Federal Reserve Policies During Presidential Elections
Federal Reserve policies during presidential elections set the stage for an intricate dance between economic stability and political pressures. This exploration dives deep into the Federal Reserve’s role, its potential vulnerabilities to political influence, and the resulting economic impacts on the nation.
The Federal Reserve, a crucial economic actor, operates independently of the political sphere. However, the timing of elections often brings unique challenges and opportunities. We’ll examine how these dynamics interact and how the Federal Reserve strives to maintain its integrity while navigating the complexities of presidential campaigns.
Federal Reserve’s Role in the Economy

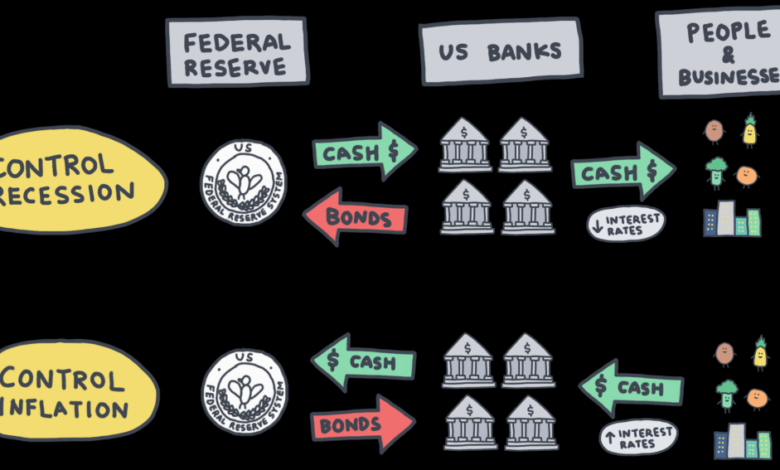
The Federal Reserve, often called the Fed, is the central bank of the United States. It plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy and stable economy by influencing money supply, interest rates, and credit conditions. Understanding its functions and tools is essential for comprehending how the economy operates and how policymakers respond to economic fluctuations.The Federal Reserve’s primary responsibilities include maintaining price stability, maximizing employment, and moderating long-term interest rates.
These goals are intertwined, and the Fed constantly strives to balance them in its actions. This delicate balancing act requires careful consideration of economic indicators and the potential impact of its decisions.
Key Functions of the Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve System is responsible for the monetary policy of the United States. This involves actions taken to manage the money supply and credit conditions to influence interest rates, inflation, and employment. These actions impact the overall health of the economy.
Tools of Monetary Policy
The Federal Reserve employs various tools to achieve its economic objectives. These tools primarily focus on influencing interest rates and the money supply. Interest rates affect borrowing costs for businesses and consumers, impacting investment and spending. The money supply, in turn, affects inflation and overall economic activity.One key tool is the federal funds rate, which is the target rate at which banks lend money to each other overnight.
Federal Reserve policies often take center stage during presidential elections, as voters scrutinize potential economic impacts. The upcoming election cycle is no different, with debates focusing on inflation and interest rates. Meanwhile, the dazzling world of couture, like the 50th anniversary celebration of Didier Ludot in Paris couture didier ludot 50th anniversary paris , offers a stark contrast, showcasing artistic expression while the economic realities of the election season unfold.
Ultimately, the Fed’s actions will have a significant bearing on the financial well-being of the country, regardless of who wins the election.
Changes in this rate influence other interest rates in the economy, affecting borrowing costs for consumers and businesses. Another crucial tool is open market operations, where the Fed buys or sells U.S. Treasury bonds. Buying bonds increases the money supply, while selling bonds decreases it. These actions impact the overall liquidity in the financial system.
Impact on Economic Variables
The Federal Reserve’s actions have a significant impact on economic growth, inflation, and unemployment. Lowering interest rates can stimulate economic activity by encouraging borrowing and investment, potentially boosting economic growth. However, excessively low rates can also lead to inflation if the money supply grows too rapidly. Similarly, raising interest rates can curb inflation but might also slow economic growth and potentially increase unemployment.
