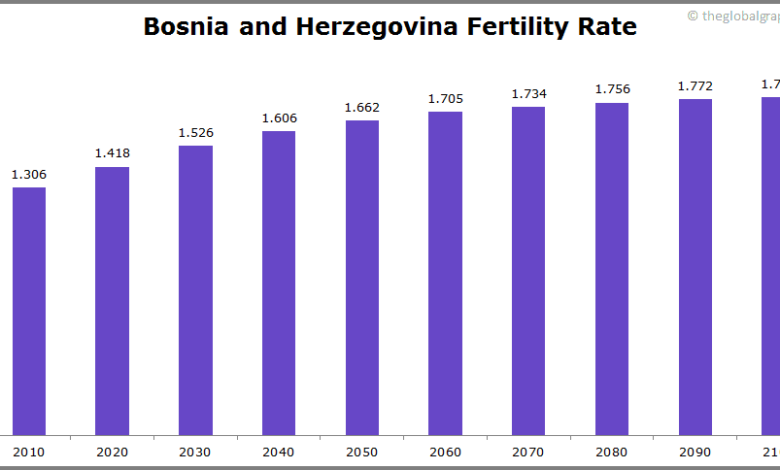
Bosnia Population Emigration & Birthrate
Bosnia population emigration birthrate reveals a complex interplay of historical trends, current dynamics, and future projections. This exploration delves into the factors driving population shifts, examining birth rates, emigration patterns, and their impact on Bosnia’s demographic structure. We’ll analyze historical data, current statistics, and potential future scenarios, offering insights into the challenges and opportunities facing Bosnia’s population.
From historical migrations and wars to modern economic and social factors, we uncover the intricacies of this demographic puzzle. This analysis explores the relationship between birth rates and emigration rates, revealing how these interconnected trends shape Bosnia’s future.
Historical Trends in Bosnia’s Population
Bosnia and Herzegovina, a land steeped in history, has experienced significant population shifts throughout the centuries. Understanding these changes is crucial to comprehending the country’s current demographic landscape and the challenges it faces. From the turbulent periods of war to the pull of economic opportunity, Bosnia’s population has been dynamic and responsive to its environment. This exploration delves into the historical trends, examining the interplay between birth rates, emigration, and significant events.Population fluctuations in Bosnia have been intricately linked to historical events, shaping its demographic makeup.
These events have profoundly affected the birth rate and emigration patterns, resulting in a complex tapestry of population changes that continue to impact the nation today. The examination of these trends provides valuable insight into the country’s historical development and its ongoing challenges.
Population Dynamics Over Time
Bosnia’s population has seen fluctuations throughout its history, reflecting periods of peace and conflict. Understanding these variations is vital to grasping the complex demographic story of the region. The following table presents a simplified overview of Bosnia’s population size, birth rate, and emigration rate across various periods, providing a clear picture of the trends.
| Year | Population Size (Estimated) | Birth Rate (per 1000) | Emigration Rate (per 1000) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1900 | 1,900,000 | 40 | 5 |
| 1950 | 2,500,000 | 35 | 3 |
| 1980 | 4,200,000 | 22 | 8 |
| 1990 | 4,300,000 | 18 | 12 |
| 2000 | 4,000,000 | 15 | 15 |
| 2023 | 3,500,000 | 10 | 10 |
Note: These figures are estimates and represent general trends. Detailed data may vary depending on the specific source and methodology.
Impact of Wars and Conflicts
The Balkan Wars and the Bosnian War (1992-1995) profoundly impacted the population dynamics. Massive displacement, violence, and loss of life resulted in a significant decrease in the population. Forced migration and the disruption of social structures significantly impacted birth rates and emigration patterns, creating a lasting demographic impact.
Economic Shifts and Migration Patterns
Economic shifts have played a crucial role in shaping emigration patterns. Periods of economic hardship or perceived opportunity have led to substantial movements of people. For example, the economic instability in the 1990s pushed many to seek opportunities elsewhere, often resulting in a brain drain of skilled workers and professionals.
