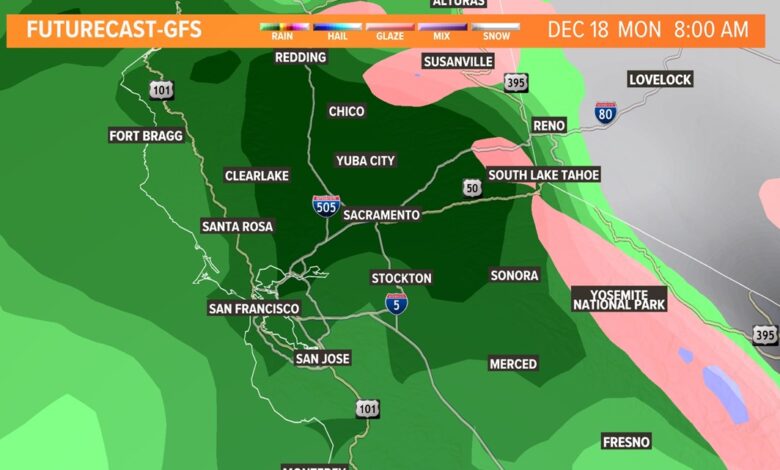
California Weather Atmospheric River Impacts
California weather atmospheric river events are a powerful force of nature, bringing both beauty and devastation. These intense weather systems, characterized by long, narrow streams of moisture in the atmosphere, can unleash torrential rain and snow, leading to flooding, mudslides, and other significant disruptions. Understanding these events and their potential impacts is crucial for residents and policymakers alike.
This post explores the science behind atmospheric rivers, examining their historical context, impacts on California’s diverse landscapes, forecasting methods, and the role of climate change. We’ll also discuss public preparedness strategies, ongoing research, and detailed examples of past events, highlighting the importance of proactive measures in mitigating their effects.
Introduction to California Weather Atmospheric Rivers
Atmospheric rivers (ARs) are narrow, concentrated bands of water vapor in the atmosphere that transport enormous amounts of moisture from tropical and subtropical regions. In the context of California’s weather, ARs are a significant driver of heavy precipitation, often leading to flooding, mudslides, and other severe weather events. Their influence on California’s water resources and ecosystems is profound.These atmospheric rivers typically form over the Pacific Ocean and move inland, often bringing substantial amounts of rain and snow to the state.
California’s atmospheric river storms are wreaking havoc, impacting everything from water supplies to everyday life. Thinking about how these extreme weather events might be affecting renters in areas like Williamsburg, Brooklyn, and even Kyiv, Ukraine, is fascinating. Renters in Williamsburg, Brooklyn, and Kyiv, Ukraine are likely facing unique challenges during these turbulent times, whether it’s flood damage or the cost of repairs.
Ultimately, the California weather patterns continue to be a major concern for many.
Their characteristics, such as the intensity of the moisture transport and the duration of the precipitation, directly impact the severity of the resulting weather phenomena. California’s mountainous terrain and complex weather patterns amplify the effects of ARs, often leading to localized extremes in precipitation.
Typical Characteristics and Behavior of ARs in California
ARs are characterized by high concentrations of water vapor, often exceeding the moisture content of typical weather systems. This concentrated moisture is transported over long distances, sometimes thousands of kilometers, from the tropics or subtropics, ultimately depositing significant amounts of precipitation as they move inland over California. The intensity and duration of precipitation from ARs are highly variable, and their paths can significantly affect the areas most impacted.
California’s atmospheric river weather has been intense lately, impacting everything from commute times to outdoor events. With the recent deluge, it’s definitely worth checking out the local events calendar, like the upcoming “subway weekend jose lasalle” subway weekend jose lasalle for any potential disruptions. Hopefully, the storm will pass soon, allowing us to get back to enjoying the sunshine and the weather.
It’s always a good idea to be prepared for any changes.
Their passage often involves periods of intense rainfall followed by periods of relative calm, leading to fluctuating stream flows and potentially unpredictable hydrological responses.
Historical Context of AR-related Weather Events in California
California has a long history of experiencing significant weather events related to atmospheric rivers. These events have varied in intensity and duration, with some impacting the state more severely than others. Historical records, although not always specifically tied to the term “atmospheric river,” show periods of heavy rainfall and flooding that have been linked to moisture transport patterns similar to those associated with ARs.
