Gaza Cease-Fire NATO, Swedens Role
Gaza cease fire nato sweden – Gaza cease-fire NATO Sweden sets the stage for a complex narrative examining the recent conflict and the roles of key international players. This intricate situation involves the historical context of the Gaza conflict, the specifics of the cease-fire agreement, and the distinct approaches of NATO and Sweden. We’ll explore the humanitarian and economic impacts, international responses, and potential future scenarios.
The Gaza Strip has been embroiled in conflict for decades. This recent cease-fire agreement, brokered with the involvement of various actors, marks a crucial moment in the region’s history. Understanding the details of the agreement, the roles of key players like NATO and Sweden, and the broader international response is vital for comprehending the complexities of this situation.
Background of the Gaza Conflict

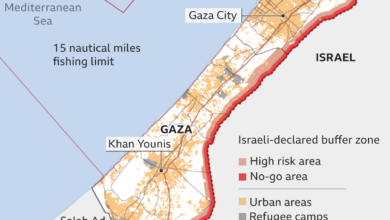
The ongoing conflict in Gaza is a complex and deeply rooted issue, marked by decades of tension and violence. This conflict has significant implications for the region and the international community, demanding a comprehensive understanding of its historical context and the interplay of political, social, and economic factors. The recent cease-fire, while offering a temporary respite, highlights the need for a sustainable resolution to this protracted dispute.The conflict is characterized by a cyclical pattern of escalation and de-escalation, punctuated by periods of intense violence and followed by fragile truces.
Understanding the underlying causes is crucial to navigating the path towards lasting peace. This includes examining the historical grievances, the political motivations of various actors, and the impact of external influences. A comprehensive understanding of the conflict requires acknowledging the multifaceted nature of the issue and exploring the interconnectedness of its various components.
Historical Overview of the Conflict
The conflict in Gaza is deeply intertwined with the broader Israeli-Palestinian conflict. The area has been a focal point of contention since the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, when large-scale displacement and population shifts occurred. The establishment of Israel, the subsequent Palestinian exodus, and the creation of refugee camps became fundamental elements in shaping the political landscape of the region.The 1967 Six-Day War saw Israel capture Gaza, along with other territories.
This marked a new phase in the conflict, with significant implications for the Palestinian population and the geopolitical dynamics of the Middle East. The 1990s saw tentative peace efforts, including the Oslo Accords, which aimed to establish a two-state solution. However, these efforts were ultimately unsuccessful in achieving lasting peace.
Specific Triggers and Escalations Leading to the Cease-Fire
Recent escalations were triggered by a complex interplay of factors. These included continued Israeli military operations, Palestinian protests and resistance actions, and a perceived lack of progress on resolving the core issues of the conflict. The presence of armed groups and the interplay of various factions further contributed to the escalation. The escalation involved multiple factors and varied forms of conflict.The recent cease-fire, while offering a temporary respite, highlights the need for a sustainable resolution to this protracted dispute.
Understanding the specific triggers is crucial to developing effective strategies for long-term peace. These factors and others, such as the presence of armed groups, contributed to the recent escalation.
Geopolitical Context and Regional Alliances
The conflict in Gaza is deeply embedded within the geopolitical context of the Middle East. Regional rivalries and alliances have played a significant role in shaping the conflict’s trajectory. The involvement of regional actors, such as Hamas, Hezbollah, and other armed groups, further complicates the issue.The regional geopolitical context is crucial to understanding the conflict. Alliances and rivalries among different regional actors and the involvement of external powers influence the dynamics of the conflict.
Role of International Organizations
International organizations, including the United Nations, have played a significant role in mediating and providing humanitarian aid. Their efforts have often been hampered by the complexities of the conflict and the lack of cooperation from all parties.The role of international organizations in mediating and providing humanitarian aid to the region has been a crucial aspect of the conflict. The ongoing involvement of these organizations is necessary for facilitating any resolution to the ongoing crisis.