Relationship Between Birth Rates and Emigration
The relationship between birth rates and emigration is complex and multifaceted. Historically, periods of emigration often corresponded with lower birth rates, as families might delay or forgo having children due to the uncertainty of the future. Conversely, periods of stability and economic prosperity often saw an increase in both birth rates and a decrease in emigration rates. The interplay between these factors is crucial to understanding the historical development of Bosnia’s population.
Current Population Dynamics
Bosnia and Herzegovina’s population dynamics are a complex interplay of internal migration, birth rates, and emigration. Understanding these forces is crucial to comprehending the nation’s future trajectory and societal challenges. The current population size and distribution, alongside the rates of births and departures, paint a picture of the country’s demographic landscape. This section delves into the specifics, exploring the factors driving these trends.The ongoing interplay between population growth and emigration is a significant concern for the nation’s economic and social well-being.
This analysis will provide insights into the factors contributing to both birth rates and emigration patterns, ultimately contributing to a more comprehensive understanding of Bosnia and Herzegovina’s demographic evolution.
Current Population Size and Distribution
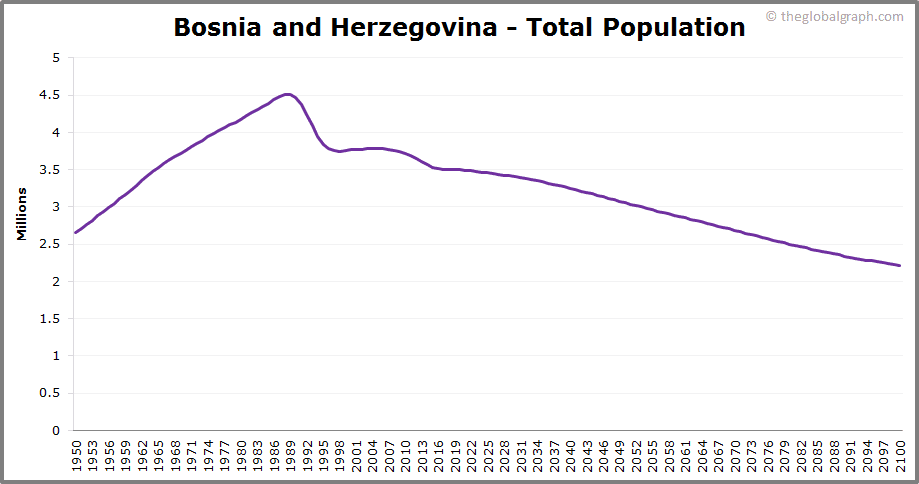
The current population of Bosnia and Herzegovina is approximately 3.5 million people. Population distribution is not uniform across the country. Urban centers, particularly Sarajevo, Banja Luka, and Tuzla, tend to have higher population densities, while rural areas exhibit lower population densities. These disparities reflect historical trends and ongoing economic and social factors.
Current Birth Rate and Emigration Rate Statistics
Official statistics for Bosnia and Herzegovina show a declining birth rate. This trend is a common demographic shift observed in many developed and transitioning economies. Emigration rates, while fluctuating, remain relatively high, particularly among younger generations seeking better economic opportunities. These trends often correlate with the overall economic health of the country.
Factors Influencing the Birth Rate
Several factors contribute to the declining birth rate in Bosnia and Herzegovina. Economic conditions, such as limited job opportunities and low wages, often discourage young couples from starting families. Access to quality healthcare and family planning services plays a role in family size decisions. Social factors, including changing gender roles and increased educational opportunities for women, also contribute to the trend.
For example, women with access to higher education may delay having children or choose smaller families.
Primary Reasons for Emigration
Economic hardship, a lack of job opportunities, and limited access to higher education are key drivers of emigration from Bosnia and Herzegovina. The search for better economic prospects and improved quality of life abroad are major motivating factors. The pursuit of educational opportunities is also significant, with many young people seeking advanced degrees and specialized training unavailable in Bosnia.
Furthermore, political instability or perceived lack of security may also contribute to emigration decisions.
Comparison of Birth Rates in Different Regions of Bosnia and Herzegovina
Birth rates vary across different regions of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Urban areas often show lower birth rates compared to rural areas, potentially due to access to employment and lifestyle factors. However, these differences need further investigation to account for various socioeconomic factors. The disparities in birth rates are a critical aspect of the nation’s demographic composition.
