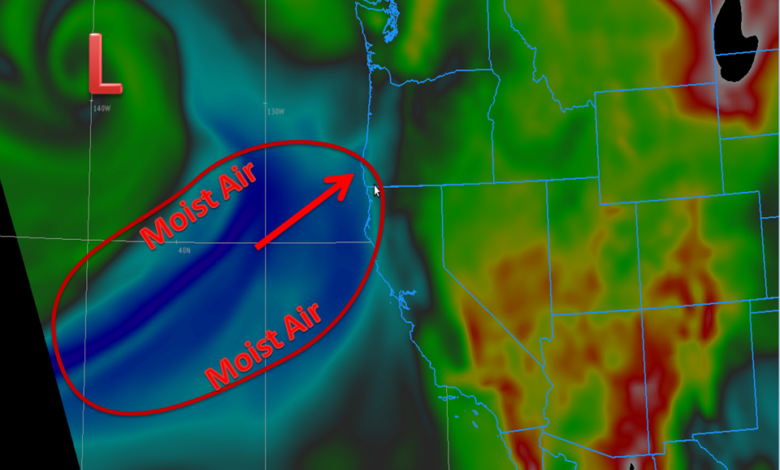
West Coast Atmospheric River Forecast
Atmospheric river west coast forecast: Prepare for the potential impacts of these powerful weather systems. This comprehensive guide explores the science behind atmospheric rivers, their unique effects on the West Coast, and how forecasts are developed and communicated. We’ll delve into past events, examine forecasting methods, and discuss community preparedness strategies.
Understanding atmospheric rivers is crucial for residents and communities along the West Coast. These concentrated bands of moisture can bring significant rainfall, leading to flooding, landslides, and other hazards. This forecast will highlight the specific vulnerabilities of the region and provide actionable insights to help navigate these powerful weather patterns.
Overview of Atmospheric Rivers
Atmospheric rivers (ARs) are a significant driver of weather patterns, particularly in coastal regions. These concentrated streams of water vapor in the atmosphere play a crucial role in delivering precipitation to various parts of the world, often leading to substantial rainfall events. Understanding their characteristics, formation, and impact is essential for effective weather forecasting and risk management.Atmospheric rivers are essentially long, narrow regions of concentrated water vapor in the atmosphere.
The atmospheric river forecast for the West Coast is looking pretty intense. With all the rain and potential flooding, it’s important to stay informed. Meanwhile, if you’re interested in learning more about the Nevada caucus primary, a great resource is the Nevada caucus primary explainer. Hopefully, all the information will help keep the West Coast safe and sound through the atmospheric river event.
They are typically several hundred kilometers wide and thousands of kilometers long, and their presence can significantly impact precipitation patterns over vast areas. These atmospheric rivers form when moist air masses are lifted and cooled, causing condensation and the formation of clouds and precipitation.
Typical Characteristics and Formation
Atmospheric rivers are characterized by high moisture content, typically containing a substantial amount of water vapor. This moisture is transported by strong winds aloft, often originating from tropical or subtropical regions. The convergence and lifting of air masses, often due to orographic effects or interactions with weather systems, lead to the formation of atmospheric rivers. These systems are often associated with strong pressure gradients and wind speeds.
The combination of these factors creates a favorable environment for the transport and condensation of water vapor, resulting in heavy rainfall events. Warmer ocean temperatures often fuel their development, providing more moisture to the atmosphere.
Impact on Weather Patterns
Atmospheric rivers significantly influence precipitation patterns, leading to heavy rainfall, floods, and potentially mudslides in affected areas. These intense precipitation events can cause significant disruptions to daily life, affecting transportation, agriculture, and infrastructure. The timing and intensity of ARs are crucial for predicting potential hazards and developing effective mitigation strategies. The impact varies greatly depending on the specific characteristics of the atmospheric river, the terrain it encounters, and the existing weather conditions.