Timeline of Significant Events
| Date | Description | Key Actors |
|---|---|---|
| 1948 | Arab-Israeli War, displacement of Palestinians | Israel, Arab states, Palestinian population |
| 1967 | Six-Day War, Israeli occupation of Gaza | Israel, Arab states, Palestinian population |
| 1990s | Oslo Accords, tentative peace efforts | Israel, Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) |
| [Recent Date] | Recent Escalation, Cease-fire | Israel, Hamas, Palestinian factions |
The Cease-Fire Agreement
The recent cease-fire in Gaza, brokered by various international actors, marks a fragile but crucial pause in the escalating conflict. Understanding the terms of this agreement is vital to assess its potential for long-term stability and to evaluate the roles of the parties involved. The intricate details of the agreement, the positions of the negotiating parties, and the efforts of mediators all contribute to the complex picture of this temporary truce.
Key Provisions of the Cease-Fire Agreement
The specifics of the cease-fire agreement are often kept confidential for strategic reasons. However, public statements and reports indicate several key provisions. These provisions aim to establish a cessation of hostilities, facilitate humanitarian aid delivery, and Artikel procedures for de-escalation. The exact wording and scope of each provision remain subject to interpretation and may vary depending on the source.
Negotiating Parties and Their Positions
The parties involved in the negotiations held differing positions, shaped by their historical grievances and geopolitical considerations. Understanding these positions is crucial for comprehending the challenges in reaching a lasting agreement. Israel’s primary concern was typically security, while Palestinian factions sought to address humanitarian needs and restore their rights. The differing perspectives and priorities between these groups often created significant hurdles in negotiations.
Mediating Roles of Relevant Actors
Several actors played crucial roles in mediating the cease-fire agreement. These mediators often worked behind the scenes, facilitating communication and finding common ground between the opposing sides. The role of these mediators varied in scope and influence, but their efforts contributed significantly to reaching a temporary resolution.
Mechanisms for Monitoring and Enforcing the Cease-Fire
Monitoring and enforcing the cease-fire agreement requires effective mechanisms to ensure compliance by all parties. This includes deploying observers, establishing communication channels, and creating a framework for reporting violations. The effectiveness of these mechanisms will depend on the commitment and cooperation of the involved parties. A robust system of verification is critical to prevent further escalation and maintain the fragile peace.
The recent Gaza cease-fire has NATO and Sweden buzzing, but the larger picture involves US President Biden’s role in mediating the conflict between Israel and Hamas. This complex situation, with its many layers of international pressure, is well-documented in the article about biden israel hamas cease fire. Ultimately, the ongoing efforts to achieve a lasting peace in Gaza still rely heavily on the involved parties’ willingness to compromise and the international community’s consistent support.
Responsibilities of Parties Involved
The following table Artikels the general responsibilities of the parties involved in the cease-fire agreement. These responsibilities are critical to ensuring compliance and maintaining the stability of the agreement. The table provides a framework, but the precise implementation and enforcement details remain complex and are subject to change.
| Party | General Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Israel | Cessation of hostilities, adherence to humanitarian protocols, and cooperation with humanitarian aid efforts. |
| Palestinian factions | Cessation of hostilities, cooperation with humanitarian aid efforts, and adherence to the terms of the agreement. |
| International Mediators | Facilitating communication, monitoring compliance, and mediating disputes. |
NATO and Sweden’s Role
The recent Gaza cease-fire saw varied responses and levels of involvement from international actors. NATO and Sweden, in particular, played distinct roles, albeit with shared goals of de-escalation and stability. While both aimed to mitigate the humanitarian crisis and foster peace, their approaches differed significantly, reflecting their unique geopolitical positions and historical contexts.