These events highlight the profound impact that ARs can have on California’s water resources and infrastructure. Notable examples include the devastating floods of 1997 and 2017, which were linked to the presence of intense atmospheric rivers.
Geographical Regions Most Vulnerable to AR Impacts
California’s diverse geography makes it susceptible to varying impacts from atmospheric rivers. The mountainous regions, particularly the Sierra Nevada, are prone to heavy snowfall, which can lead to significant snowmelt runoff and subsequent flooding in downstream areas. Coastal regions are often impacted by intense rainfall, which can cause flooding and coastal erosion. The Central Valley, with its flat terrain and extensive agricultural lands, is vulnerable to widespread flooding.
The varying elevation and topography of the state’s landscape mean that different areas experience varying degrees of impact, often with severe localized effects.
- Coastal Regions: Coastal areas are vulnerable to intense rainfall leading to flooding and coastal erosion. The proximity to the ocean and the steep topography exacerbate the effects of ARs, often leading to flash flooding and rapid runoff.
- Mountainous Regions: Mountainous areas, such as the Sierra Nevada, are prone to heavy snowfall, which can cause significant snowmelt runoff and downstream flooding. The accumulation of snow and subsequent melt are crucial factors in the water cycle and can cause issues if the melt rate is accelerated by intense rainfall events.
- Central Valley: The Central Valley, with its flat terrain and extensive agricultural lands, is vulnerable to widespread flooding, potentially impacting agriculture, transportation, and human settlements. The valley’s flatness allows water to accumulate and spread quickly, exacerbating flood risks.
Impacts of Atmospheric Rivers
Atmospheric rivers (ARs) are potent carriers of moisture, bringing significant precipitation to California. While crucial for the state’s water supply, these intense weather systems can also unleash devastating impacts, particularly when the precipitation falls rapidly and in high volumes. Understanding these impacts is vital for developing effective mitigation strategies and preparedness plans.The relentless nature of atmospheric rivers can lead to a cascade of problems, from flooding and mudslides to power outages and damage to critical infrastructure.
California’s atmospheric river weather patterns are intense right now, causing significant flooding and disruption. Meanwhile, the ongoing geopolitical situation in Gaza, with the cease-fire negotiations involving Russia and NATO, gaza cease fire russia nato , highlights the complex global challenges. Despite these global events, California’s weather will undoubtedly continue to be a major concern for residents and infrastructure.
These events often have cascading effects, impacting agriculture, human health, and the economy. This post delves into the diverse impacts of ARs in California, highlighting examples and the economic repercussions of these severe weather events.
Flooding and Mudslides
Heavy rainfall associated with ARs frequently saturates the ground, leading to devastating floods. Flooding can inundate homes, businesses, and infrastructure, causing significant property damage and disrupting transportation networks. The rapid runoff and saturated soil conditions also increase the risk of mudslides, especially in mountainous regions. These mudslides can bury homes, roads, and infrastructure, resulting in substantial loss of life and property.
For instance, the 2017 atmospheric river event in Northern California triggered significant mudslides, causing widespread devastation and claiming numerous lives.
Power Outages
The intense rainfall and strong winds often accompanying ARs can cause widespread power outages. Fallen trees, downed power lines, and flooding can disrupt power grids, leaving communities without electricity for extended periods. These outages can have significant impacts on daily life, affecting access to essential services like communication, healthcare, and water treatment. The 2022 atmospheric river event caused extensive power outages in Southern California, highlighting the vulnerability of the electricity infrastructure to severe weather events.
Impacts on Agriculture
Atmospheric rivers can bring vital rainfall to California’s agricultural regions, supporting crop growth and water supplies. However, extreme precipitation can also disrupt agricultural activities. Heavy rainfall can damage crops, wash away topsoil, and flood irrigation systems, leading to significant losses for farmers. Prolonged flooding can also affect livestock, disrupting their access to food and water. In addition, the increased risk of mudslides can destroy farmland, further impacting agricultural production.