Comparison of Atmospheric River Types
| Type | Intensity | Geographic Location | Typical Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weak Atmospheric River | Relatively low precipitation amounts | Can occur anywhere, but often in less populated or less susceptible areas. | Localized rainfall, minor flooding. |
| Moderate Atmospheric River | Significant precipitation, potentially leading to localized flooding | Generally found in coastal regions and mountainous areas. | Disruptions to transportation, minor infrastructure damage. |
| Intense Atmospheric River | Extreme precipitation, high risk of widespread flooding, mudslides, and landslides | Often found in coastal areas with mountainous terrain. | Major disruptions to transportation, significant infrastructure damage, potential loss of life. For example, the 2017 atmospheric river that caused devastating floods in California. |
This table provides a basic comparison. The specific impact of an atmospheric river depends on various factors, including its intensity, the terrain it crosses, and the existing weather conditions. The intensity of an atmospheric river is often measured by the total amount of moisture it carries and the duration of the precipitation. Geographic location plays a crucial role, as some areas are more susceptible to the impacts of atmospheric rivers due to their topography and existing infrastructure.
West Coast Specific Impacts

Atmospheric rivers, while a global phenomenon, have a particularly profound impact on the West Coast of North America. Their unique characteristics, combined with the region’s geography and climate, create a potent cocktail of hazards. Understanding these vulnerabilities is crucial for effective preparedness and mitigation strategies.The West Coast’s topography, characterized by towering mountain ranges and densely populated coastal areas, makes it highly susceptible to the intense rainfall and flooding that atmospheric rivers often bring.
The steep slopes increase the risk of landslides and debris flows, while the intricate river systems can quickly overwhelm their capacity, leading to devastating consequences.
Vulnerabilities of the West Coast
The West Coast’s mountainous terrain and dense population centers, coupled with the inherent variability and intensity of atmospheric river events, create a unique set of vulnerabilities. The rapid influx of water from these atmospheric rivers can overwhelm drainage systems, leading to widespread flooding, and the steep slopes exacerbate the risk of landslides and debris flows. This combination of factors makes the West Coast particularly susceptible to damage from these events.
Potential Hazards
Atmospheric rivers on the West Coast often lead to a cascading series of hazards. Heavy rainfall can saturate the ground, triggering landslides and mudslides. These events can cause significant damage to infrastructure, disrupt transportation, and displace communities. Additionally, flooding in low-lying areas and along rivers is a common occurrence. The combination of these hazards presents a significant threat to the region’s safety and well-being.
Timing and Frequency
Atmospheric river events on the West Coast tend to occur most frequently during the winter months, from November to March. This period coincides with the region’s rainy season, and the intense precipitation associated with atmospheric rivers can significantly impact the timing and magnitude of streamflow and runoff. These events are not infrequent; the region experiences these storms multiple times each winter.
Past Events and Consequences
Several significant atmospheric river events have impacted the West Coast, leaving a lasting mark on communities and infrastructure. For instance, the 2017 atmospheric river that impacted the Northern California region caused widespread flooding and landslides, resulting in significant property damage and displacement. The intense rainfall overwhelmed infrastructure and led to significant disruptions in transportation and daily life. The 2022 event in the Pacific Northwest caused substantial flooding and landslides, highlighting the importance of preparedness and mitigation efforts.
Each event, though varying in intensity and location, illustrates the potential for widespread damage and disruption. A detailed historical record of these events can be found in reports from the National Weather Service and other relevant agencies.
Forecasting Methodology
Unveiling the secrets of atmospheric rivers requires a multifaceted approach, combining sophisticated models with meticulous data analysis. Accurate predictions are crucial for mitigating potential impacts, from flooding to power outages. This section delves into the intricate methods employed by forecasters to anticipate the arrival and intensity of these powerful weather systems.Forecasting atmospheric rivers is a complex task, demanding a combination of observational data, advanced numerical models, and skillful interpretation.
The models themselves are not perfect, and human expertise is essential to refine predictions and account for uncertainties.
Atmospheric River Development Stages
Understanding the various stages of atmospheric river development is critical for effective forecasting. This allows for timely interventions and resource allocation. Each stage presents unique characteristics, requiring different forecasting approaches.
