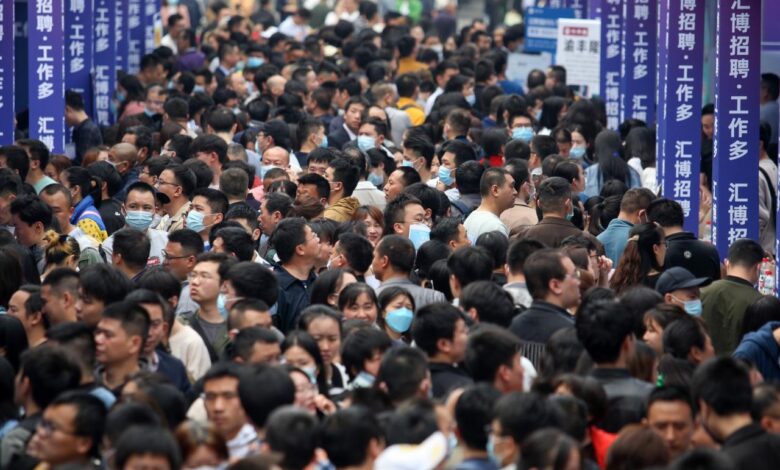
China Economy Job Market Young Adults Future
China economy job market young adults is a complex and multifaceted issue. The Chinese economy, a global powerhouse, is experiencing significant shifts, impacting the employment landscape for young adults. From the rise of technology to government policies, numerous factors influence job prospects and career paths for this crucial demographic. This exploration delves into the current state of the Chinese economy, analyzes job market dynamics, and examines the unique challenges and opportunities faced by young adults navigating this landscape.
This blog post provides a comprehensive overview of the factors shaping the Chinese job market for young adults. We will analyze current economic indicators, explore the challenges young people face in securing employment, and discuss government initiatives and industry-specific trends. The aim is to present a balanced picture, highlighting both the opportunities and hurdles in this dynamic environment.
Overview of the Chinese Economy

China’s economy, the world’s second-largest, continues to evolve at a rapid pace. While challenges persist, including global economic uncertainties and the ongoing transition from an export-oriented model, the country’s resilience and vast domestic market remain significant strengths. Understanding the current state, historical trajectory, and key sectors is crucial for comprehending China’s role in the global economy.
Current Economic Indicators
The Chinese economy demonstrates a complex interplay of factors. Recent data indicates a mixed performance. GDP growth, while still positive, has shown signs of deceleration, potentially influenced by factors like global headwinds and domestic policy adjustments. Inflationary pressures, a recurring theme, have remained relatively stable, although this is closely watched. The employment market, though facing challenges, has maintained a relatively healthy outlook.
Navigating the Chinese job market for young adults is tough, with fierce competition and often, a struggle to find fulfilling work. Considering the pressure and potential challenges, it’s interesting to see how cultural norms around naming, like choosing a baby’s name, also play a role. For example, understanding the traditions and rules surrounding apellido bebe madre padre might give us some insight into the broader societal expectations influencing young people’s choices and paths in the job market.
Ultimately, these interconnected cultural elements shape the experiences of young Chinese adults in a significant way.
| Indicator | Current Value | Previous Value | Percentage Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| GDP Growth (%) | 4.5 | 4.8 | -0.3 |
| Inflation Rate (CPI) (%) | 2.1 | 2.0 | 0.5 |
| Unemployment Rate (%) | 5.2 | 5.1 | 0.2 |
Historical Trajectory of the Chinese Economy
China’s economic rise has been remarkable, transitioning from a centrally planned economy to a global economic powerhouse. The period following economic reforms in the late 20th century saw substantial growth driven by export-oriented manufacturing. More recently, there’s been a focus on innovation, technological advancement, and domestic consumption as key drivers of future growth. This shift reflects a strategic recalibration of the economy.
Major Sectors Driving Economic Growth
China’s economic landscape is diversified, with multiple sectors contributing significantly. The service sector, including finance and technology, has experienced robust growth, indicating a transition from a predominantly manufacturing-based economy. High-tech industries, including artificial intelligence, 5G, and renewable energy, are poised for significant expansion, driven by substantial government investment and private sector initiatives.
- Manufacturing: While still a vital sector, its role in overall economic growth is gradually shifting. China’s manufacturing prowess remains significant, but the focus is increasingly on higher value-added products and technological sophistication.