Impacts on Infrastructure
The heavy rainfall and strong winds associated with atmospheric rivers can severely damage roads, bridges, and other infrastructure. Flooding can wash away sections of roads and bridges, while strong winds can topple trees and power lines, disrupting transportation and communication networks. The damage to infrastructure can necessitate significant repair and reconstruction efforts, leading to considerable economic losses. The 2023 atmospheric river event in Central California resulted in significant damage to roads and bridges, highlighting the vulnerability of transportation networks to these extreme weather events.
Impacts on Human Health
ARs can have significant implications for human health. Flooding can lead to water contamination, increasing the risk of waterborne diseases. Power outages can disrupt access to essential medical services and increase the risk of heat-related illnesses, especially during summer events. The increased stress and trauma associated with these events can also contribute to mental health issues. For example, the 2018 atmospheric river event led to numerous reports of waterborne illnesses and mental health issues in affected communities.
Economic Consequences
The damages caused by atmospheric rivers have substantial economic consequences. Property damage, infrastructure repairs, agricultural losses, and disruptions to business operations can lead to significant economic losses. The cost of recovery and rebuilding efforts can be substantial, straining resources and impacting the local economy. For instance, the 2020 atmospheric river event resulted in estimated economic losses of billions of dollars due to damage to homes, businesses, and infrastructure.
California’s atmospheric river weather patterns are a fascinating study, but they’re also a stark reminder of the interconnectedness of global events. The powerful storms, often triggered by these rivers in the sky, can have a huge impact on daily life. Meanwhile, the escalating tensions between the US and Russia, and their involvement in nuclear space programs, alongside Pakistan and Asia’s geopolitical dynamics, us russia nuclear space pakistan asia could potentially influence global weather patterns in unforeseen ways, though the direct correlation is debatable.
Ultimately, the unpredictable nature of California’s atmospheric river weather still remains a primary focus for those of us who live here.
Severity Levels of Impacts
| Impact Type | Potential Severity Level |
|---|---|
| Flooding | Low (minor flooding), Medium (major flooding), High (catastrophic flooding) |
| Mudslides | Low (minor slides), Medium (moderate slides), High (catastrophic slides) |
| Power Outages | Low (brief outages), Medium (extended outages), High (widespread and prolonged outages) |
| Agricultural Losses | Low (minor crop damage), Medium (significant crop damage), High (total crop loss) |
| Infrastructure Damage | Low (minor damage), Medium (major damage), High (catastrophic damage) |
| Human Health Impacts | Low (minor health concerns), Medium (significant health concerns), High (major health crisis) |
Forecasting and Monitoring ARs
California’s atmospheric rivers (ARs) pose significant challenges due to their unpredictable nature and potentially devastating impacts. Accurate forecasting and monitoring are crucial for mitigating risks and enabling effective preparedness. Real-time data and sophisticated modeling techniques are essential to anticipate AR arrival and intensity, allowing communities to take necessary precautions.
Methods for Forecasting and Monitoring ARs
AR forecasting relies on a combination of observational data and sophisticated numerical weather prediction (NWP) models. These models simulate the atmospheric processes that drive AR development, movement, and precipitation patterns. Crucial to this process is the comprehensive collection and analysis of atmospheric data. Satellite imagery, radar, and surface observations provide essential information about moisture content, wind patterns, and precipitation intensity, which are vital inputs for the models.
Tools and Technologies for Tracking AR Development
Numerous tools and technologies are employed in tracking AR development. Satellite-based sensors, like those on the GOES-West satellite, provide crucial information on the large-scale structure and movement of ARs, often hours or even days in advance. Doppler radar systems, strategically positioned across California, offer detailed information on precipitation intensity and location in real time, providing crucial data for localized warnings.
Sophisticated numerical weather prediction (NWP) models, such as the Global Forecast System (GFS), incorporate these data sources to simulate AR behavior and predict their potential impacts. Advanced computer systems process and analyze this data, enabling early identification and tracking of ARs.
Role of Weather Agencies in Warning the Public
California’s weather agencies, such as the National Weather Service (NWS) and the California Department of Water Resources, play a vital role in informing the public about potential AR impacts. These agencies issue warnings and advisories based on the predicted intensity and duration of ARs, enabling communities to prepare for possible flooding, mudslides, and power outages. These warnings are disseminated through various channels, including social media, news outlets, and emergency alerts, ensuring timely dissemination of information.