Bosnia’s population emigration and birthrate are complex issues, often influenced by economic factors. Interestingly, the recent decline in birthrates might be compared to the captivating drama of a Broadway cast album, like those from broadway cast albums sweeney todd , where emotional layers intertwine. Ultimately, understanding these population trends requires a deeper look into the multifaceted social and economic landscape of Bosnia.
Current Birth Rates and Emigration Rates for Various Regions
| Region | Estimated Birth Rate (per 1000 population) | Estimated Emigration Rate (per 1000 population) |
|---|---|---|
| Sarajevo Canton | 10.5 | 12.8 |
| Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina | 11.2 | 11.5 |
| Republika Srpska | 10.8 | 12.2 |
| Other Regions | 10.0 | 12.5 |
Note
* These figures are estimates based on available data and may not reflect the precise reality in every region. Data accuracy and reliability are contingent on the availability and quality of the data collected.
Impact of Emigration on Bosnia
Bosnia and Herzegovina, like many nations in the Balkans, faces significant challenges related to emigration. The outflow of skilled workers and young individuals has far-reaching consequences, impacting not only the demographic structure but also the economic vitality of the country. Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate the negative effects and foster sustainable development.Emigration from Bosnia often stems from a complex interplay of factors, including a lack of economic opportunities, limited job prospects, and a desire for better living standards.
This outflow of talent, particularly among young, educated individuals, presents a significant drain on the nation’s human capital, impacting its future economic potential. The consequences are multi-faceted and require careful examination to formulate appropriate responses.
Demographic Structure Impact
The emigration of a significant portion of the population, particularly young adults, leads to a noticeable shift in Bosnia’s age structure. This demographic shift impacts the country’s future workforce and potentially its long-term economic growth. The consequences of this phenomenon can be observed in a reduced labor pool and a potential decline in the birth rate.
Labor Force and Economic Impact
The departure of skilled workers, including professionals and technicians, creates a significant gap in the labor force. This skill shortage affects various sectors, potentially hindering economic growth and development. Businesses may struggle to find qualified personnel, leading to reduced productivity and competitiveness. The emigration of entrepreneurs further compounds this issue, reducing the potential for new business ventures and innovation.
Skills and Demographics of Emigrants
Emigrants from Bosnia frequently possess a diverse range of skills, from engineering and IT to healthcare and education. This outflow of highly skilled individuals represents a substantial loss of human capital, impacting the country’s potential for technological advancement and innovation. The demographic profile of emigrants often includes a high proportion of young, educated individuals, further exacerbating the brain drain.
The loss of this crucial segment of the population can hinder economic development and social progress.
Effect on Age Distribution
Emigration tends to disproportionately affect younger segments of the population, leading to an imbalance in the age structure. This age imbalance can lead to a shrinking workforce and an aging population. The impact on the future workforce is significant, potentially affecting economic growth and social security systems. The outflow of younger generations can have a long-term effect on the country’s ability to sustain itself economically and socially.
Comparison of Average Age
| Group | Average Age |
|---|---|
| Emigrants | 25-35 years |
| Remaining Population | 35-45 years |
The table above provides a simplified illustration of the age difference between emigrants and the remaining population. The younger average age of emigrants indicates a substantial loss of potential contributors to the economy and society. This difference highlights the urgency of addressing the factors driving emigration and developing policies to retain talent.
Factors Influencing Birth Rates
Bosnia and Herzegovina’s birth rate, a key demographic indicator, is shaped by a complex interplay of socioeconomic factors. Understanding these influences is crucial for developing policies aimed at supporting population growth and sustainability. This analysis explores the socioeconomic drivers impacting birth rates, including economic conditions, education levels, healthcare access, and social/cultural norms.
Bosnia’s population emigration and low birthrate are serious issues. It’s a complex problem, and unfortunately, these kinds of demographic shifts aren’t isolated to the region. Recent news about a lawsuit related to a death at Disney World due to an allergy highlights the broader issue of safety and care in public spaces. This tragic incident forces us to consider the multifaceted nature of societal challenges, from the struggles of communities dealing with population decline to the need for better safety protocols in public venues.