NATO’s Statements and Actions
NATO’s involvement in the Gaza conflict primarily focused on maintaining regional security and providing support to its member states. Their statements emphasized the importance of a lasting cease-fire and condemned the violence. Public pronouncements focused on the need for de-escalation and emphasized the need for accountability for actions that violated international humanitarian law. Specific actions, such as intelligence sharing or logistical support for member states involved in the region, were not explicitly publicized, likely due to operational security concerns.
While the Gaza cease-fire negotiations with NATO and Sweden are ongoing, it’s hard not to notice the tragic news coming out of NYC. A recent shooting on the D train, as reported in nyc shooting d train , highlights the persistent need for safety and security in our urban areas. Hopefully, the focus on these crucial issues in Gaza will eventually translate into better solutions for communities everywhere.
NATO’s role was largely behind the scenes, coordinated with existing efforts and focusing on the long-term security implications of the conflict rather than direct intervention.
Sweden’s Diplomatic Efforts
Sweden, though not a NATO member, actively engaged in diplomatic efforts to achieve a ceasefire. Sweden’s historical commitment to neutrality and mediation in international conflicts has made it a sought-after facilitator. Their efforts included direct communication with parties involved, promoting dialogue, and working closely with other international actors to secure a lasting peace. Sweden’s role was primarily focused on facilitating negotiations and promoting a humanitarian response.
They actively supported the UN efforts in mediating the crisis and in providing humanitarian aid.
Comparison of NATO and Sweden’s Approaches
NATO’s approach leaned toward a more collective and multilateral strategy, focusing on broader security concerns and coordination with other international players. Their focus was on maintaining stability in the region and upholding international norms. Sweden’s approach, while still multilateral, was more focused on direct dialogue and mediation, employing its history of neutrality and experience in conflict resolution. Sweden’s actions emphasized humanitarian aid and direct engagement with the parties in conflict.
Historical Context for Sweden’s Role
Sweden’s long history of neutrality and its involvement in international mediation efforts have provided a solid foundation for their current role in conflict resolution. Historically, Sweden has actively participated in international forums and peace initiatives, demonstrating a consistent commitment to peaceful conflict resolution. This history of neutral diplomacy and mediation provides a valuable context for their current involvement.
Table Comparing NATO and Sweden’s Actions and Statements
| Aspect | NATO | Sweden |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Regional security, stability, international norms | Diplomacy, mediation, humanitarian aid |
| Statements | Emphasis on cease-fire, condemnation of violence, accountability | Emphasis on dialogue, support for humanitarian efforts, lasting peace |
| Actions | Intelligence sharing, logistical support (likely, not publicized) | Direct communication with parties, support to UN efforts |
| Approach | Collective, multilateral, behind-the-scenes | Direct, focused on mediation, humanitarian assistance |
Impact and Implications
The recent Gaza cease-fire, while offering a reprieve from the intense violence, casts a long shadow of humanitarian and economic hardship. The conflict’s devastating consequences extend far beyond the immediate battlefield, impacting the lives of civilians and the region’s long-term stability. Understanding these implications is crucial to fostering a sustainable peace.The conflict has left an indelible mark on the lives of Gazans, inflicting severe damage on the already fragile infrastructure and economy.
The recent Gaza cease-fire negotiations involving NATO and Sweden have been quite complex. While the focus is understandably on the humanitarian crisis, it’s worth noting that the ongoing tragedy in Gaza is unfortunately reminiscent of the tragic incident at Disney World, where a guest reportedly died due to an allergic reaction. Cases like the disney world allergy death lawsuit highlight the critical need for preparedness and clear protocols in such settings.
This, of course, shouldn’t overshadow the ongoing efforts to achieve a sustainable peace in Gaza.
The humanitarian crisis demands urgent attention, as millions face uncertainty and struggle to rebuild their lives. The long-term implications of this conflict for the region, and the lives of Palestinians in particular, are significant.
Humanitarian Consequences
The relentless bombardment and the resulting displacement have created a profound humanitarian crisis. Thousands have been injured, and countless homes and infrastructure have been destroyed. The impact on civilian populations, especially children, is particularly devastating.