Significance of Real-time Data in Predicting AR Impacts
Real-time data is paramount in predicting AR impacts. Data from various sources, including river gauges, streamflow models, and rainfall measurements, provide critical information on the ground conditions and potential risks. For example, the rate of rainfall combined with the soil moisture content determines the likelihood of flooding. Early and accurate warnings are significantly enhanced by the ability to observe the rapid changes that ARs can bring, and these observations are key to providing accurate predictions.
This enables timely actions to mitigate potential hazards.
Comparison of Forecasting Models
| Model | Accuracy (based on historical performance) | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Global Forecast System (GFS) | High accuracy for large-scale AR characteristics | Widely used, readily available | May underestimate localized impacts, especially in mountainous terrain |
| Regional models (e.g., WRF) | Higher accuracy for localized impacts | Detailed spatial resolution, capturing complex terrain | Computational resources intensive, not always readily available for every forecast |
| Ensemble forecasting | Improved accuracy by combining predictions from multiple models | Provides a range of possible outcomes, helping to assess uncertainty | Requires more computational resources and can be complex to interpret |
The accuracy of AR forecasting models is constantly being improved through research and development.
Climate Change and ARs
California’s atmospheric rivers (ARs) are becoming increasingly impactful, and climate change is a significant contributing factor. The rising global temperatures are altering weather patterns in complex ways, and ARs are a prime example of how these changes manifest. Understanding these connections is crucial for effective adaptation and mitigation strategies.
Potential Influence of Climate Change on AR Frequency and Intensity
Warmer air holds more moisture. This fundamental principle directly affects ARs. As global temperatures rise, the atmosphere can absorb and transport more water vapor, potentially leading to more intense AR events. Increased evaporation from warmer oceans further exacerbates this effect, providing a larger reservoir of water for ARs to draw upon.
Mechanisms of Climate Change Impact on ARs
Several mechanisms link climate change to altered AR behavior. First, warmer temperatures directly increase the amount of water vapor in the atmosphere, which fuels more intense precipitation events. Second, changes in atmospheric circulation patterns, driven by warming, can alter the paths and trajectories of ARs, potentially increasing their frequency in certain regions. Finally, the melting of glaciers and ice caps contributes to increased sea-level rise, which can impact the coastal areas vulnerable to flooding during AR events.
Evidence Linking Climate Change to Increased AR Events
Numerous studies provide evidence linking climate change to observed increases in AR-related events. These studies often employ statistical analyses of historical precipitation data, coupled with climate model simulations. Observed trends show a correlation between rising global temperatures and more frequent and intense AR events in California. For instance, the record-breaking storms of 2022 and 2023, which caused widespread flooding and damage, were significantly influenced by unusually large amounts of moisture transported by ARs.
The increase in the severity of these events is consistent with climate change projections.
Comparison of Historical AR Patterns with Recent Trends
Historical data reveals shifts in AR behavior over time. While past AR events have occurred, recent patterns show a notable increase in both the frequency and intensity of these events. Analysis of historical precipitation records reveals a growing trend towards more intense rainfall in short bursts, characteristic of AR events. This trend is consistent with climate models’ projections of a changing climate.
Projected Changes in AR Behavior
| Climate Model | Projected Change in AR Frequency | Projected Change in AR Intensity | Projected Change in AR Trajectories |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model A | Increase by 15-20% | Increase by 20-30% | Shifting towards more coastal regions |
| Model B | Increase by 10-15% | Increase by 15-25% | No significant shift in trajectories |
| Model C | Increase by 20-25% | Increase by 25-35% | Shifting towards inland areas |
Different climate models project varying degrees of change in AR behavior. These projections emphasize the need for ongoing monitoring and adaptation strategies to prepare for the increasing impact of these events. It’s crucial to note that these models are complex, and uncertainty remains regarding specific details. However, the general trend across models is towards increased frequency and intensity of ARs.
Public Preparedness and Mitigation Strategies
Atmospheric rivers (ARs) pose a significant threat to California, demanding proactive public preparedness and mitigation strategies. Understanding the potential impacts and implementing effective measures are crucial for minimizing damage and ensuring community resilience. This section Artikels key strategies for individuals, communities, and government agencies to navigate the challenges posed by these powerful weather systems.