- Initiation: The initial stage involves the identification of atmospheric conditions conducive to the formation of an atmospheric river. This includes tracking the moisture content of the air mass, analyzing the wind patterns, and assessing the atmospheric instability. A key indicator is the presence of moisture transport in the upper troposphere, which can be detected through satellite imagery and radiosonde measurements.
Early detection is crucial to predict the potential trajectory and strength of the atmospheric river.
- Organization: As the atmospheric river intensifies, the moisture transport becomes more organized. This stage involves a more concentrated moisture source, and its movement over the terrain plays a key role. The forecasting accuracy improves during this phase as the system structure is more defined, leading to better estimations of the precipitation amounts. For example, the development of a well-defined trough can be identified by weather models, aiding in accurate forecasting.
The atmospheric river forecast for the West Coast is looking pretty intense. While the rain is expected to bring some much-needed moisture, it’s also causing some serious concerns about potential flooding. Meanwhile, the news about Arthur Smith being hired as the Steelers offensive coordinator is certainly a fascinating development, raising questions about the team’s offensive strategy going forward.
Hopefully, this won’t impact the West Coast’s atmospheric river forecast too much. It’s a busy time for weather patterns, to say the least. arthur smith hired steelers offensive coordinator The potential for flooding is a significant factor, no matter what.
- Interaction with Terrain: The interaction between the atmospheric river and the terrain, including mountains and valleys, plays a critical role in precipitation patterns. This stage necessitates analyzing the orographic effects, which significantly influence the distribution and intensity of precipitation. Sophisticated models incorporating terrain data are crucial for accurate predictions of localized impacts. For example, the Cascades mountains significantly affect precipitation patterns during atmospheric river events.
- Dissipation: Eventually, the atmospheric river weakens and dissipates. The forecasting challenge in this phase lies in accurately predicting the timing and location of the final precipitation events. This stage is marked by a decrease in moisture transport and a change in wind patterns. This is often the most difficult stage to forecast precisely due to the variability of atmospheric processes.
Weather Models in Forecasting
Numerical weather prediction (NWP) models are instrumental in atmospheric river forecasting. These sophisticated computer programs simulate the atmospheric processes, allowing forecasters to project the future behavior of the system. High-resolution models, incorporating finer details of the terrain and atmospheric structure, are crucial for accurate predictions of localized impacts.
- Model Types: Various types of NWP models, ranging from global to regional models, are used in forecasting. Global models provide a broad overview of atmospheric conditions, while regional models offer more detailed information over a specific region. The choice of model depends on the forecast lead time and the spatial scale of interest.
- Model Inputs: Accurate model forecasts rely on reliable input data, including observations from satellites, weather stations, and radar. These observations are assimilated into the models to improve the accuracy of the simulations. The quality of the initial conditions directly affects the forecast’s accuracy, and the continuous assimilation of data throughout the forecast period is crucial.
Forecasting Accuracy by Stage
| Stage of Atmospheric River Development | Model Outputs | Forecasting Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Initiation | Moisture transport patterns, wind shear, upper-level trough | Moderate to high, depending on the initial data quality and model resolution |
| Organization | Precipitation intensity, track, and duration | High, as the system structure becomes more defined |
| Interaction with Terrain | Localized precipitation amounts, flooding potential, wind gusts | Moderate to high, depending on the accuracy of terrain representation in the model |
| Dissipation | Timing and location of final precipitation | Lower, due to the variability of atmospheric processes in this phase |
Forecasting accuracy is typically assessed using metrics like root mean square error (RMSE) and bias.
Forecast Information Dissemination
Keeping the West Coast informed about atmospheric river (AR) threats is crucial for preparedness and safety. Effective communication channels and formats are vital in ensuring timely and accurate information reaches diverse communities, enabling proactive measures to mitigate potential impacts. This section details the various methods used to disseminate AR forecasts, emphasizing clear and concise communication.
Communication Channels
Disseminating AR forecasts effectively involves utilizing a multifaceted approach. Multiple channels, each with strengths and weaknesses, are employed to reach a broad audience. These channels ensure that information reaches various communities and demographics in a timely manner.
