
Japan Economy, Population, and Politics A Deep Dive
Japan economy population politics is a complex interplay of economic performance, demographic shifts, and political decisions. This exploration delves into the intricate relationship between these three facets, examining Japan’s historical economic trajectory, its aging population, and the evolution of its political system. We’ll analyze the key drivers of Japan’s economy, from manufacturing to technology, and how they’re impacted by population trends and political choices.
This in-depth look will provide a comprehensive understanding of the current state and future prospects of Japan. We’ll examine the challenges and opportunities facing the country, considering both internal factors and the influence of global events. The data will be presented visually, using tables and charts for clarity and comparison.
Japanese Economy
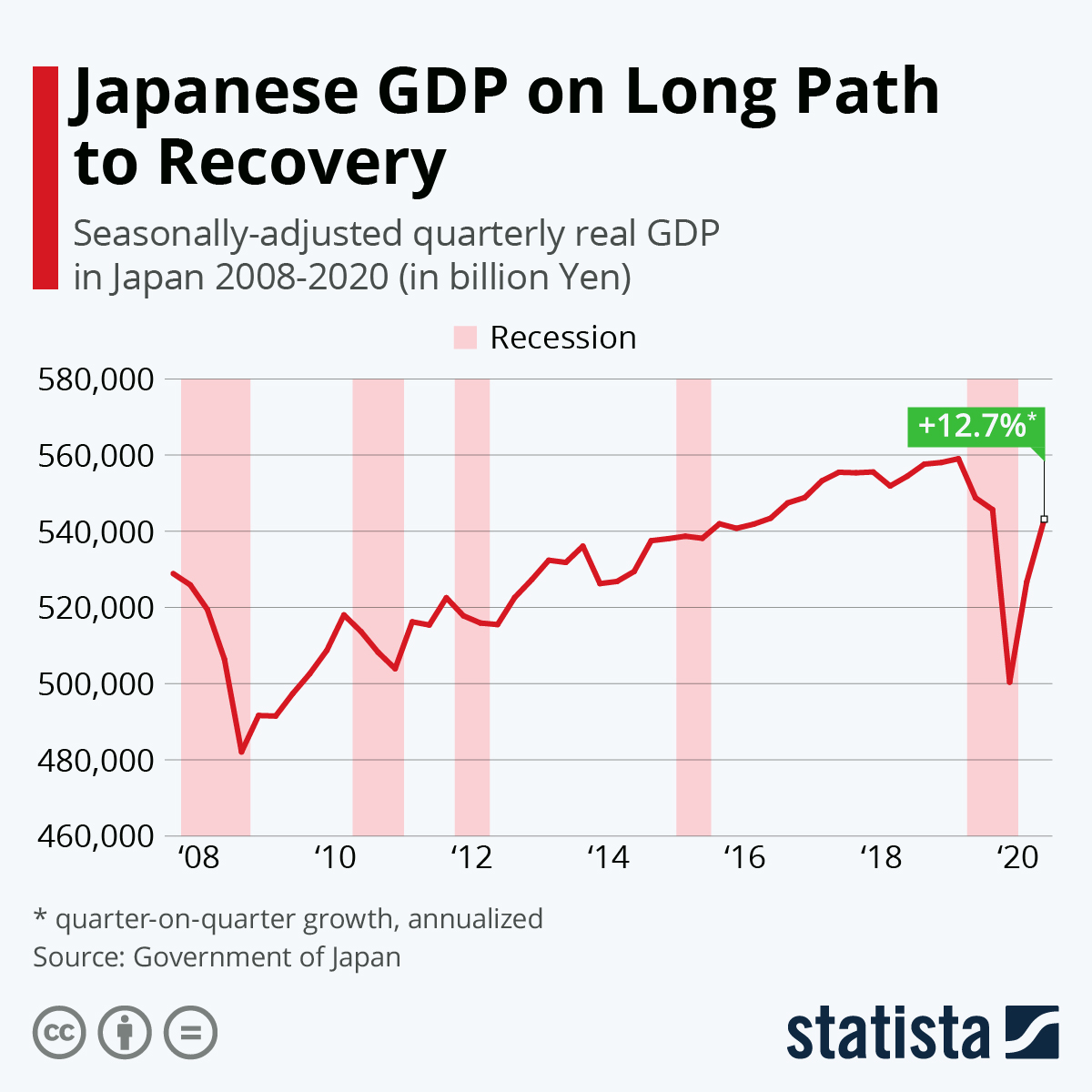
Japan, a global economic powerhouse, has experienced a fascinating and complex economic trajectory. From its post-war economic miracle to the challenges of the 21st century, the nation’s economic performance has been a significant driver of global trends. This overview delves into Japan’s economic history, key sectors, challenges, and future prospects.Japan’s post-war economic growth was remarkable, fueled by export-oriented manufacturing and a highly skilled workforce.