Individual Preparedness
Effective individual preparedness involves taking proactive steps to safeguard oneself and one’s property during AR events. This proactive approach is essential to minimize potential damage and personal risks.
California’s atmospheric river weather is wreaking havoc, with torrential downpours and flooding causing widespread disruption. Meanwhile, the recent controversy surrounding Rick Pitino’s comments about St. John’s recruiting, as detailed in this article , highlights the delicate nature of college basketball recruiting and the need for careful consideration of statements made in public. Hopefully, this weather will calm down soon, allowing for a return to more typical California weather patterns.
- Develop an emergency plan. This includes identifying evacuation routes, assembling an emergency kit with essential supplies, and communicating the plan with family members. For instance, having a designated meeting point in case of separation during an evacuation is critical.
- Stay informed. Monitoring weather forecasts and warnings from reliable sources like the National Weather Service is vital. Knowing the predicted intensity and duration of the AR is crucial for taking necessary precautions.
- Secure property. Protecting vulnerable structures and belongings from flooding, debris, and strong winds is important. This includes securing outdoor furniture, covering windows, and ensuring gutters are clear.
- Have a communication strategy. Establish a method for staying in touch with family and friends during an AR event, especially if communication systems are disrupted. This includes having a backup communication plan.
Community-Level Mitigation
Community-level mitigation strategies focus on enhancing the collective ability of residents to withstand AR impacts. These measures aim to strengthen the resilience of communities as a whole.
- Implement early warning systems. Enhancing communication infrastructure and developing community-based early warning systems is vital for rapid dissemination of information during AR events. These systems should be accessible to all community members, including those with limited mobility or language barriers.
- Conduct community outreach and education. Educating residents about ARs, their impacts, and mitigation strategies through workshops, seminars, and community meetings is crucial. These efforts should include accessible information for diverse demographics.
- Strengthen infrastructure. Investing in flood control measures, drainage improvements, and resilient building codes is crucial to reduce the vulnerability of communities to AR-related damage. These investments contribute to the overall safety and well-being of the community.
- Establish community-based response teams. Training and equipping volunteers to assist during and after AR events is essential. These teams can provide critical support and aid in disaster response efforts.
Government Agency Role
Government agencies play a critical role in disaster response and recovery efforts. Effective disaster response is vital for ensuring community well-being and minimizing long-term impacts.
- Develop comprehensive AR response plans. These plans should Artikel procedures for early warning, evacuation, and resource allocation during and after an AR event. These plans should also address potential vulnerabilities and incorporate lessons learned from previous events.
- Invest in monitoring and forecasting technologies. Supporting the development and implementation of advanced forecasting and monitoring technologies to provide accurate and timely information about AR events is crucial. This will improve public awareness and preparedness.
- Establish robust communication networks. Maintaining reliable communication channels during AR events is critical to ensure coordination among agencies, emergency responders, and the public. These networks should also include alternative communication channels.
- Coordinate disaster relief efforts. Government agencies must coordinate disaster relief efforts with non-governmental organizations and other stakeholders. This ensures a comprehensive and effective response to community needs.
Resources and Support Systems
This table Artikels resources and support systems for affected communities during and after an AR event.