- Technology and Innovation: This sector is a crucial engine of growth, with investments in areas like artificial intelligence, 5G, and renewable energy driving innovation and future opportunities.
- Real Estate: The real estate sector has historically been a key component of China’s economic engine. Recent regulatory changes and market fluctuations have had notable impacts, affecting both consumer confidence and broader economic trends.
- Consumer Goods and Services: The increasing affluence and urbanization have fueled growth in the consumer sector. Domestic demand now plays a critical role in maintaining economic momentum.
Job Market Dynamics
The Chinese job market is a complex tapestry woven from threads of rapid urbanization, technological advancement, and evolving economic priorities. Understanding the nuances of employment trends, particularly for young adults, is crucial for navigating the opportunities and challenges inherent in this dynamic environment. The overall employment landscape is constantly shifting, impacting both urban and rural areas, and requiring a nuanced understanding of sectoral growth and decline.The job market is no longer a simple equation of factory jobs and agricultural work.
Today’s economy demands adaptability and a workforce equipped with skills that match the evolving needs of various sectors. This necessitates a focus on both existing employment trends and emerging opportunities for young adults entering the workforce. Furthermore, the disparities between urban and rural employment scenarios highlight the necessity of targeted policies and support systems to ensure equitable access to opportunities for all.
Overall Employment Trends
China’s employment landscape is characterized by a shift from traditional industries to more technologically advanced sectors. Urban areas experience a higher concentration of these evolving opportunities, while rural regions continue to grapple with the transition. The overall trend points towards a more diversified and complex job market, demanding adaptable skills and knowledge. The continued expansion of the service sector is creating numerous new roles in areas like technology, finance, and e-commerce.
Sectors Experiencing Growth and Decline
The service sector, encompassing technology, finance, and e-commerce, is a primary driver of job growth in urban centers. This sector demands specialized skills, which presents a challenge for young adults entering the workforce. Conversely, traditional manufacturing sectors, while still present, are experiencing a decline in job opportunities, often requiring retraining and upskilling to adapt to the changing needs of the market.
The agricultural sector, while vital, is facing challenges due to automation and urbanization.
Challenges and Opportunities for Young Adults
Young adults entering the job market face a multitude of challenges, including fierce competition for limited positions and the necessity to acquire advanced skills. High competition necessitates a strong educational background and practical experience. Opportunities exist in the burgeoning technology and innovation sectors, offering higher-paying roles but demanding advanced knowledge and adaptability. Furthermore, the pressure to achieve financial independence and secure a fulfilling career in a fast-paced environment can create considerable stress.
The challenge is to identify opportunities that align with individual aspirations and skills.
Table: Job Market Trends by Age Group
| Age Group | Employment Trend | Challenges | Opportunities |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18-25 | High competition, need for specialized skills | Limited experience, difficulties in securing jobs | Emerging tech sector, entrepreneurial opportunities |
| 26-35 | More established career paths, greater stability | Potential for stagnation in career trajectory | Management roles, specialized positions |
| 36+ | Experienced professionals, leadership roles | Adapting to new technologies, maintaining relevance | Mentorship opportunities, consulting roles |
Young Adult Perspectives
Young adults in China are navigating a complex job market, shaped by rapid economic changes and evolving societal expectations. Their aspirations, fueled by access to information and global perspectives, are often intertwined with the realities of fierce competition and evolving skill requirements. Understanding their perspectives is crucial to crafting effective policies and supporting their aspirations for a fulfilling future.
Expectations and Aspirations
Young Chinese adults typically desire stable, well-paying jobs that offer opportunities for growth and professional development. They value companies with strong reputations and a positive work environment. Many seek roles that align with their personal values and allow for a balance between work and personal life. Furthermore, the increasing prevalence of entrepreneurship and gig work is evident, reflecting a desire for greater autonomy and flexibility in their careers.
Challenges in Finding Suitable Jobs
The job market presents significant challenges for young adults in China. Intense competition, fueled by a large graduating class, makes securing a desirable position difficult. Furthermore, employers often express concerns about the practical skills and adaptability of job applicants, creating a skill gap. This gap highlights the need for education and training programs that better equip young adults for the demands of the modern workplace.
In some sectors, especially those related to technology and innovation, the competition for top talent is fierce, requiring a high level of specialized skills.