However, the nation has since faced headwinds, including a shrinking workforce, aging population, and the rise of new global competitors. Understanding these shifts is crucial to assessing Japan’s current economic standing and future potential.
Historical Overview of Economic Performance
Japan’s economic performance has been marked by distinct phases. The post-war era saw rapid industrialization and export-led growth, transforming Japan into a global economic powerhouse. The 1980s witnessed a period of remarkable prosperity, culminating in a speculative bubble. The subsequent burst led to a prolonged period of stagnation, known as Japan’s “lost decades,” characterized by deflation and sluggish growth.
More recently, Japan has navigated a complex mix of global economic trends, including the 2008 financial crisis and the rise of new economic powers.
Key Sectors Driving the Economy
Japan’s economy is driven by a diverse range of sectors. Manufacturing, particularly in automobiles, electronics, and machinery, remains a cornerstone. Technology, including robotics, semiconductors, and software, is becoming increasingly important. The service sector, encompassing finance, retail, and tourism, plays a significant role in the economy. This multi-faceted approach is crucial to sustaining economic growth and adaptability in a globalized world.
Comparison to Other Major Economies
Comparing Japan’s economic growth to other major economies reveals a mixed picture. While Japan’s post-war growth was impressive, it has lagged behind some other economies in recent decades. This relative performance reflects the unique challenges Japan faces, such as its aging population and dependence on exports. Understanding these comparative data points is vital to crafting effective economic strategies.
Challenges and Opportunities
Japan faces several significant challenges, including a shrinking workforce, an aging population, and persistent deflation. These demographic shifts place pressure on productivity and social security systems. However, Japan also possesses significant opportunities. Its advanced technology, skilled workforce, and established infrastructure provide a strong foundation for future growth. The interplay of these factors will shape Japan’s economic future.
GDP Growth Rate Comparison (Last Decade)
| Country | Average Annual GDP Growth Rate (2014-2023) |
|---|---|
| Japan | 0.9% |
| United States | 2.1% |
| China | 6.5% |
| Germany | 1.7% |
Note: Data represents averages and may vary depending on specific sources and methodologies.
Role of Government Policies
Government policies have significantly influenced Japan’s economic trajectory. Fiscal and monetary policies have been employed to stimulate growth and manage economic downturns. Furthermore, regulatory frameworks and industrial policies have shaped the development of specific sectors. The effectiveness of these policies in achieving desired outcomes is a subject of ongoing debate and analysis.
Major Economic Indicators
| Indicator | Japan (2023 Estimate) |
|---|---|
| Inflation Rate | 2.5% |
| Unemployment Rate | 2.7% |
| Trade Balance | USD -150 billion |
Note: Data represents estimates and may differ based on reporting agency.
Impact of Global Events
Global events, such as the 2008 financial crisis and the COVID-19 pandemic, have had a profound impact on Japan’s economy. The global slowdown and supply chain disruptions have affected exports and overall economic activity. The ability to adapt to such external shocks is a key indicator of resilience.
Current Economic Standing and Future Prospects
Japan’s current economic standing is characterized by a complex mix of strengths and weaknesses. While the economy shows signs of recovery, the nation faces persistent challenges. Future prospects hinge on the ability to address demographic shifts, foster innovation, and maintain global competitiveness. This will require a multifaceted approach encompassing government policies, private sector initiatives, and societal adaptation.
Japan’s complex interplay of economy, population, and politics is fascinating. The aging population and shrinking workforce are significant factors, impacting everything from labor markets to long-term economic strategies. Interestingly, the meticulous detail in some Broadway cast albums, like the broadway cast albums sweeney todd , reminds me of the intricate calculations needed to understand the various forces shaping Japan’s future.
Ultimately, understanding these elements is crucial for anyone trying to comprehend the nation’s trajectory.
Japanese Population
Japan’s population, a cornerstone of its societal and economic fabric, is experiencing a profound demographic shift. This transformation, characterized by an aging population and declining birth rate, poses significant challenges to the nation’s future prosperity. Understanding these trends is crucial for comprehending the complex interplay between population dynamics and economic productivity.
Current Demographics
Japan’s population is characterized by an aging profile and increasing urbanization. A significant portion of the population resides in densely populated urban centers, while rural areas face population decline. This concentration of population in urban areas leads to various social and infrastructural challenges.