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Emergency Shelters | Designated locations for temporary housing during evacuations. |
| Food and Water Supplies | Provision of essential resources to affected populations. |
| Medical Assistance | Access to medical services and supplies. |
| Financial Aid | Support for individuals and families experiencing financial hardship due to AR impacts. |
| Mental Health Services | Support for individuals experiencing psychological distress following AR events. |
Scientific Research and Understanding: California Weather Atmospheric River
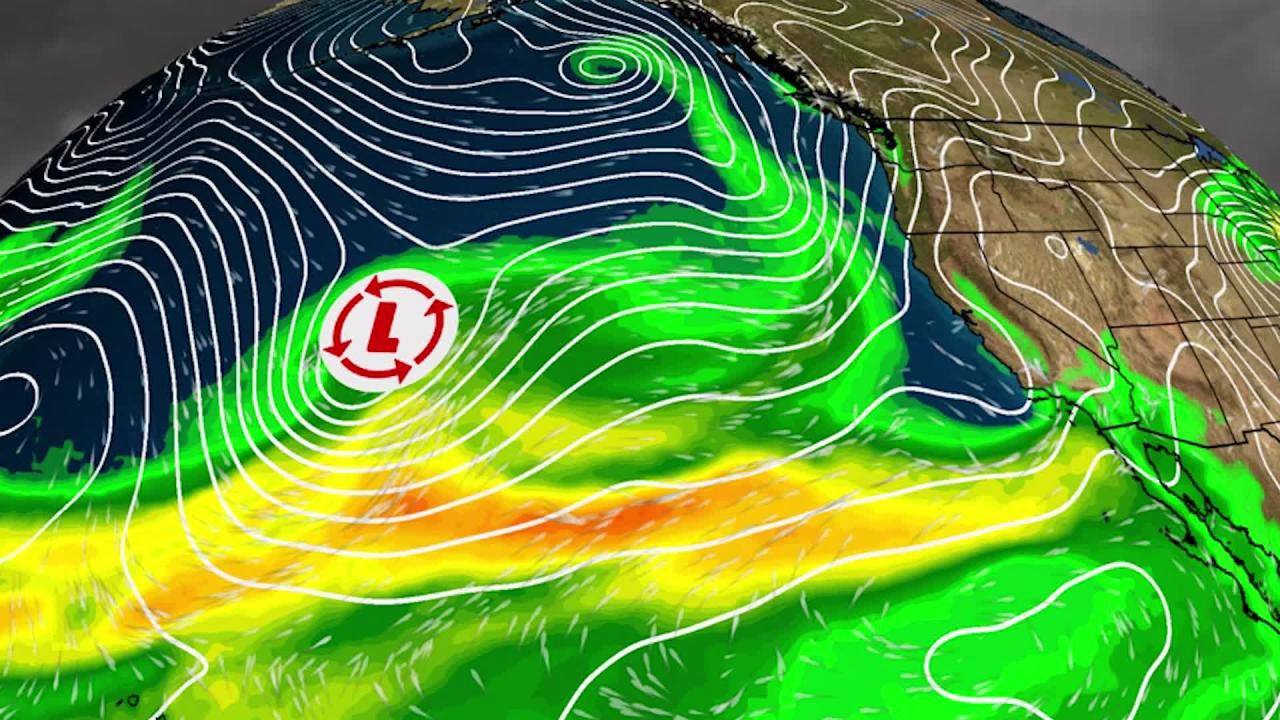
Unraveling the mysteries of atmospheric rivers (ARs) requires a deep dive into ongoing scientific research. This exploration focuses on understanding their complex behavior, impacts, and potential for future forecasting improvements. California’s vulnerability to these weather patterns underscores the critical need for enhanced scientific understanding.Ongoing research into atmospheric rivers and their impacts in California is multifaceted, encompassing numerous areas of study.
This includes investigating the formation mechanisms, the trajectory patterns, and the intensity variations of these weather systems. Researchers are also exploring the intricate interactions between ARs and other climate phenomena, like wildfires and drought.
Ongoing Research Areas
California’s vulnerability to atmospheric rivers necessitates a multifaceted approach to research. Researchers are actively investigating AR formation, tracking their movement, and examining their impact on various aspects of the environment and society. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for improving predictions and developing effective mitigation strategies.
- Formation Mechanisms: Scientists are meticulously analyzing the atmospheric conditions that lead to the development of ARs. This includes studying the interplay of factors such as atmospheric instability, moisture transport, and the role of topography. This research seeks to identify the triggers and characteristics that distinguish strong, impactful ARs from less consequential ones.
- Impact Assessment: Research into the impacts of ARs on California’s diverse ecosystems is ongoing. This includes studying the effects on water resources, agriculture, infrastructure, and human health. For example, the impact of ARs on snowpack accumulation and subsequent water availability is a significant focus.
- Predictive Modeling: Researchers are developing and refining numerical weather prediction models to improve AR forecasting accuracy. These models incorporate complex atmospheric physics and utilize high-resolution data to better simulate the behavior of these weather systems.
Current Knowledge Gaps
Despite significant advancements, knowledge gaps persist in our understanding of atmospheric rivers. These gaps hinder the development of even more accurate predictions and effective mitigation strategies.
- Predicting Intensity and Timing: Current models have difficulty precisely predicting the intensity and timing of AR precipitation events. This uncertainty creates challenges in effective water management and infrastructure preparedness.