The Fed continuously monitors economic indicators to gauge the appropriate course of action.
Federal Reserve Actions During Economic Expansion and Recession
| Policy Tool | Action Taken (Expansion) | Intended Impact (Expansion) | Action Taken (Recession) | Intended Impact (Recession) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Federal Funds Rate | Increase | Cooling down the economy, reducing inflation | Decrease | Stimulating the economy, encouraging borrowing and investment |
| Open Market Operations | Sell bonds | Reducing money supply, controlling inflation | Buy bonds | Increasing money supply, stimulating economic activity |
| Reserve Requirements | Maintain | Maintaining stability in the financial system | Lower | Increasing the availability of lending to banks |
The table above highlights how the Federal Reserve adjusts its policies to manage economic expansion and recession. During expansion, the Fed often raises interest rates to temper inflation, while during recession, it lowers rates to stimulate growth. Open market operations and reserve requirements are also used in conjunction with interest rate changes to fine-tune the economy’s response to these situations.
It’s important to note that these actions are intended impacts, and the actual outcomes can be influenced by various other economic factors.
Federal Reserve policies during presidential elections are always a hot topic. The recent move by Israel’s foreign minister to Brussels, amidst domestic turmoil over the war ( israels foreign minister heads to brussels amid discord at home over war ), highlights global uncertainty that can inevitably influence the Fed’s decisions. Ultimately, these complex international events, alongside economic indicators, will likely shape the Fed’s approach to interest rates and monetary policy during the election cycle.
Presidential Influence on the Federal Reserve: Federal Reserve Policies During Presidential Election
The Federal Reserve, often referred to as the central bank of the United States, plays a crucial role in managing the nation’s economy. Its independence, however, doesn’t insulate it entirely from political pressures. Presidential influence, though constrained by the Fed’s mandate for stable prices and maximum employment, can still subtly shape its actions. Understanding this interplay is key to grasping the complexities of economic policymaking.The relationship between the President and the Federal Reserve Board is one of influence rather than direct control.
The President appoints the members of the Board of Governors, including the Chairman, who serves a four-year term. This appointment power gives the President a degree of influence on the direction of monetary policy. Appointing individuals with similar economic philosophies or policy goals can subtly steer the Fed’s decisions. However, the Federal Reserve’s structure is designed to ensure a degree of independence, preventing immediate political pressures from dictating policy.
Presidential Appointments and Policy Decisions
The President’s power to appoint Federal Reserve Board members is a significant tool in influencing policy. These appointees often share similar economic views as the President, leading to potential alignment in policy decisions. Appointing individuals with a strong belief in a particular economic theory, for instance, might lean the Fed towards policies that promote that theory. A president advocating for fiscal conservatism, for example, might appoint members who share that view, and those appointments can potentially influence the Fed’s decisions on interest rates or other monetary policy instruments.
Presidential Economic Agenda and Federal Reserve Actions
A president’s economic agenda can subtly shape the Federal Reserve’s actions. For instance, if a president prioritizes economic growth, they might implicitly encourage the Fed to adopt policies that stimulate economic activity. Conversely, if a president prioritizes price stability, they might influence the Fed towards policies that curb inflation. These implicit pressures can stem from public statements, policy pronouncements, and even the overall economic climate the president aims to create.
Historical Examples of Presidential Influence
Historical examples illustrate the interplay between presidential agendas and Federal Reserve policies. During periods of economic recession, presidents often advocate for policies that stimulate economic activity. The Fed, responding to these pressures and economic conditions, might adjust interest rates or implement quantitative easing programs. For instance, in the wake of the 2008 financial crisis, presidents and the Federal Reserve worked together to avoid a deeper depression, highlighting the interplay between political and economic forces.