Aging Population and its Impact
Japan’s aging population is placing immense pressure on the workforce and social security systems. The shrinking pool of working-age individuals is struggling to support a growing number of retirees. This demographic imbalance threatens the sustainability of Japan’s social security net. The dependency ratio, a key indicator of this phenomenon, is rising, potentially leading to a reduction in tax revenues and increased pressure on government spending.
Causes of Declining Birth Rate
Several factors contribute to Japan’s declining birth rate. Economic pressures, particularly the high cost of raising children in a developed nation, are significant factors. The societal expectation for women to balance career and family life presents further obstacles. Additionally, cultural norms and societal attitudes regarding family size and gender roles play a part in shaping reproductive choices.
Comparison with Other Developed Countries
Compared to other developed countries, Japan’s population decline is relatively pronounced. While many developed nations experience similar trends, Japan’s pace of decline is often more rapid. Factors such as cultural norms, economic structures, and social support systems contribute to these differences.
Japan’s economy, population, and politics are fascinatingly complex, with constant shifts and challenges. Recent trends in the Japanese economy, alongside demographic shifts, are intertwined with the political landscape. This, in turn, raises questions about the future stability of the nation. Sadly, events like the tragic armorer Alec Baldwin Rust shooting highlight the importance of safety protocols in all industries, a lesson that applies just as much to the intricate tapestry of Japan’s economic and political structures.
Effects on Economic Productivity and Social Welfare
The shrinking population directly impacts economic productivity. Labor shortages in various sectors become more acute, hindering economic growth. The burden on social welfare systems increases, potentially straining public finances and necessitating reforms. The decreasing workforce reduces innovation and economic dynamism, making it harder for Japan to maintain its global competitiveness.
Population Distribution by Age Groups, Japan economy population politics
| Year | 0-14 years | 15-64 years | 65+ years |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1993 | 15.5% | 68.5% | 16.0% |
| 2003 | 13.0% | 65.0% | 22.0% |
| 2013 | 11.5% | 61.0% | 27.5% |
| 2023 | 10.0% | 57.0% | 33.0% |
This table displays the population distribution by age groups in Japan over the past three decades, highlighting the shift towards an aging population. The data showcases a steady increase in the proportion of elderly individuals and a corresponding decrease in the working-age population. This trend is projected to continue, requiring proactive measures to mitigate the potential negative impacts.
Potential Solutions to Address Declining Birth Rate
Government policies aimed at promoting family-friendly environments, such as subsidized childcare and parental leave, can be crucial in encouraging higher birth rates. Addressing economic pressures and making childcare more affordable is also paramount. These measures, alongside social and cultural initiatives that foster a more supportive environment for families, can be considered as part of a comprehensive strategy.
Challenges in Attracting Foreign Workers
Attracting foreign workers to fill labor shortages is a complex undertaking. Cultural differences, language barriers, and bureaucratic hurdles pose significant obstacles. Effective integration programs, comprehensive immigration policies, and clear pathways for legal employment are vital for attracting skilled workers from abroad. Addressing potential social anxieties about foreign workers and promoting a welcoming environment are equally important for success.
Social and Cultural Factors Influencing Population Dynamics
Cultural norms and societal expectations play a vital role in shaping Japan’s population dynamics. Traditional values regarding marriage, family, and gender roles can impact reproductive choices. Encouraging a more flexible and inclusive societal structure can help create a more supportive environment for families. Addressing deeply ingrained cultural norms and promoting a more open and supportive environment for families are important considerations.
Projected Population Trends
A projected population chart illustrates the expected future population trends in Japan. This visual representation will depict the anticipated decline in the working-age population and the rise in the elderly population. The chart can help visualize the magnitude of the demographic shift and the need for proactive responses to the evolving situation. This projection should be interpreted as a possible future scenario, as real-world situations can vary.
Japanese Politics
Japan’s political landscape is a fascinating blend of tradition and modernity. The country, while known for its economic strength, faces unique challenges in its political system, including balancing the needs of a rapidly aging population with economic growth. Understanding the intricacies of Japanese politics is crucial for comprehending the nation’s actions on the global stage.
Japan’s economic struggles, coupled with its aging population and complex political landscape, are fascinating to observe. It’s a complex web of factors, and the recent news surrounding grief is for people sloane crosley grief is for people sloane crosley highlights a different kind of societal challenge. Ultimately, these issues – economic health, demographics, and governance – all intertwine in ways that demand careful consideration, shaping the future of the nation.