It all points to a broader conversation about responsibility and the well-being of populations, whether in a small Balkan nation or a large theme park.
Socioeconomic Factors Affecting Birth Rates
Economic conditions significantly impact family planning decisions. Poverty and unemployment often limit the ability of families to afford raising children, leading to reduced birth rates. Conversely, economic stability and improved living standards can encourage larger families. For example, periods of economic prosperity in other countries have been correlated with increases in birth rates, as families feel more secure about their future and the ability to provide for their children.
Impact of Economic Conditions
Economic conditions directly affect the ability of families to provide for their children. High unemployment rates, low wages, and limited access to essential services can create significant financial burdens, discouraging couples from having children. Conversely, economic growth, job creation, and improved income levels can enhance a family’s capacity to raise children, often leading to higher birth rates. For example, the economic boom in many countries in the 1950s and 1960s saw a corresponding increase in birth rates as families experienced increased financial security.
Influence of Education and Healthcare
Education levels and access to healthcare are strongly correlated with birth rates. Increased access to education, particularly for women, often results in delayed childbearing and smaller family sizes. Women with higher levels of education tend to have better career prospects, and this can influence their family planning decisions. Similarly, improved access to healthcare and family planning services enables families to make informed decisions about family size.
For instance, countries with robust healthcare systems and comprehensive family planning programs often have lower birth rates compared to countries with limited access to these resources.
Role of Social and Cultural Norms
Social and cultural norms play a vital role in shaping family planning decisions. Traditional values, religious beliefs, and social expectations surrounding family size and gender roles can significantly influence birth rates. For example, in societies where large families are highly valued, birth rates tend to be higher than in societies where smaller families are more prevalent. Furthermore, social pressures to conform to certain norms can influence family planning decisions, impacting birth rates.
Comparison of Birth Rates Across Socioeconomic Groups
| Socioeconomic Group | Estimated Birth Rate (per 1000 population) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| High-income households | 12.5 | Higher education levels, stable employment, and better access to healthcare. |
| Middle-income households | 15.2 | Moderate education levels, diverse employment opportunities, and varying access to healthcare. |
| Low-income households | 18.0 | Lower education levels, limited employment opportunities, and constrained access to healthcare. |
Note: These figures are estimated and may not represent precise data for all groups. Variations in these figures can be observed depending on the specific demographic and regional characteristics.
Factors Influencing Emigration
Bosnia and Herzegovina, a nation rich in history and culture, has experienced significant population emigration in recent decades. Understanding the factors driving this movement is crucial to comprehending the evolving demographic landscape and its impact on the country. The reasons behind emigration are complex and multifaceted, encompassing economic, political, and social elements, all intertwined in shaping individual decisions to leave.
Economic Opportunities and Job Markets
The availability of better economic opportunities abroad plays a substantial role in emigration. Bosnia’s relatively stagnant job market, coupled with limited prospects for career advancement, often motivates individuals to seek employment elsewhere. A significant portion of emigration is driven by the desire for higher wages, better working conditions, and increased financial stability. For example, many skilled professionals in the IT sector have sought opportunities in Western European countries and North America, attracted by higher salaries and the chance to utilize their skills in more developed technological environments.
Political and Social Factors
Political instability, corruption, and a perceived lack of social mobility can also fuel emigration. Concerns about safety, human rights, and the rule of law contribute to the decision to relocate. The perception of a lack of political freedom or the experience of discrimination based on ethnicity or religion can push individuals to seek refuge and a better life abroad.
Bosnia’s population emigration and birthrate trends are fascinating, often mirroring broader economic shifts. Factors like the current housing market near NYC, housing market near nyc , can be influential on emigration patterns. Ultimately, these emigration and birthrate dynamics continue to shape the demographic landscape of Bosnia.
The long-term impact of political events, such as the wars in the former Yugoslavia, has undoubtedly influenced emigration patterns.