Table: Presidential Administrations and Federal Reserve Chairs
| President | Chair | Key Policy Decisions |
|---|---|---|
| Example President 1 | Example Chair 1 | Example: Lowering interest rates to stimulate economic growth during a recession. |
| Example President 2 | Example Chair 2 | Example: Maintaining low interest rates to control inflation in a period of economic expansion. |
| Example President 3 | Example Chair 3 | Example: Implementing quantitative easing to boost the economy in response to a financial crisis. |
Federal Reserve Policies During Elections

The Federal Reserve’s (Fed) role in maintaining a stable economy is paramount, yet its independence from political pressures is crucial for its effectiveness. Election cycles, with their inherent political dynamics, can introduce unique challenges to the Fed’s ability to conduct monetary policy objectively. Understanding these potential pressures is essential for evaluating the Fed’s actions and assessing their impact on the economy.Political pressures can manifest in various forms during election years.
Candidates may advocate for specific policies, such as lower interest rates or increased spending, that could influence the Fed’s decisions. Public perception of the economy’s health plays a significant role, and the Fed’s actions are often scrutinized to ensure they align with prevailing political narratives.
Potential Political Pressures on the Federal Reserve
The Fed operates under a mandate to maintain price stability and maximum employment. However, during election years, this mandate can be subject to political interpretations. Politicians might pressure the Fed to prioritize short-term economic gains, even if those gains conflict with long-term stability. The desire to boost economic indicators like GDP growth or unemployment rates before an election could lead to policies that have unintended consequences.
This could lead to inflation or other issues in the future. Examples of such pressures can be found in historical instances where presidents have publicly voiced opinions about the Fed’s policies, influencing public perception and potentially creating pressure on the Fed’s decision-making process.
Motivations for Perceived Politically Motivated Actions
Several motivations could drive the Fed to act in a way that appears politically motivated. A desire to avoid jeopardizing their reputation and credibility among the public and political figures is a strong motivator. The Fed may try to maintain stability and avoid exacerbating economic anxieties in the lead-up to an election. Furthermore, the desire to avoid being perceived as partisan or biased, especially when facing criticism from different political parties, is also a powerful factor.
This might result in the Fed adopting policies that are seen as politically neutral.
Comparing Fed Policies Under Different Administrations
The Fed’s approach to monetary policy can vary across different presidential administrations. For instance, a president focused on stimulating the economy might encourage lower interest rates, while another focused on controlling inflation might advocate for higher rates. These differing approaches, while seemingly political, often reflect the specific economic challenges and priorities of each administration. Historically, there have been cases where presidents have attempted to influence the Fed’s decisions, but the Fed’s independence has generally allowed it to maintain its mandate and act accordingly to economic conditions.
Concerns Regarding the Fed’s Independence
A common concern during election years is the potential erosion of the Fed’s independence. Critics fear that political pressures might lead to policies that prioritize short-term gains over long-term economic stability. Public perception and political narratives can sway public opinion, which might impact the Fed’s decisions. The Fed’s decisions are frequently scrutinized, with critics often seeking to link their actions to political outcomes.
Maintaining the Fed’s credibility is essential for the stability of the financial system.
Maintaining Fed Independence During Elections
The Fed can maintain its independence during election cycles by adhering to its mandate and focusing on economic data, not political considerations. Transparency in its decision-making processes can help build public trust. Clear communication about the rationale behind policy decisions can mitigate concerns about political influence. Maintaining a reputation for impartiality and objectivity is crucial for the Fed’s long-term credibility and effectiveness.
It’s important for the Fed to resist pressures to take actions based on political expediency rather than economic necessity.