The Gaza cease-fire, with NATO and Sweden involved, is definitely a hot topic right now. But, while global politics are heating up, the housing market near NYC is also experiencing some interesting shifts. If you’re looking to buy or sell in that area, checking out the latest insights on housing market near nyc could be really helpful.
Regardless of real estate trends, the Gaza situation still needs careful consideration and resolution.
- Widespread displacement and loss of life are major concerns. Many families have lost everything, forcing them to seek refuge in overcrowded and under-resourced shelters.
- The lack of essential resources, including food, water, and medical supplies, exacerbates the crisis. This scarcity of essential goods poses a severe threat to public health and safety.
- The destruction of essential infrastructure, such as hospitals and schools, creates long-term challenges in providing basic services. This disruption of vital infrastructure severely hampers the ability to provide essential services.
Economic Impact
The conflict’s economic toll on the region is substantial. The damage to infrastructure and agricultural lands, combined with the disruption of trade and economic activity, will have long-lasting effects.
- The destruction of infrastructure, including homes, businesses, and vital services, creates a substantial economic burden. This damage hampers economic recovery and significantly reduces productivity.
- Disruptions in supply chains and trade routes lead to shortages of essential goods and services. This can result in significant inflation and economic instability, as seen in previous conflicts in similar regions.
- The loss of agricultural lands and reduced agricultural output creates food security concerns, particularly in a region already vulnerable to food shortages. The destruction of farmland, combined with reduced agricultural output, threatens the long-term food security of the region.
Long-Term Implications for Regional Stability
The cease-fire, while a positive step, raises concerns about the sustainability of peace in the region. The underlying issues that fueled the conflict remain unresolved, potentially leading to future instability.
- The lack of a comprehensive political solution to the root causes of the conflict leaves the region vulnerable to further violence. The absence of a long-term political solution to the conflict raises the possibility of future escalation.
- The ongoing political tensions and mistrust between the parties create a high risk of renewed conflict. This ongoing mistrust and unresolved political tensions create a persistent risk of future conflict.
- The conflict’s impact on regional stability is undeniable. The conflict has significantly disrupted the regional balance of power, which has far-reaching implications for international relations.
Potential Future Challenges and Risks
Several challenges and risks could hinder the long-term stability of the region. The ongoing tensions and the lack of sustainable solutions pose significant threats to the region’s future.
- The potential for renewed violence due to unresolved issues is a major concern. The possibility of further escalation remains a serious concern, given the unresolved issues and ongoing tensions.
- The long-term impact on the lives of Palestinian civilians is particularly critical. The devastating consequences of the conflict on the lives of Palestinians are profound and multifaceted.
- The economic and social consequences of the conflict will likely persist for years to come. The economic and social fallout of the conflict is likely to persist for years to come, affecting generations to come.
Long-Term Effects on the Lives of Palestinians
The conflict has had a devastating and enduring impact on the lives of Palestinians. The effects will continue to shape their lives for years to come.
- The trauma and psychological distress suffered by Palestinians during the conflict are likely to have lasting effects. The psychological impact of the conflict on Palestinians is substantial and will continue to impact their lives for years to come.
- The displacement and loss of livelihoods will create long-term economic hardship and social disruption. The long-term economic hardship and social disruption will continue to affect the lives of displaced Palestinians.
- The destruction of homes and infrastructure will hinder their ability to rebuild their lives and communities. The destruction of homes and infrastructure will significantly impede the ability of Palestinians to rebuild their lives and communities.