- Official Government Websites: These platforms often serve as the primary source for official AR forecasts. Detailed maps, charts, and text summaries are readily available, providing essential information for the public. Examples include the National Weather Service (NWS) websites for specific regions.
- News Media Outlets: Reputable news organizations play a vital role in translating complex weather data into easily digestible formats for the public. News reports often include simplified explanations, visual aids like maps and graphs, and interviews with experts, making the information accessible to a wider audience. This is especially useful for those who may not routinely check official websites.
- Social Media Platforms: Social media’s instantaneous nature makes it a powerful tool for disseminating AR forecasts. Agencies can use platforms like Twitter and Facebook to issue alerts, share crucial updates, and provide links to more comprehensive information. However, the speed of social media necessitates careful verification of information sources to avoid the spread of misinformation.
- Mobile Apps: Dedicated weather apps are increasingly used for delivering AR forecasts. These apps often provide customized alerts based on location, allowing users to receive timely warnings and information specific to their area. This personalized approach enhances public preparedness.
Forecast Communication Formats
The formats used for communicating AR forecasts are tailored to the channel and the target audience.
The atmospheric river west coast forecast is looking intense, folks. Heavy rain and potential flooding are a definite possibility. While we’re bracing for the storm, it got me thinking about the impressive career trajectory of Chita Rivera, a true legend in the entertainment world. Her incredible talent and dedication to her craft are truly inspiring, and you can delve deeper into her key moments by checking out this article on chita rivera key moments career.
Hopefully, this storm will pass quickly and without major damage, but in the meantime, staying informed about the atmospheric river west coast forecast is crucial.
- Text Messages and Alerts: Concise summaries of AR impacts, including potential risks like heavy rainfall, flooding, and landslides, are communicated through text messages. These alerts are often location-specific, enhancing the effectiveness of the warnings.
- Maps and Graphics: Visual representations, such as rainfall forecasts, flood inundation maps, and wind patterns, are crucial for understanding AR impacts. Color-coded maps and charts provide at-a-glance information about the extent and intensity of the event.
- Interactive Web Tools: Some websites offer interactive tools that allow users to input their location and receive customized information about potential AR impacts. These tools often integrate with weather data and provide detailed forecasts, enhancing user engagement.
- Videos and Animations: These formats can visually explain complex phenomena like atmospheric rivers. Animations can illustrate the movement and characteristics of the AR, improving public understanding and comprehension.
Importance of Clear and Concise Communication
Accurate and timely communication is critical for successful AR preparedness. Clear and concise information minimizes confusion and maximizes public understanding, enabling proactive measures. Ambiguous or overly technical language can hinder effective response, leading to delays in necessary actions. For instance, a well-written alert about potential flooding should clearly explain the expected severity and timeframe of the event, not just the general possibility of rain.
Effectiveness of Communication Methods
The effectiveness of different communication channels varies depending on the target audience. A table showcasing the relative effectiveness across different demographics can be valuable for refining communication strategies.
| Communication Method | Demographics Reached | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Official Websites | Tech-savvy individuals, researchers, and policymakers | High |
| News Reports | Broad general public, older demographics | High |
| Social Media | Younger generations, mobile-first users | Medium to High, depending on content and engagement strategies |
| Mobile Apps | Mobile-first users, those seeking personalized information | High |
Impacts on Communities and Infrastructure
Atmospheric rivers, with their potent water delivery, bring significant benefits but also pose considerable risks to communities and infrastructure along the West Coast. Understanding the diverse impacts, from flooding and landslides to power outages, is crucial for effective preparedness and response. This section will explore the specific challenges faced by different communities and the vital role of proactive strategies in mitigating these risks.
Potential Effects on Communities, Atmospheric river west coast forecast
Different communities along the West Coast experience atmospheric rivers in unique ways. Rural communities, often with limited infrastructure and dispersed populations, are particularly vulnerable to flooding, mudslides, and road closures. These events can isolate residents, disrupt essential services, and cause significant economic hardship. Urban areas, with their dense populations and intricate infrastructure, face the risk of flash floods, widespread power outages, and damage to critical facilities.