Potential Scenarios for Fed Policies During Election Years
| Scenario | Policy Action | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Economic downturn, high unemployment | Lowering interest rates | Stimulate economic activity and job creation. |
| High inflation, rising prices | Raising interest rates | Control inflation and maintain price stability. |
| Economic uncertainty, volatile markets | Maintaining stable policy | Maintain market confidence and avoid destabilizing the financial system. |
| Political pressure for stimulus | Resisting pressure to act politically | Maintain independence and prioritize long-term economic stability. |
Economic Impacts of Election-Year Policies
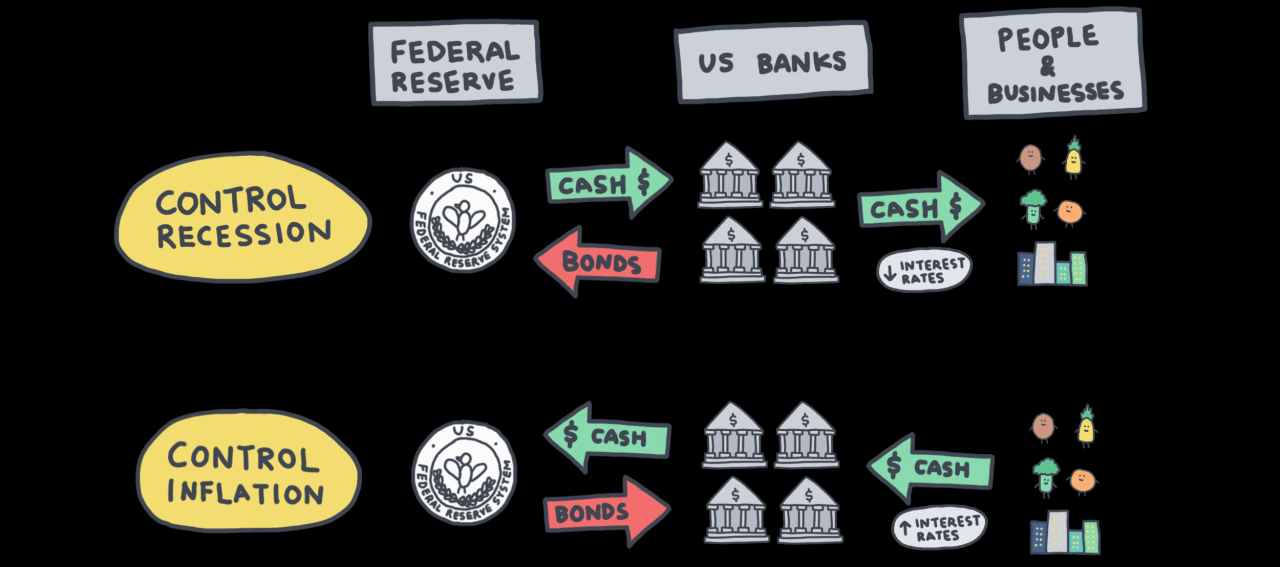
Election years often bring unique economic pressures, and the Federal Reserve’s actions during these periods can significantly impact various sectors. The interplay between political agendas and economic realities creates a complex environment, influencing investor sentiment, consumer spending, and overall market stability. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for anyone seeking to navigate the economic landscape during presidential election cycles.The Federal Reserve’s decisions during election years are frequently scrutinized and often subject to heightened speculation.
This heightened attention can lead to market volatility as investors attempt to anticipate the Fed’s response to economic developments, and political pronouncements, and to the political climate. The policies implemented can have both immediate and long-term effects, affecting everything from interest rates to employment levels and ultimately, the trajectory of the economy.
Potential Short-Term Economic Effects
The short-term effects of Federal Reserve policies during election years can be quite pronounced. For example, a decision to lower interest rates in an election year could stimulate borrowing and investment, potentially boosting economic growth in the short run. Conversely, a decision to maintain or raise interest rates might curb inflation but could also dampen economic activity, particularly if coupled with concerns about economic recession.
Federal Reserve policies often take center stage during presidential election years, as economic anxieties rise. However, the upcoming Taiwan election, with the Democratic Progressive Party at the forefront, Taiwan election democratic progressive party , could subtly influence the Fed’s decisions. Ultimately, the Fed’s approach hinges on the overall economic climate and potential market reactions, regardless of any political events.