International Response: Gaza Cease Fire Nato Sweden
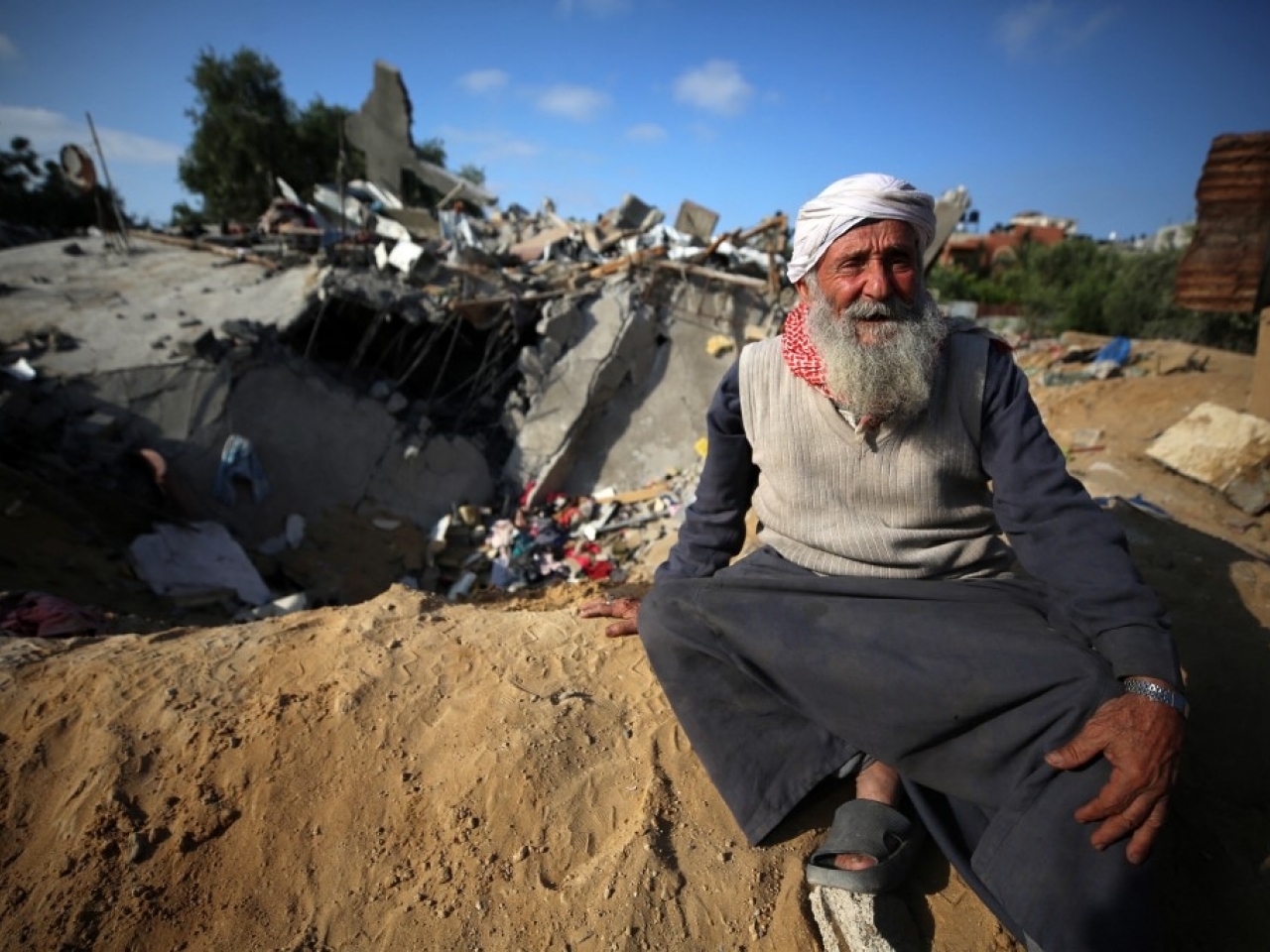

The Gaza cease-fire, while bringing a temporary respite from the violence, highlights the complex web of international responses to the ongoing conflict. Understanding these varied reactions, from humanitarian aid to diplomatic efforts, is crucial to comprehending the dynamics at play. Different nations and organizations approach the situation with unique perspectives, shaped by their own geopolitical interests and moral stances.