The atmospheric river forecast for the West Coast is looking intense, with potential for significant flooding and disruption. Meanwhile, the results of the New Hampshire Democratic primary are shaping up to be quite interesting, and I’m keen to see how these early signals will impact the overall race. Hopefully, the deluge predicted by the atmospheric river won’t wash away any momentum from the candidates, and we can have a clear picture of the field heading into the next primaries.
results new hampshire democratic primary will be key in understanding the current political climate and how that might influence the West Coast weather situation, at least in a metaphorical sense.
Coastal communities, particularly those in low-lying areas, are susceptible to storm surges and coastal erosion, potentially leading to displacement and property damage. The unique characteristics of each community—population density, elevation, and proximity to waterways—all contribute to their vulnerability.
The atmospheric river west coast forecast is looking pretty intense. While heavy rain is predicted, it’s fascinating to consider how such powerful natural forces can contrast with the human stories, like the tragic tale of lovers in Auschwitz, Keren Blankfeld, and the cold crematorium of József Debreczeni. This heartbreaking narrative, detailed in this article , reminds us of the enduring human spirit even amidst unimaginable horrors.
Regardless, the west coast’s atmospheric river forecast is set to bring significant weather changes.
Impact on Infrastructure
Atmospheric rivers can wreak havoc on various infrastructure elements. Roads and bridges, especially those in mountainous regions or near waterways, are susceptible to flooding, landslides, and debris flows, leading to closures and impeding transportation. Power grids, particularly those located in areas prone to flooding or strong winds, are vulnerable to damage from falling trees, downed power lines, and water intrusion.
This can lead to widespread outages, impacting essential services and daily life. Damage to critical infrastructure, such as water treatment plants and wastewater systems, can create further challenges to public health and safety.
Importance of Preparedness and Response Strategies
Preparedness and effective response strategies are paramount in mitigating the impacts of atmospheric rivers. These strategies encompass a range of actions, from developing early warning systems to educating communities about potential hazards and implementing evacuation plans. A proactive approach to infrastructure maintenance, such as strengthening bridges and roads in vulnerable areas, and improving the resilience of power grids, can significantly reduce the potential for extensive damage.
Community-based preparedness programs, including drills and workshops, empower residents to take actions to protect themselves and their property.
Risk Assessment for Different Communities
| Community Type | Vulnerability Factors | Historical Data (Example) | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rural | Limited infrastructure, dispersed population, steep terrain | 2017 floods resulted in significant road closures and isolation in rural Sonoma County | High |
| Urban | Dense population, complex infrastructure, high property values | 2023 storm surge caused significant flooding in low-lying areas of Seattle | Moderate to High |
| Coastal | Proximity to water, low-lying areas, erosion | 2018 atmospheric river led to widespread coastal flooding and erosion in Oregon | High |
Historical data and vulnerability assessments are essential for prioritizing resources and developing targeted preparedness plans.
These assessments help communities understand their specific risks and tailor their responses to best mitigate the effects of atmospheric rivers.
Visualizing the Forecast
Decoding the potential deluge of an atmospheric river requires more than just words. Visual aids are crucial in understanding the projected path, intensity, and overall impact. The maps and graphs used for these forecasts aren’t just pretty pictures; they’re powerful tools for interpretation, allowing communities and infrastructure managers to prepare for the potential challenges ahead.
Projected Path and Intensity Map
This map, a cornerstone of the forecast, illustrates the predicted path of the atmospheric river over the West Coast. Crucially, it depicts the intensity of the system, highlighting areas expected to experience the heaviest precipitation. The map’s visual representation makes it easy to grasp the overall scale and distribution of the potential impacts.
The map employs a gradient color scale, with hues ranging from light blue (low intensity) to deep purple or red (high intensity). Regions predicted to receive significant rainfall will be depicted in darker shades. Different symbols, like arrows, can indicate the projected movement and speed of the atmospheric river. This visual layering allows for a comprehensive understanding of the system’s trajectory and the expected precipitation amounts in different locations.
For example, a heavy concentration of dark purple could indicate a major storm surge along the California coast.