The impact is not uniform across sectors. Some industries, like housing, might experience a surge in activity, while others, especially those dependent on high consumer confidence, could see a downturn.
Potential Long-Term Economic Effects
Long-term consequences of election-year policies are more nuanced and less predictable. A policy intended to boost short-term economic growth might inadvertently lead to higher inflation or unsustainable debt levels in the future. Similarly, a policy designed to control inflation might stifle long-term investment and economic growth. The effectiveness of any policy depends on various factors, including the overall health of the economy, the specific circumstances surrounding the election, and the degree to which the Fed’s actions align with prevailing market sentiment.
Market Volatility and Uncertainty
Election years often bring heightened market volatility. Investors may react to perceived political risks, creating uncertainty and speculation about the direction of the economy. The Federal Reserve’s actions, or the perceived impact of those actions on election outcomes, can exacerbate this volatility. This can manifest in fluctuating stock prices, shifts in bond yields, and increased uncertainty regarding future investment decisions.
Historical data often shows a correlation between election years and market fluctuations, highlighting the need for investors and economists to carefully consider the context of the election cycle.
Federal Reserve policies during presidential elections are often a hot topic, with economists and pundits debating the potential impact on the economy. Recent news about the Oilers’ Stuart Skinner defeating the Blue Jackets in a nail-biting hockey match ( oilers stuart skinner defeat blue jackets ) might seem unrelated, but the underlying economic anxieties and market speculation often play a role in such sporting events.
Regardless, the Fed’s approach to interest rates and inflation continues to be a crucial factor in the coming election cycle.
Federal Reserve’s Response to Economic Events
The Federal Reserve’s response to economic events during election years can vary. In periods of economic expansion, the Fed might maintain its current course, or in cases of recession, a more aggressive approach could be warranted. The Fed’s actions might also be influenced by political pressures, though the Federal Reserve is mandated to operate independently from political influences.
For example, if inflation rises unexpectedly, the Fed might respond with interest rate hikes, but the timing and extent of those hikes could be influenced by the political calendar.
Federal Reserve policies during presidential elections are often a hot topic, with speculation swirling about potential impacts on the economy. The delicate balance of maintaining economic stability while navigating political pressures is always fascinating to observe. For example, consider the tragic stories of love and loss during the Holocaust, like the one highlighted in the heartbreaking article about lovers in Auschwitz, Keren Blankfeld, and the cold crematorium of József Debreczeni.
Ultimately, these stark reminders of history serve as a backdrop to the more nuanced considerations of economic policy during elections.
Factors Influencing Federal Reserve Decision-Making
Numerous factors influence the Federal Reserve’s decision-making during election years. These include economic indicators like inflation rates, unemployment figures, and GDP growth. The political climate and the election’s outcome are also crucial factors. Policymakers might be more cautious about implementing significant changes if the election outcome is uncertain. Public sentiment and market reactions also play a role.
The Federal Reserve aims to maintain price stability and maximum employment, and any decision must consider these overarching goals.
- Economic indicators (inflation, unemployment, GDP) directly affect the Fed’s decisions, influencing the pace of monetary policy.
- Political considerations, including the upcoming election and the possibility of shifts in political power, can impact the Fed’s willingness to act decisively or avoid significant policy changes.
- Market sentiment and investor reactions to policy decisions shape the overall economic environment and can further influence the Fed’s actions.
Public Perception and Communication
The Federal Reserve’s actions during presidential election years often come under intense scrutiny, and public perception plays a crucial role in shaping the effectiveness of its policies. Understanding how the public interprets these actions, and how the Fed communicates its approach, is essential for navigating the political landscape and maintaining the central bank’s credibility. The Fed’s communication strategy is therefore paramount, especially in politically charged environments.The public’s perception of the Federal Reserve during election cycles is often influenced by political narratives and media coverage.