Role of Education and Training
Education and training play a critical role in preparing young adults for the job market. Formal education, including university degrees, remains important, but increasingly, young adults recognize the value of practical skills and certifications. Vocational training, internships, and mentorship programs can bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application. These programs provide young adults with opportunities to develop valuable skills, refine their portfolios, and build networks, increasing their employability.
Further, continuous learning through online courses and workshops is becoming increasingly crucial in a rapidly evolving job market.
Desired Job Roles vs. Available Opportunities
| Desired Job Roles | Actual Job Opportunities |
|---|---|
| Software Engineer | High demand, but specialized skills are often required |
| Data Scientist | Growing demand, but requires advanced degrees and specific skills |
| Financial Analyst | Competitive, with strong academic backgrounds preferred |
| Marketing Specialist | Varied opportunities, but creativity and digital marketing skills are crucial |
| Entrepreneur | Opportunities exist, but success requires innovation and risk-taking |
| Educator | Demand for qualified educators, particularly in STEM fields |
The table above highlights a common trend: while young adults desire roles that offer career advancement and are in high-growth sectors, the availability of these opportunities can be limited by specific skill requirements and competitive pressures. This mismatch underscores the importance of tailoring education and training programs to better equip young adults with the skills needed for the jobs available.
Government Policies and Initiatives
China’s government has implemented a multifaceted approach to address youth unemployment, recognizing it as a critical social and economic issue. These initiatives aim to provide support through various channels, including job creation programs, skill development initiatives, and targeted interventions for specific demographics. The effectiveness of these policies is constantly being evaluated and adjusted based on evolving market conditions and feedback from young adults.The Chinese government’s commitment to supporting employment, particularly for young adults, is demonstrated through a range of policies and programs.
These efforts are designed to address the specific challenges faced by this demographic, including the evolving job market, technological advancements, and shifts in industry demands. The ultimate goal is to create a more inclusive and dynamic employment landscape that caters to the needs of the younger generation.
Government Programs for Youth Employment
The Chinese government actively pursues various programs to tackle youth unemployment. These programs encompass diverse initiatives, aiming to equip young people with the skills and opportunities required to thrive in the modern job market. A critical component is providing financial assistance and incentives to businesses willing to hire recent graduates and those in vulnerable groups.
- Job Creation Programs: Targeted initiatives aim to stimulate job creation in specific sectors, like technology and renewable energy, with incentives and subsidies for companies creating new positions. This often involves collaborations between the government and private sector entities to foster growth and employment opportunities.
- Skill Development and Vocational Training: The government recognizes the importance of upskilling and reskilling the workforce to match the demands of the evolving job market. Various programs offer vocational training and courses, often in conjunction with industry partners, to equip young people with specialized skills in high-demand fields. Examples include training programs in digital technologies, artificial intelligence, and advanced manufacturing.
- Targeted Support for Specific Demographics: Recognizing the diverse needs of young people, the government implements programs catering to particular demographic groups. This may include initiatives specifically designed for recent graduates, rural youth, and those from underprivileged backgrounds, ensuring equitable access to opportunities.
- Financial Incentives for Hiring: To encourage hiring, the government often offers tax breaks, subsidies, and other financial incentives to businesses that hire recent graduates, especially in industries experiencing growth. These initiatives create a more favorable environment for both businesses and young job seekers.
Effectiveness of Policies, China economy job market young adults
Assessing the effectiveness of these policies is complex, demanding a multifaceted approach. While some programs demonstrate positive impacts, challenges remain. Factors influencing the outcomes include the adaptability of the programs to changing economic landscapes and the extent to which they address the underlying causes of youth unemployment. Monitoring the employment rate of young adults, along with the qualitative feedback from the job seekers, is crucial in evaluating the success of these programs.
Government Policies Regarding Skills Development
The Chinese government prioritizes the development of a skilled workforce, which is essential to its economic growth and competitiveness in the global arena. This includes a wide range of initiatives focused on vocational training, professional certifications, and continuing education opportunities.
- Emphasis on Technical and Vocational Education: The government promotes technical and vocational education, offering a wide range of programs to equip students with practical skills and knowledge in specific trades and professions. This emphasis aims to address the gap between the skills demanded by the job market and the skills possessed by graduates.