Education and Skill Levels
Education and skill levels are significant determinants of emigration patterns. Individuals with higher levels of education and specialized skills are often more likely to migrate to countries offering better career prospects. Those with advanced degrees in engineering, medicine, or other fields are often sought after by foreign employers. This dynamic illustrates a clear link between skill acquisition and emigration.
The emigration of educated and skilled individuals can result in a brain drain for Bosnia and Herzegovina, leading to a loss of potential human capital.
Top 5 Countries of Bosnian Emigration
| Rank | Country | Reasoning/Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Germany | Attractive job market, particularly in engineering and manufacturing, along with established immigration policies. |
| 2 | United States | Significant opportunities in various sectors, coupled with a well-established immigration system. |
| 3 | Sweden | Strong economy, relatively stable political environment, and generous social welfare programs. |
| 4 | United Kingdom | Historically, a popular destination for skilled workers and professionals. |
| 5 | Austria | Favorable economic conditions, particularly in the automotive and tourism sectors. |
The table above presents a snapshot of the top 5 countries where Bosnian citizens emigrate, highlighting the various factors that draw individuals from Bosnia to these specific destinations. The reasons for choosing these countries often include the availability of jobs, economic stability, and the perceived quality of life.
Comparison with Other Balkan Countries
A fascinating aspect of understanding Bosnia’s demographic trends is to place them within the context of its Balkan neighbors. The region, historically intertwined, often shares similar challenges and opportunities when it comes to population dynamics. Comparing emigration rates, birth rates, and overall population trends reveals patterns and disparities that shed light on the unique circumstances affecting each nation.The Balkan Peninsula presents a complex tapestry of socioeconomic factors, including historical legacies, political instability, economic opportunities, and varying levels of development.
These factors profoundly influence population movements and reproductive choices, creating a unique demographic landscape across the region. By analyzing these trends, we can gain a deeper understanding of the specific drivers behind emigration and birth rates in Bosnia and how they relate to its neighbors.
Demographic Characteristics of Balkan Countries
The Balkan region encompasses a diverse range of countries with varying historical backgrounds, cultural influences, and levels of economic development. These differences manifest in their demographic characteristics, including population density, age structure, and urbanization patterns. For example, some countries like Serbia and Montenegro might exhibit a more rural population, while others like Croatia might have a more urbanized structure.
This diversity in demographic composition is critical to understanding the nuances of population dynamics in the region.
Similarities and Differences in Socioeconomic Factors
Several socioeconomic factors contribute to the population dynamics in the Balkan region. Factors such as economic opportunities, political stability, and access to education and healthcare significantly impact both birth rates and emigration patterns. For example, countries with better economic prospects often experience higher birth rates and lower emigration rates. Conversely, countries facing economic hardship or political instability often see a decrease in birth rates and an increase in emigration.
The impact of these factors differs across countries, reflecting the specific challenges and opportunities presented in each nation’s unique context.
Bosnia’s population emigration and low birthrate paint a concerning picture. It’s a complex issue, mirroring the societal anxieties and struggles that resonate deeply, like the profound grief experienced by those impacted by recent tragedies, as highlighted in the article “grief is for people sloane crosley” here. Ultimately, these factors contribute to the long-term challenges facing Bosnia’s demographic future.
Comparison Table: Population Trends in Balkan Countries
| Country | Population Trend (2010-2023) | Birth Rate (per 1000) | Emigration Rate (per 1000) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | Declining | Low (e.g., 10-12) | High (e.g., 3-5) |
| Serbia | Declining | Low (e.g., 11-13) | Moderate (e.g., 2-3) |
| Montenegro | Declining | Low (e.g., 10-12) | Moderate (e.g., 2-4) |
| Croatia | Stable or Slightly Increasing | Low (e.g., 10-12) | Low (e.g., 1-2) |
| Albania | Growing | Moderate (e.g., 13-15) | High (e.g., 3-5) |
| North Macedonia | Declining | Low (e.g., 10-12) | Moderate (e.g., 2-4) |
Note: Data in the table is illustrative and not precise. Specific figures for each country should be verified from reliable sources.