Key information, such as the location of mountain ranges, major rivers, and populated areas, is also overlaid on the map. This contextualization helps users quickly identify areas most susceptible to flooding or other related impacts. This allows for informed decisions about potential evacuations or infrastructure safeguards.
How to Interpret the Map: By combining the color scale and symbols, one can deduce the intensity and trajectory of the atmospheric river. The map provides a snapshot of the projected impact at various points along its path. A user can assess the relative severity of the storm’s impact on different regions, helping them prepare and respond effectively.
Precipitation Amounts Graph
A crucial element of the forecast is the predicted precipitation amounts for different regions. This is best visualized through a graph showing the expected accumulation over a specific timeframe. The graph clearly presents the projected precipitation amounts for each region, facilitating a precise understanding of the potential rainfall totals over a particular duration.
The graph uses a line graph format, with different lines representing the predicted precipitation for various locations. The x-axis represents time (e.g., days), while the y-axis represents the accumulated rainfall (in inches or millimeters). For example, one line might show the predicted rainfall for San Francisco, while another line could represent the predicted rainfall for Los Angeles. The graph should be designed to be easily readable, allowing for the comparison of projected precipitation amounts across different regions and timeframes.
This is critical for informing emergency response and infrastructure planning. By visualizing the precipitation in this manner, communities can proactively plan for the anticipated water levels.
The graph’s accuracy is essential for assessing the potential risks of flooding, landslides, or other weather-related incidents. Data presented in this format, when coupled with the map, provides a complete picture of the expected atmospheric river event. This allows for better preparedness and potentially mitigates the negative impacts on communities and infrastructure.
Preparedness and Mitigation Strategies
Atmospheric rivers, with their potent rainfall and flooding potential, demand proactive preparedness measures. Understanding how to respond to these events is crucial for minimizing damage and ensuring community safety. Effective strategies involve a combination of community-level planning, individual actions, and robust infrastructure designs.Effective preparedness is not just about reacting to an event; it’s about anticipating its potential impacts and taking proactive steps to lessen their severity.
This involves understanding the specific vulnerabilities of your community and tailoring strategies to address those concerns. It also necessitates a collaborative approach, bringing together residents, local officials, and experts to develop and implement comprehensive plans.
Community Preparedness Measures
Communities can significantly reduce the impact of atmospheric rivers through proactive measures. Early warning systems, robust evacuation plans, and community education programs are vital components of a comprehensive preparedness strategy. Residents should familiarize themselves with evacuation routes and designated safe zones. Understanding the specific floodplains and high-risk areas in their community empowers residents to take necessary precautions.
Importance of Early Warning Systems
Early warning systems are paramount in mitigating the effects of atmospheric rivers. These systems provide crucial time for individuals and communities to take protective actions. Real-time information about potential rainfall, flooding, and wind conditions empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their safety and property. The timely dissemination of accurate information is crucial; reliable communication channels are essential to ensure that warnings reach everyone in the impacted area.
The 2017 atmospheric river event, for example, highlighted the importance of efficient warning systems in minimizing property damage and loss of life.
Individual and Family Preparedness Actions
Taking individual and family-level precautions is a critical aspect of preparedness. These measures include having emergency supplies on hand, creating a communication plan, and reinforcing vulnerable structures. A well-stocked emergency kit containing water, food, first-aid supplies, and essential medications is critical. A detailed family communication plan, outlining contact information and meeting points, is vital during emergencies. Fortifying vulnerable areas of the home, such as securing loose objects or reinforcing roofs, can also lessen potential damage.
- Stock emergency supplies: Include non-perishable food, bottled water, first-aid kit, medications, and essential documents.
- Develop a communication plan: Designate a meeting point and ensure all family members know how to contact each other in case of separation.
- Secure vulnerable structures: Reinforce roofs, secure loose objects, and protect windows from potential damage.
- Learn evacuation routes and procedures: Familiarize yourself with evacuation plans and designated safe zones.
- Be aware of local hazards: Identify potential floodplains, high-risk areas, and other local vulnerabilities.