United Nations Response
The United Nations, particularly the UN Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near East (UNRWA), plays a critical role in providing humanitarian assistance to Palestinian refugees. Their efforts are often hampered by the complex political landscape and the limitations imposed by the ongoing conflict. UN Security Council resolutions, while intended to promote peace, often face difficulties in implementation due to differing national interests.
European Union Response
The European Union (EU) has consistently condemned the violence in Gaza and has called for a cessation of hostilities. EU member states have often coordinated their efforts in providing humanitarian aid, although their capacity to influence the situation is constrained by the regional dynamics. The EU’s approach reflects a commitment to international law and human rights.
Other International Actors, Gaza cease fire nato sweden
Various other international actors, including individual nations and international organizations, have also responded to the conflict. Their interventions, ranging from diplomatic efforts to humanitarian aid, often reflect their specific geopolitical relationships and priorities. The diversity of responses highlights the multifaceted nature of the conflict and the difficulties in achieving a lasting resolution.
Comparison of Reactions
Different countries and organizations exhibit varying levels of engagement and commitment to resolving the conflict. Some nations prioritize diplomatic solutions, while others focus on humanitarian aid. These differing approaches are often influenced by their own political and economic interests, as well as their historical relationships with the parties involved. This disparity in reactions complicates the process of achieving a comprehensive and sustainable resolution.
Humanitarian Aid Provided
The humanitarian crisis in Gaza requires significant and sustained international aid. This aid encompasses a wide range of necessities, including food, shelter, medical supplies, and clean water. The scale of the crisis often overwhelms the capacity of aid organizations, necessitating coordinated efforts to ensure that assistance reaches those most in need.
Perspectives on the Conflict
Diverse perspectives on the conflict exist, reflecting the complex geopolitical dynamics of the region. These perspectives often align with the geopolitical interests of individual nations and organizations, impacting their responses and influencing the perception of the conflict. The varying viewpoints complicate efforts toward a consensus and lasting peace.
Summary Table of International Responses
| International Actor | Methods of Intervention | Specific Actions |
|---|---|---|
| United Nations | Humanitarian aid, peacekeeping efforts, diplomatic mediation | Providing food, shelter, medical supplies; issuing resolutions; facilitating negotiations |
| European Union | Economic sanctions, diplomatic pressure, humanitarian aid | Imposing sanctions on relevant actors; mediating between parties; providing funding to aid organizations |
| United States | Diplomatic engagement, arms sales, humanitarian assistance | Negotiating with regional actors; supplying military aid; supporting humanitarian relief efforts |
| Other Countries (e.g., Russia, China) | Diplomatic engagement, economic incentives, humanitarian aid | Negotiating with regional actors; offering economic aid; supporting relief efforts, possibly with varying priorities |
Possible Future Scenarios
The recent Gaza cease-fire, while offering a respite, leaves the region teetering on the brink of future instability. Understanding potential scenarios is crucial for crafting effective strategies to prevent further conflict and promote long-term peace. The complex interplay of political motivations, economic realities, and social tensions creates a volatile environment demanding careful consideration.
Potential Scenarios for the Future of the Region
The future of the region hinges on several interwoven factors, including the continued commitment of various actors to the cease-fire, the ability of Palestinian authorities to restore stability, and the willingness of Israeli authorities to address Palestinian concerns. Multiple scenarios are plausible, ranging from relative stability to renewed conflict.
- Escalation of Violence: Continued grievances and unresolved issues, coupled with a lack of effective preventative measures, could lead to further conflict. This scenario is fueled by factors like unresolved border disputes, economic hardship, and the absence of a just and sustainable peace agreement. Examples of similar situations include the Syrian Civil War, where escalating conflicts were driven by a confluence of political, economic, and social factors.
