies, salads, or stir-fries. Include a variety of colorful vegetables in your meals. Experiment with different ways to prepare them.
How can I manage cravings without resorting to unhealthy foods?
Identify your triggers, keep healthy snacks readily available, practice mindful eating, and engage in stress-reducing activities. Try substituting unhealthy cravings with healthier options.
What are some common mistakes people make when trying to eat healthy?
Skipping meals, focusing solely on restrictive diets, not considering individual needs, and overlooking portion control are some common mistakes. Prioritize balanced meals over extreme measures.
How can I make healthy eating a sustainable lifestyle?
Set realistic goals, make gradual changes, find healthy recipes you enjoy, and build a support system. Don’t try to overhaul your diet overnight.