Political System Structure
Japan operates under a parliamentary democracy. The Emperor serves as a symbolic head of state, while the Prime Minister, the head of government, is appointed by the Diet (the parliament) and holds executive power. The Diet, comprised of two chambers—the House of Representatives and the House of Councillors—is responsible for legislation. The judiciary, independent of the executive and legislative branches, interprets laws and ensures their application.
This separation of powers is crucial to maintaining a stable and just society.
Major Political Parties and Ideologies
Several political parties hold significant influence in Japan. The Liberal Democratic Party (LDP) is the dominant party, generally advocating for conservative policies, including economic growth and strong national defense. The Democratic Party of Japan (DPJ) typically holds more progressive views, emphasizing social welfare and international cooperation. Other parties, such as the Komeito, often align with specific religious or social agendas.
The diversity of viewpoints and ideologies contributes to the dynamic nature of Japanese politics.
Key Issues Shaping Japanese Politics
Several key issues shape contemporary Japanese politics. These include economic stagnation, the aging population, and social security concerns, alongside security issues and the nation’s role in international affairs. These pressing concerns influence policy decisions and shape the political discourse.
Economic Influence on Political Decisions
Economic factors significantly impact political decisions in Japan. The country’s economic performance directly affects the public’s support for political parties and shapes policy priorities. For example, during periods of economic recession, policies focusing on job creation and economic stimulus tend to gain prominence.
Comparison to Other Countries
Compared to other developed nations, Japan’s political system demonstrates unique characteristics. The long-standing dominance of the LDP, for example, stands in contrast to the more fluid party systems in some other democracies. The emphasis on consensus-building and the role of bureaucracy are also notable features distinguishing Japan’s political process from those in other countries.
Impact of International Relations
International relations significantly influence Japan’s domestic politics. The country’s position in East Asia and its relationship with other global powers impact public opinion and policy decisions on security and trade. The need to maintain peace and stability in the region is a key consideration for Japanese policymakers.
Role of the Media
The media plays a crucial role in shaping public opinion in Japan. News outlets, both print and broadcast, provide information and analysis that influence public discourse and voting patterns. The media’s coverage of political events and policy debates significantly impacts how the public perceives different parties and issues.
Japan’s economy, population, and politics are fascinatingly complex issues. Recent trends suggest a need for innovative solutions to address the demographic shift. Meanwhile, tragic events like the recent Disney World allergy death lawsuit highlight the critical need for safety protocols in public spaces. Understanding these societal factors, including the complexities of public health and safety regulations, is essential to analyzing Japan’s economic future and political landscape.
This lawsuit underscores the delicate balance between freedom and responsibility, which is something we should all be thinking about when discussing public safety and economic policies in Japan.
Significant Political Events and Consequences
Several significant political events have shaped Japan’s recent history. For example, the 2011 earthquake and tsunami had a profound impact on policy decisions regarding disaster preparedness and energy security. Other events, such as economic downturns or diplomatic crises, have also resulted in significant shifts in political priorities.
Evolution of Foreign Policy
Japan’s foreign policy has evolved considerably over time. From its post-war pacifist stance to its growing role in international affairs, the country’s foreign policy reflects its evolving economic and political standing.
Major Political Parties’ Representation (Last 20 Years)
| Party | Representation (Approx.) |
|---|---|
| Liberal Democratic Party (LDP) | Dominant, with fluctuating percentages |
| Democratic Party of Japan (DPJ) | Significant influence, periods of strength and decline |
| Komeito | Consistent representation |
| Other Parties | Varying representation, often with limited seats |
Note: Precise representation figures vary depending on election cycles and coalition dynamics.
Interrelation of Economy, Population, and Politics

Japan’s complex interplay of economy, population, and politics has shaped its trajectory for decades. The nation’s aging population, declining birthrate, and economic stagnation have created a dynamic feedback loop where each element significantly impacts the others. Understanding this intricate relationship is crucial to predicting future challenges and opportunities.The interconnected nature of Japan’s economy, population, and politics creates a system where changes in one area often trigger reactions in the others.
For instance, a shrinking workforce directly impacts economic productivity, which in turn influences government policy decisions related to labor, investment, and social security. This intricate dance of influence demands a deep understanding of the historical context, current trends, and potential future scenarios.
Population Trends and Economic Policy
Japan’s rapidly aging population and declining birthrate have profound implications for economic policy. The shrinking workforce reduces the tax base, making it challenging to fund social welfare programs like pensions and healthcare. This demographic shift necessitates proactive government intervention to stimulate economic growth and support a growing elderly population. Government policies often focus on encouraging immigration, increasing labor force participation, and promoting automation to offset the impact of a shrinking workforce.