- Relative Stability: The cease-fire might hold, but only if underlying issues are addressed. This scenario assumes the international community will actively support the implementation of long-term solutions, and that the parties involved will work towards a durable peace. This is dependent on the commitment of external actors and the willingness of local actors to cooperate. However, the history of similar agreements often demonstrates the fragility of this situation.
The recent Gaza cease-fire negotiations involving NATO and Sweden are definitely fascinating, but sometimes I find myself daydreaming about the dramatic flair of Broadway cast albums, like those from Sweeney Todd. Exploring the haunting melodies and intense performances of broadway cast albums sweeney todd offers a unique contrast to the serious geopolitical discussions. Regardless of the creative expression, the Gaza situation still requires careful consideration and resolution.
It’s a complex issue with no easy answers.
- Frozen Conflict: The current conflict might enter a state of stalemate, where intermittent violence persists, but a major escalation is avoided. This scenario could result from a lack of political will from any side to achieve a decisive resolution. The ongoing conflict in Northern Ireland provides a historical example of such a “frozen conflict.”
- Regional Instability: The conflict in Gaza could exacerbate regional tensions, potentially triggering wider conflicts involving neighboring countries. The involvement of external actors or regional powers could exacerbate the situation. The ongoing conflicts in Yemen and Syria are illustrative of how regional instability can have far-reaching consequences.
Likelihood of Future Conflicts and Escalations
Predicting the likelihood of future conflicts is complex. Factors such as the level of commitment from key actors, the implementation of the cease-fire agreement, and the willingness of involved parties to pursue long-term solutions will significantly influence the probability of future escalations.
| Scenario | Probability | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Escalation of Violence | Medium-High | Unresolved issues, lack of preventative measures, and ongoing grievances contribute to the potential for further conflict. |
| Relative Stability | Medium | Dependent on international support, implementation of long-term solutions, and the cooperation of local actors. |
| Frozen Conflict | Low-Medium | Lack of decisive action from involved parties to achieve a resolution, resulting in intermittent violence. |
| Regional Instability | High | Potential for conflicts to spread to neighboring countries due to involvement of external actors or regional powers. |
Strategies to Prevent Future Conflicts
Addressing the root causes of the conflict is paramount. This includes ensuring the implementation of the cease-fire agreement, fostering economic opportunities, and addressing the underlying grievances of both Israelis and Palestinians. The creation of a framework for long-term solutions is crucial.
- Strengthening the cease-fire agreement through international monitoring and enforcement mechanisms.
- Facilitating economic development in Gaza and the West Bank to create opportunities for Palestinians.
- Promoting dialogue and negotiation between Israeli and Palestinian leaders.
- Addressing the root causes of the conflict through the creation of a long-term, just, and sustainable peace agreement.
Need for Long-Term Solutions
Long-term solutions are not just desirable; they are essential. These solutions should address the core issues that fuel the conflict, including the need for a secure and recognized Palestinian state. This requires a multifaceted approach that incorporates political, economic, and social dimensions.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the Gaza cease-fire, with NATO and Sweden’s involvement, represents a delicate attempt at achieving peace and stability in the region. However, the long-term implications remain uncertain. The humanitarian consequences, economic repercussions, and potential for future conflicts are critical factors to consider. This event highlights the multifaceted nature of international relations and the need for continued diplomacy and humanitarian aid.
FAQs
What were the key triggers for the recent escalation in Gaza?
The recent escalation stemmed from a combination of factors, including ongoing political tensions, economic hardship, and past grievances. Specific events leading up to the cease-fire are Artikeld in the provided background information.
What specific humanitarian aid was provided to the affected areas?
Information on humanitarian aid will be presented in the section on international responses, outlining the types of aid provided by different organizations.
What are the potential long-term effects of the cease-fire on Palestinian lives?
The long-term effects are complex and will be explored in the impact and implications section. Factors like economic recovery, rebuilding infrastructure, and the restoration of daily life for Palestinians will be addressed.