- Regional Variability: The varying impacts of ARs across different regions of California necessitate further research. Understanding regional sensitivities and vulnerabilities is essential for targeted preparedness measures.
- Long-Term Trends: The long-term trends of AR activity and their potential connection to climate change remain an area of active investigation. A better understanding of these trends is crucial for developing long-term mitigation strategies.
Importance of Continued Research
Continued research into atmospheric rivers is critical for enhancing forecasting accuracy and mitigation efforts. This includes improved prediction models, more precise impact assessments, and the development of targeted preparedness measures.
- Enhanced Predictions: Further research will lead to more accurate forecasts, enabling communities to prepare for AR events effectively. This preparedness includes efficient water management strategies and infrastructure protection.
- Targeted Mitigation: A deeper understanding of AR impacts allows for the development of targeted mitigation strategies. This includes better planning for infrastructure development and improved water management practices.
Role of Universities and Research Institutions
Universities and research institutions play a pivotal role in advancing atmospheric river research. These institutions are hubs for collaborative research, data analysis, and the development of new models.
- Research Collaboration: Universities often facilitate collaborations between researchers, government agencies, and private organizations to advance understanding and application of AR knowledge.
- Data Analysis: These institutions possess the resources and expertise to analyze vast amounts of data related to ARs, leading to new insights and improved models.
Key Research Findings, California weather atmospheric river
| Research Area | Key Findings |
|---|---|
| Formation Mechanisms | Studies show that ARs are often triggered by atmospheric instability and large-scale moisture transport. |
| Impact Assessment | ARs can lead to significant flooding, landslides, and damage to infrastructure. They can also affect water availability and agriculture. |
| Predictive Modeling | Improved numerical models are continually being developed to better simulate AR behavior. |
Illustrative Examples of AR Impacts
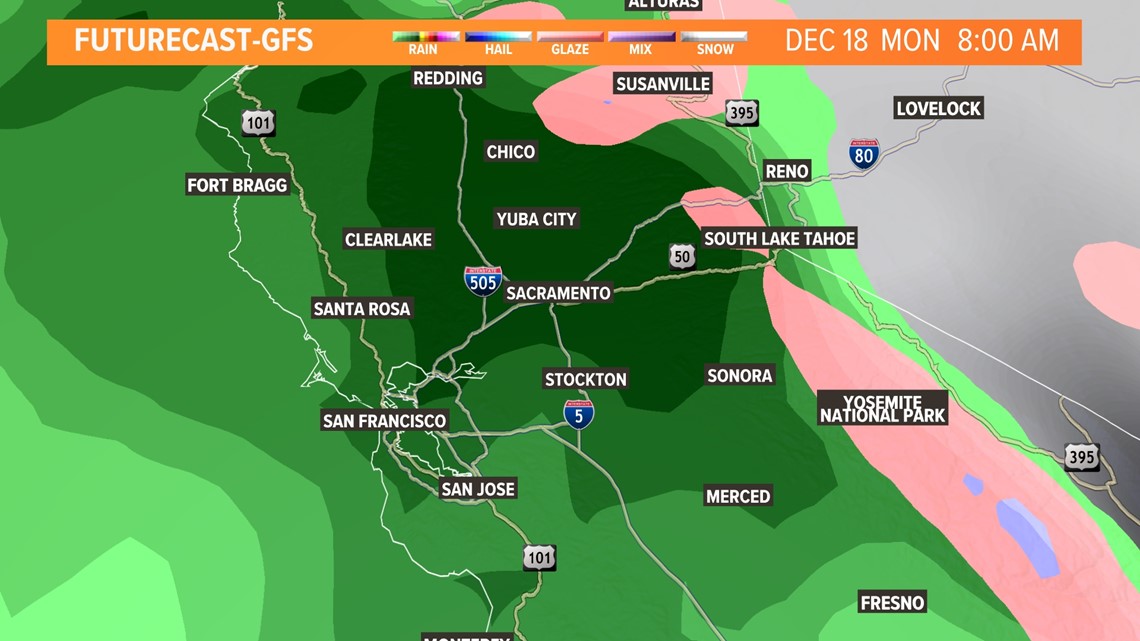
Atmospheric rivers (ARs) are powerful forces of nature, and their impacts on California are significant and varied. These concentrated streams of moisture in the atmosphere can bring substantial rainfall and flooding, impacting communities and ecosystems in profound ways. Understanding these past events provides valuable insights into the potential consequences of future AR events.California’s history is marked by devastating AR events, underscoring the need for preparedness and mitigation strategies.