If the Fed’s actions are perceived as politically motivated, it can erode public trust and undermine the institution’s independence. Conversely, if the Fed’s actions are seen as impartial and supportive of economic stability, public trust is strengthened. This perception can significantly affect the effectiveness of the Fed’s policies.
Public Perception of Fed Actions
The public often interprets the Federal Reserve’s actions during election cycles through a political lens. Economic policies are frequently intertwined with political agendas, and public discourse surrounding these policies is often polarized. This political context can lead to misunderstandings and misinterpretations of the Fed’s motivations and objectives. For example, if the Fed raises interest rates during an election year, some might view this as an attempt to damage the incumbent’s chances of reelection, while others might see it as a necessary step to control inflation.
Public perception of the Fed’s actions is thus highly contingent on the prevailing political climate and the specific narrative being presented.
Fed Communication Strategies, Federal reserve policies during presidential election
The Federal Reserve employs various communication strategies to convey its policies to the public. These include press conferences, speeches by policymakers, economic reports, and publications. The Fed aims to explain its rationale behind its decisions and the expected economic consequences of its actions. Clear and transparent communication is vital for maintaining public trust and understanding. For instance, the Fed may issue statements explaining the rationale behind an interest rate hike, emphasizing the need for price stability.
Challenges in Effective Communication
Communicating economic policy effectively during periods of intense political polarization can be challenging. Differing interpretations of economic data and conflicting political narratives can hinder the public’s ability to grasp the nuanced aspects of the Fed’s decisions. This polarization can lead to mischaracterizations and distortions of the Fed’s intentions. Moreover, the complexity of economic policies can make it difficult for the public to understand the Fed’s actions without simplification.
Examples of Successful and Unsuccessful Communication
Examples of successful communication strategies include clear, concise explanations of the Fed’s policies and their intended outcomes, as well as transparency in the decision-making process. Conversely, examples of unsuccessful strategies include ambiguous statements, overly technical language, or a lack of engagement with diverse perspectives. During periods of economic uncertainty, a robust communication strategy is essential for maintaining public trust and ensuring that the Fed’s policies are understood and supported.
Comparison of Communication Styles
| Communication Method | Target Audience | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Press conferences | Broad public and financial markets | Generally effective, but susceptible to misinterpretation if not carefully managed. |
| Speeches by policymakers | Specific groups, including economists and analysts | Effective for conveying nuanced perspectives, but may not always resonate with the general public. |
| Economic reports | Economists and financial analysts | Effective for providing data-driven insights, but often requires interpretation for wider understanding. |
| Public education initiatives | General public | Potentially effective for improving public understanding of economic concepts, but may not always translate to widespread agreement. |
Closure
In conclusion, the Federal Reserve’s actions during presidential elections are a fascinating study in economic policymaking under pressure. The independence of the central bank is paramount, but political considerations inevitably influence the public’s perception and the economy’s response. Understanding these interactions is vital for comprehending the interplay between economic policy and the political landscape.
Clarifying Questions
What are some common concerns about the Federal Reserve’s independence during election seasons?
Concerns often arise about potential political pressure on the Federal Reserve to act in ways that favor a particular presidential candidate or party. This pressure can stem from a desire to boost the economy before an election, even if it means sacrificing long-term stability.
How does the President’s economic agenda influence the Federal Reserve’s actions?
The President’s economic agenda, including proposed policies and spending plans, can influence the Federal Reserve’s actions by creating expectations about future economic conditions. The Federal Reserve may adjust its policies in response to these anticipated changes.
What are some ways the Federal Reserve can maintain its independence during presidential elections?
Maintaining transparency and clear communication about its policy decisions is crucial. The Federal Reserve can also highlight the long-term economic benefits of its independent actions, even if they don’t align with short-term political objectives.
What is the potential for market volatility and uncertainty during election periods due to Federal Reserve actions?
Market uncertainty can arise if the Federal Reserve’s actions are perceived as politically motivated or if the public doubts the central bank’s ability to remain independent. This can lead to fluctuations in stock prices and other market indicators.