Political Decisions and Their Impact
Political decisions directly affect both the economy and the population. Fiscal policies, such as tax reforms and government spending, significantly influence economic performance. For example, stimulus packages can boost economic activity, but they also contribute to national debt. Social policies, such as policies on childcare and education, influence the population’s well-being and potential participation in the labor market.
Japan’s complex interplay of economy, population, and politics is fascinating, but global health concerns like HIV/AIDS prevention are equally important. Understanding the factors affecting Japan’s demographic shifts and economic stability requires looking at the vital role of comprehensive sexual health education, including the use of condoms for preventing the spread of HIV/AIDS. Cordon prevencion vih sida is a crucial aspect of maintaining a healthy and productive population, which, in turn, affects Japan’s economic trajectory.
Ultimately, these interconnected issues highlight the need for a multifaceted approach to societal well-being.
Political decisions also impact the ease of doing business, foreign investment, and overall economic competitiveness.
Potential Conflicts and Synergies
Conflicts often arise when policies designed to address one aspect, such as economic growth, inadvertently harm another, such as the environment. For example, policies promoting rapid industrialization may lead to environmental damage, impacting the well-being of the population. Conversely, policies focused on sustainability can sometimes slow economic growth. Finding a balance between these competing interests is a significant challenge for policymakers.
However, synergies also exist. For example, policies encouraging innovation and technological advancement can stimulate economic growth while improving the lives of citizens.
Interplay of Government Policies, Economic Performance, and Population Demographics
Government policies directly influence economic performance and population demographics. Policies related to labor, immigration, education, and healthcare shape the skills and availability of the workforce. Changes in economic performance, such as periods of recession or boom, can alter the social fabric and influence political priorities. For example, high unemployment during a recession can lead to social unrest, requiring the government to implement measures to mitigate the impact on the population.
Historical Examples of Interrelation
The 1990s economic stagnation in Japan, known as the “Lost Decade,” was partly attributed to a combination of demographic shifts, political indecision, and the bursting of the asset price bubble. The subsequent efforts to address these issues through various government stimulus packages highlight the complex interplay between these three elements. The rise of the Japanese economy post-WWII, on the other hand, shows how political stability and investment in infrastructure fostered economic growth and prosperity, impacting population demographics.
Comparison to Other Countries
Comparing Japan’s approach to other countries reveals diverse strategies. Some nations focus on immigration to counter declining birthrates, while others prioritize investments in education and technology. Analyzing these differing approaches provides insights into potential solutions for Japan’s unique circumstances. The demographic profiles and economic structures of various nations vary greatly, leading to differing policies and outcomes.
Potential Future Challenges and Opportunities
Japan faces potential future challenges, including a shrinking workforce, an aging population, and the need to maintain economic competitiveness. Addressing these challenges will require a multi-pronged approach encompassing economic reforms, social policies, and technological advancements. Opportunities exist in leveraging technology, encouraging innovation, and fostering a more inclusive economy to create sustainable growth.
Long-Term Implications
The long-term implications of the interaction between economy, population, and politics in Japan are substantial. Maintaining a thriving economy and a supportive social safety net for an aging population requires careful and comprehensive planning. This will necessitate a long-term vision that incorporates demographic projections, economic forecasts, and political strategies to ensure the nation’s continued prosperity.
Epilogue
In conclusion, Japan’s economy, population, and politics are deeply intertwined. The country’s aging population and declining birth rate present significant challenges to economic productivity and social security. Simultaneously, the government’s economic policies and political decisions play a crucial role in navigating these challenges. This analysis reveals the complexities of Japan’s current situation and the potential for future growth and development.
Addressing the interplay between these elements is essential for Japan’s long-term success.
FAQ Explained: Japan Economy Population Politics
What are the main challenges facing Japan’s economy?
Japan faces challenges such as an aging workforce, a shrinking population, and deflationary pressures. Competition from other global economies and the impact of global events also pose significant hurdles.
How does Japan’s aging population impact its economy?
An aging population leads to a smaller workforce, impacting productivity and potentially increasing the burden on social security systems. This necessitates policies that support both the elderly and the working-age population.
What are some potential solutions to Japan’s declining birth rate?
Solutions could include financial incentives for families, improved childcare facilities, and flexible work arrangements to support working parents. Attracting skilled foreign workers to fill labor shortages is also a potential avenue.
What is the role of the media in shaping public opinion in Japan?
The media plays a significant role in shaping public opinion in Japan, influencing political discourse and shaping public perception of various issues. The influence of different media outlets and their biases should be considered.