- Integration of Skills Development into Educational Systems: The integration of skills development into the educational system from early stages to university level is vital to create a workforce well-equipped for the evolving needs of the job market. This integration aims to cultivate practical skills alongside theoretical knowledge.
- Partnerships with Industry: Collaborations with industry leaders are critical in ensuring that skills training programs are relevant and aligned with the demands of the job market. Industry involvement allows for continuous updates and improvements to the curriculum and programs.
Industry-Specific Trends
The Chinese job market is a complex tapestry woven from diverse industry threads. Understanding the unique trends within specific sectors is crucial for navigating the opportunities and challenges facing young adults. The dynamism of technology, the resilience of manufacturing, and the expanding service sector all contribute to the overall picture. Analyzing these sectors reveals potential pathways for career development and highlights the evolving skillsets required for success.The diverging paths of various industries present a multifaceted view of the job market.
While some sectors experience robust growth, others face challenges and adjustments. Understanding these distinctions empowers young professionals to make informed career choices aligned with the specific demands and opportunities within each sector.
Technology Sector Trends
The technology sector in China is experiencing rapid growth, fueled by innovation and government support. This sector demands highly specialized skills and knowledge, with a particular emphasis on digital literacy and technical expertise. Companies are actively seeking individuals with strong problem-solving abilities and adaptability to navigate the ever-evolving technological landscape. Examples include software development, artificial intelligence, and data science.
Manufacturing Sector Trends
Manufacturing remains a significant sector in China, though its landscape is evolving. Automation and digitalization are transforming traditional manufacturing processes, creating a demand for workers with both technical and digital skills. The focus is shifting from simply operating machinery to understanding and maintaining complex automated systems. Adaptability and continuous learning are vital for success in this industry.
The Chinese economy’s job market for young adults is facing some serious headwinds. Recent reports suggest a lot of uncertainty, and finding stable employment is proving challenging. This is a significant issue, especially considering the scale of the Chinese economy. Meanwhile, news about the Eugene Weekly embezzlement printing scandal here highlights a different kind of economic pressure, albeit on a much smaller scale.
Ultimately, these issues, while seemingly disparate, both contribute to the complex picture of economic pressures facing young adults in China.
Service Sector Trends
The service sector is a crucial component of China’s economic growth, with diverse employment opportunities ranging from hospitality to finance. The sector’s growth is influenced by urbanization and consumer demand. This industry demands strong communication skills, customer service experience, and adaptability to changing market conditions. Specific areas of growth include e-commerce, online education, and financial services.
Emerging Industries and Potential Employment Opportunities
Renewable energy, biotechnology, and sustainable technology are emerging industries with significant growth potential. These sectors require specialized skills in areas such as engineering, research, and development. These industries often present opportunities for innovative problem-solving and a chance to contribute to a more sustainable future.
Skills and Qualifications for Success
The evolving demands of various industries highlight the importance of adaptability and continuous learning. Individuals with a strong foundation in core skills like communication, problem-solving, and teamwork, coupled with specialized expertise in their chosen fields, are well-positioned for success. Furthermore, proficiency in foreign languages and an understanding of global business practices can enhance career prospects.
Industry-Specific Job Trends Table
| Industry | Projected Growth | Required Skills |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | High | Coding, Data Analysis, Problem Solving, Digital Literacy |
| Manufacturing | Moderate, with emphasis on automation | Technical skills, digital literacy, adaptability, automation maintenance |
| Services | Steady | Communication, customer service, adaptability, problem-solving |
| Emerging (Renewable Energy) | High | Engineering, renewable energy technologies, environmental awareness |
Impact of Technological Advancements
The rapid pace of technological advancements, particularly in automation and artificial intelligence (AI), is reshaping the global job market, and China is no exception. Young adults in China face both opportunities and challenges as these technologies transform industries and create new demands for skills. This evolution necessitates a proactive approach to education and training to ensure a smooth transition for the workforce.The integration of automation and AI is fundamentally altering the nature of work across various sectors.
Repetitive tasks are increasingly being handled by machines, requiring human workers to focus on more complex, creative, and critical thinking roles. This shift demands a reevaluation of existing skill sets and the development of new competencies to thrive in this evolving landscape.
China’s young adults are facing a tough job market, with fierce competition and limited opportunities. However, cities like Hefei, focusing on the electric vehicle (EV) industry, are showing promise for job creation. A look at china hefei ev city economy reveals how this sector is potentially boosting the local economy, which could indirectly impact the overall job market for young people in China.