Infrastructure Mitigation Strategies
Implementing effective mitigation strategies for infrastructure is vital. These strategies focus on strengthening existing infrastructure to withstand the intense impacts of atmospheric rivers. This includes measures like improving drainage systems, reinforcing levees, and constructing flood-resistant buildings. The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) has a wealth of resources and guidelines on how to prepare for and mitigate the impacts of natural disasters.
“Robust infrastructure design, including flood-resistant construction techniques and improved drainage systems, is critical for minimizing the damage from atmospheric rivers. Thorough risk assessments and the implementation of preventative measures are essential for safeguarding community assets.”
Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA)
Conclusion
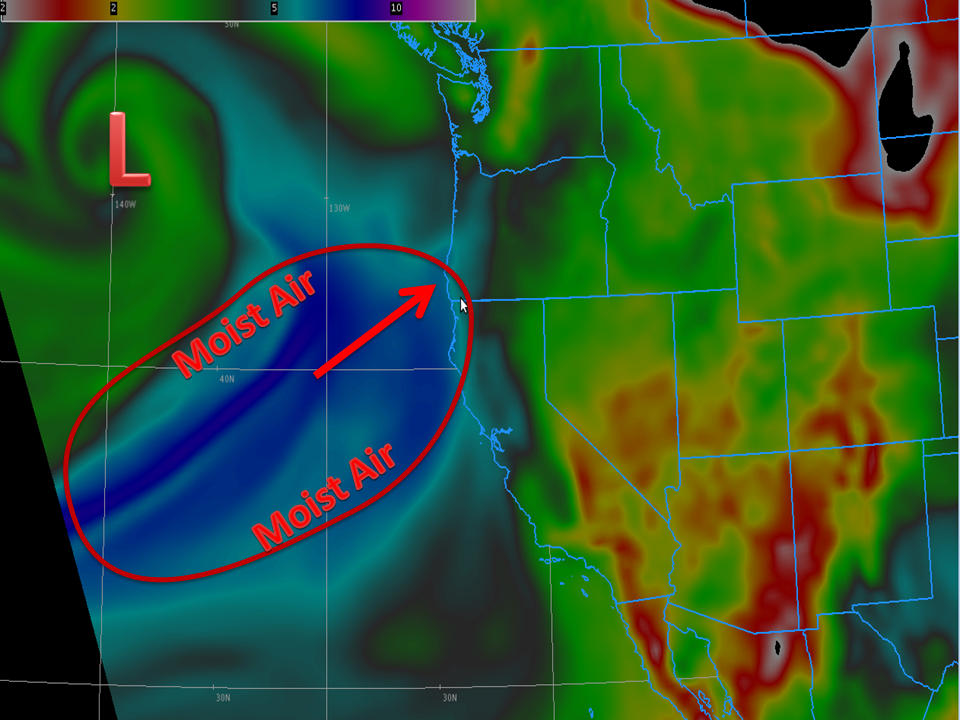
In conclusion, the atmospheric river west coast forecast is a vital tool for communities to prepare for and mitigate the effects of these intense weather systems. By understanding the science behind these events, the forecasting methodology, and the importance of preparedness, individuals and communities can better navigate these challenges. Stay informed and be prepared!
Essential Questionnaire: Atmospheric River West Coast Forecast
What is the difference between an atmospheric river and a typical rain storm?
Atmospheric rivers are much larger and carry significantly more moisture than typical rain storms. They can result in much higher rainfall totals over a longer period, increasing the risk of flooding and other severe weather.
How accurate are the forecasts for atmospheric rivers?
Forecasting atmospheric rivers is a developing science, and accuracy varies depending on the lead time and the specific characteristics of the event. While models are improving, there’s always some degree of uncertainty in predicting the exact timing, location, and intensity of rainfall.
What resources are available to help me prepare for an atmospheric river event?
Local emergency management agencies, weather services, and community organizations typically provide information on preparedness. Familiarize yourself with your local evacuation plans, have emergency supplies on hand, and stay tuned to official communication channels.
What are the long-term impacts of atmospheric rivers on the West Coast environment?
Long-term impacts include potential changes in water availability, altered ecosystems, and increased risk of erosion and landslides. Research continues to investigate the full extent of these impacts.