The long-term effects, ranging from infrastructure damage to altered ecosystems, highlight the importance of continuous research and adaptation. This section delves into specific examples of AR impacts, showcasing how these events have affected different regions and communities.
Past AR Events in California
Several notable AR events have shaped California’s landscape and infrastructure. The impacts of these events vary greatly depending on factors such as the intensity of the AR, the terrain, and the existing infrastructure. Understanding these past events allows for better preparedness and mitigation strategies.
Examples of AR Impacts on Different Communities
AR events disproportionately affect different communities within California. Rural areas often face challenges with limited infrastructure, leading to more extensive damage and slower recovery times. Urban areas, on the other hand, may experience flooding in low-lying areas and disruptions to transportation systems. The economic consequences can be significant, impacting businesses and livelihoods.
- The 2017 atmospheric river event: This event brought record rainfall to Northern California, resulting in widespread flooding and mudslides. The devastation was particularly severe in the mountainous regions, where the combination of heavy rain and saturated ground led to landslides that destroyed homes and infrastructure. Communities in the Sacramento Valley faced severe flooding, impacting agriculture and transportation.
- The 2022 atmospheric river event: This event resulted in significant flooding in Southern California, impacting urban areas such as Los Angeles and San Diego. The flooding led to power outages, transportation disruptions, and damage to homes and businesses. The event highlighted the vulnerability of coastal communities to intense rainfall events. This event further demonstrated the need for robust flood control measures in urban environments.
Long-Term Consequences of AR Events
The impacts of AR events extend beyond the immediate aftermath. Long-term consequences include altered ecosystems, damaged infrastructure, and economic losses. The disruption to agricultural activities can have cascading effects on the food supply chain. Mental health issues are also a concern, particularly for those directly affected by loss and displacement. The need for robust recovery plans and long-term adaptation strategies becomes paramount.
Comparative Analysis of AR Impacts on Different California Regions
A comparison of the impacts of different AR events across various California regions provides valuable insights into regional vulnerabilities and the need for tailored mitigation strategies.
| AR Event | Northern California | Central California | Southern California |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 Event | Widespread flooding, mudslides, damage to infrastructure, agriculture disruption | Significant rainfall, localized flooding, river overflow | Localized flooding in urban areas, coastal erosion concerns |
| 2022 Event | Heavy rainfall, but less extensive damage compared to 2017 due to better preparedness | Moderate rainfall, but disruption to agriculture | Significant flooding in urban areas, transportation disruptions, power outages |
Visual Illustration of AR Impacts
Imagine a landscape saturated with water. The lush green vegetation is now submerged under a layer of muddy water. Rivers and streams overflow their banks, carrying debris and sediment. The landscape is transformed into a chaotic scene of destruction. Roads and bridges are submerged under the floodwaters, making travel and access to essential services impossible.
Trees are uprooted and scattered across the affected areas.
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, California’s atmospheric rivers are a complex and impactful weather phenomenon. From their formation to their devastating consequences, understanding these systems is vital for protecting communities and infrastructure. By combining scientific research, improved forecasting, and community preparedness, we can better navigate the challenges posed by these powerful atmospheric rivers. The future of California’s resilience hinges on our collective understanding and proactive responses.
Answers to Common Questions
What are the long-term consequences of atmospheric river events?
Long-term consequences can include significant damage to infrastructure, agricultural losses, and long-term health issues for impacted communities. Erosion, altered water supplies, and changes in local ecosystems can also persist for months or even years after the initial event.
How do atmospheric rivers differ from other types of storms?
Atmospheric rivers are distinct from typical storms because they deliver a concentrated band of moisture, often over a large area. This concentrated precipitation can lead to more intense rainfall and flooding compared to other types of storms.
What role do government agencies play in AR response and recovery?
Government agencies play a crucial role in disaster response and recovery, coordinating relief efforts, providing emergency services, and assisting affected communities with rebuilding and recovery. This includes managing resources, delivering aid, and providing long-term support.