This positive development, though, doesn’t fully resolve the broader challenges young adults face in the Chinese job market.
Automation and Artificial Intelligence’s Impact on Work
Automation is progressively taking over routine tasks in manufacturing, logistics, and customer service. AI-powered systems are capable of analyzing vast amounts of data, identifying patterns, and making decisions with increasing precision. This has the potential to increase productivity and efficiency but also necessitates a realignment of the workforce. For example, assembly lines in factories are being equipped with robots that perform intricate tasks previously done by human workers.
This trend is evident across multiple industries, from manufacturing to customer service.
Required Skills for Adapting to the Changing Job Market
Adaptability, critical thinking, and problem-solving are becoming paramount in the face of rapid technological change. Young adults need to develop skills that machines cannot easily replicate. These include:
- Creativity and Innovation: The ability to generate novel ideas and solutions is essential for tackling complex challenges in an increasingly automated world. This includes adapting existing processes to new technologies, identifying new market opportunities, and designing innovative products and services.
- Data Analysis and Interpretation: The ability to collect, process, and interpret data is critical for understanding trends and making informed decisions. This involves using data analytics tools and techniques to extract insights from large datasets.
- Digital Literacy and Programming Skills: Proficiency in using digital tools and technologies is essential for navigating the digital landscape. Understanding programming languages and software development can open up new career paths and enable individuals to adapt to new technologies.
- Interpersonal and Communication Skills: Even with automation, human interaction remains vital. Strong communication and collaboration skills are essential for working effectively in teams and building relationships with clients and colleagues.
Upskilling and Reskilling Programs: Addressing the Skills Gap
Recognizing the need for a skilled workforce, the Chinese government is actively promoting upskilling and reskilling initiatives. These programs aim to equip young adults with the necessary competencies to navigate the changing job market.
- Government-funded training programs: Various government initiatives offer subsidized or free training programs in areas like coding, data analysis, and digital marketing. These programs often partner with leading companies to ensure that the skills taught are relevant to industry needs.
- Corporate training programs: Companies are increasingly recognizing the importance of upskilling their employees. They offer internal training programs to equip their workforce with the skills required to adapt to new technologies and maintain competitiveness.
- Online learning platforms: Online learning platforms have emerged as a valuable resource for acquiring new skills. These platforms offer a wide range of courses on various subjects, making it easier for individuals to upskill or reskill at their own pace.
Global Economic Context
The Chinese economy, a vital player in the global landscape, is deeply intertwined with the fortunes of other nations. Understanding the global economic context is crucial to comprehending the challenges and opportunities facing young adults in the Chinese job market. Global economic conditions, international trade, and investment all exert a powerful influence on employment prospects. A comparative analysis of the Chinese job market with those in other major economies reveals unique strengths and weaknesses, while examining the impact of global shocks helps predict future trends.The interconnected nature of the global economy means that events in one region can have ripple effects across the globe.
This is especially true for a country like China, a major exporter and recipient of foreign investment. Fluctuations in global demand, shifts in trade policies, and financial crises can significantly impact Chinese businesses and employment opportunities. For example, a global recession often leads to reduced demand for Chinese exports, impacting manufacturing sectors and related jobs. Conversely, strong global growth can create new opportunities for Chinese companies and attract investment, leading to job creation.
The Chinese economy’s job market for young adults is a hot topic right now, with anxieties rising about prospects. It’s a complex situation, but it’s worth remembering that human stories of hardship and resilience often come from unexpected places, like the tragic tale of lovers in Auschwitz, Keren Blankfeld and József Debreczeni, found in the cold crematorium. This powerful account reminds us of the enduring human spirit, which perhaps offers a parallel perspective on the pressures faced by young people in China’s job market.
Ultimately, both situations highlight the delicate balance between personal hardship and economic realities.
Impact of International Trade and Investment
International trade and investment are fundamental drivers of economic growth and job creation in China. Increased export demand for Chinese goods often translates into more manufacturing jobs, while foreign direct investment (FDI) can foster technological advancements and create jobs in various sectors. However, trade tensions and protectionist policies can disrupt supply chains and reduce employment opportunities. For instance, trade disputes between China and other major economies can negatively impact specific sectors and lead to job losses.