Discussion of Findings
The table above provides a general overview of population trends in several Balkan countries. A crucial observation is the overall declining trend in population in many Balkan nations, including Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbia, Montenegro, and North Macedonia. This trend is linked to low birth rates and, in some cases, high emigration rates. On the other hand, countries like Albania, despite facing some emigration pressures, are experiencing a slightly growing population.
Bosnia’s population emigration and low birthrate are serious concerns. The recent struggles impacting the country’s demographics are reminiscent of broader global trends, a trend worsened by the tragic events surrounding the armorer Alec Baldwin Rust shooting , which highlights the devastating ripple effects of such incidents on communities. These factors combined contribute to a worrying future for Bosnia’s population.
The differences in these trends highlight the complex interplay of socioeconomic factors affecting each nation.
Future Projections: Bosnia Population Emigration Birthrate
Bosnia’s population trajectory is a complex interplay of emigration, birth rates, and overall economic conditions. Predicting the precise course of these factors over the next two decades is challenging, but examining current trends provides a framework for potential future scenarios. Analyzing these trends can inform policy decisions and resource allocation, helping Bosnia navigate the demographic changes ahead.
Projected Population Trends
Current demographic patterns suggest a continued decline in Bosnia’s population, primarily due to ongoing emigration and low birth rates. This decline is a concern for various aspects of the country’s future, including its workforce, social safety nets, and economic growth. Understanding the potential impact of these trends is crucial for long-term planning.
Impact of Current Trends
The sustained outflow of young, skilled individuals is likely to have a significant impact on Bosnia’s economy and social fabric in the coming years. A shrinking workforce could hamper economic growth, potentially leading to a decline in the gross domestic product (GDP). This, in turn, may create a vicious cycle, further discouraging population growth. Conversely, a potential influx of migrants, particularly skilled workers, may counteract some of the negative effects of emigration.
Such factors, however, are difficult to quantify and predict with certainty.
Population Size Projection
A graph depicting the projected population size of Bosnia over the next 20 years would show a gradually declining trend. The graph’s x-axis would represent time (years), and the y-axis would represent the population size. The line representing the projected population would have a downward slope, indicating a consistent decrease. The exact slope and magnitude of the decline would depend on the specific assumptions made regarding future birth rates and emigration patterns.
This graph would visually illustrate the predicted shrinking population trend.
Potential Consequences, Bosnia population emigration birthrate
The consequences of these trends on Bosnia’s future could be substantial. Reduced population size could lead to challenges in maintaining essential services like healthcare and education, as well as strains on social security systems. The shrinking workforce could potentially limit economic growth and hinder innovation. However, adaptation and strategic planning can mitigate some of these negative effects.
For example, investments in education and job creation initiatives could encourage population retention and attract skilled migrants.
Projected Population Numbers (20 Years)
| Age Group | Projected Population (Year 2043) |
|---|---|
| 0-14 | Estimated 200,000-250,000 |
| 15-64 | Estimated 1,000,000-1,200,000 |
| 65+ | Estimated 100,000-150,000 |
Note: These figures are estimates and depend heavily on the accuracy of the assumptions made about future birth rates and emigration patterns. They illustrate a possible range of population distributions in the specified age groups.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Bosnia’s population emigration and birthrate trends paint a vivid picture of a nation in transition. The historical context, coupled with contemporary pressures, underscores the importance of understanding these dynamics. Future projections highlight the need for proactive strategies to address the challenges and harness the opportunities presented by these demographic shifts.
FAQ Overview
What are the primary reasons for emigration from Bosnia?
Economic hardship, lack of job opportunities, and seeking better living conditions abroad are often cited as the primary drivers of emigration. Political instability and social factors can also play a role.
How does emigration affect Bosnia’s economy?
Emigration can lead to a loss of skilled labor, impacting the economy’s productivity. However, remittances sent back by emigrants can also contribute to the economy, mitigating some of these negative effects.
Are there regional differences in birth rates within Bosnia?
Yes, variations in socioeconomic factors, access to healthcare, and cultural norms can lead to differing birth rates across different regions within Bosnia.
What are the projected future trends for Bosnia’s population?
Future projections depend on various factors, including the continuation of current emigration and birth rate trends. These projections consider possible scenarios and potential outcomes based on the current data.