Conversely, increased foreign investment can bring in advanced technologies and management practices, potentially improving productivity and job quality.
Comparative Analysis of Chinese Job Market with Others
The Chinese job market differs significantly from those in other major economies. While China boasts a large and growing workforce, the quality and nature of employment can vary greatly. China often focuses on manufacturing and export-oriented industries, which can be susceptible to global economic fluctuations. Countries like Germany, known for their robust manufacturing sector, tend to have a more developed vocational training system, leading to skilled labor forces.
The Chinese economy’s job market for young adults is a complex issue, with many factors at play. While economic growth is robust, finding fulfilling employment remains a challenge for many recent graduates. Interestingly, the dedication and hard work required in the job market mirrors the perseverance displayed by legendary Texas Rangers player, Adrian Beltre, on his path to the Hall of Fame.
Adrian Beltre’s Hall of Fame career demonstrates the importance of commitment and skill development. Ultimately, navigating this competitive landscape requires similar determination and adaptability from young adults seeking their place in the Chinese job market.
The US, with its emphasis on innovation and technology, presents a dynamic but often highly competitive job market. Comparing these differences highlights the diverse paths that nations take to manage their economies and provide employment opportunities.
Impact of Global Economic Shocks on China’s Economy
Global economic shocks, such as financial crises, pandemics, or geopolitical tensions, have a significant impact on the Chinese economy. The 2008 global financial crisis, for example, significantly affected China’s export-oriented industries, causing job losses in certain sectors. More recently, the COVID-19 pandemic exposed vulnerabilities in global supply chains and impacted China’s economy, though China’s swift response helped mitigate the impact.
These shocks highlight the interconnectedness of the global economy and the importance of China’s resilience and adaptability in navigating such challenges. The Chinese government’s response to these events often shapes the recovery and future direction of the economy.
Future Outlook
The Chinese economy and job market for young adults are poised for a period of significant transformation. While challenges persist, opportunities abound, driven by technological advancements, evolving industry needs, and government policies. Understanding these trends is crucial for navigating the future and ensuring a successful career trajectory.The coming years will likely see a continued shift towards a more innovation-driven economy, requiring a new skillset among young professionals.
This shift will be characterized by both opportunities and difficulties, making adaptability and continuous learning paramount.
Potential Future Trends
The Chinese economy is projected to experience steady growth, albeit at a potentially moderated pace compared to previous decades. This moderated growth is expected to be more sustainable, focusing on quality over quantity. Industry diversification and the development of new sectors, like renewable energy and advanced technologies, are anticipated to be key drivers of future economic growth.
Challenges and Opportunities
The job market will present both challenges and opportunities. Automation and AI are transforming industries, demanding a workforce capable of adapting to new technologies. This necessitates continuous upskilling and reskilling initiatives for young adults to remain competitive. However, emerging sectors like artificial intelligence, biotechnology, and renewable energy are creating new job opportunities, offering exciting prospects for skilled professionals.
Examples of these opportunities include roles in data science, software development, and renewable energy engineering.
Projections for Economic Growth and Employment Rates
Projections for China’s economic growth rate are expected to remain positive, though potentially at a lower rate than in previous years. Employment rates for young adults will likely be influenced by the pace of technological adoption and the government’s policies to support employment creation in emerging sectors. Real-world examples of similar trends in other countries, like the increasing automation of manufacturing jobs in developed economies, can be used as a comparison and a cautionary tale, highlighting the importance of continuous adaptation.
Key Factors Shaping the Future of the Chinese Job Market
Several key factors will influence the future of the Chinese job market. These include:
- Technological advancements: The increasing use of automation and artificial intelligence will transform many industries, requiring young adults to develop new skills to remain competitive.
- Government policies: Government initiatives focused on supporting innovation and entrepreneurship will play a critical role in shaping job market dynamics.
- Industry diversification: The shift towards a more diversified economy will create new job opportunities in sectors like renewable energy and advanced technologies.
- Education and training: Investment in education and training programs that equip young adults with the skills needed for the future job market will be crucial.
- Global economic context: The overall global economic climate will significantly impact China’s economic performance and, consequently, its job market.
These factors highlight the dynamic and complex nature of the Chinese job market, and a focus on adaptability and continuous learning will be essential for young adults navigating this evolving landscape.
Final Summary: China Economy Job Market Young Adults
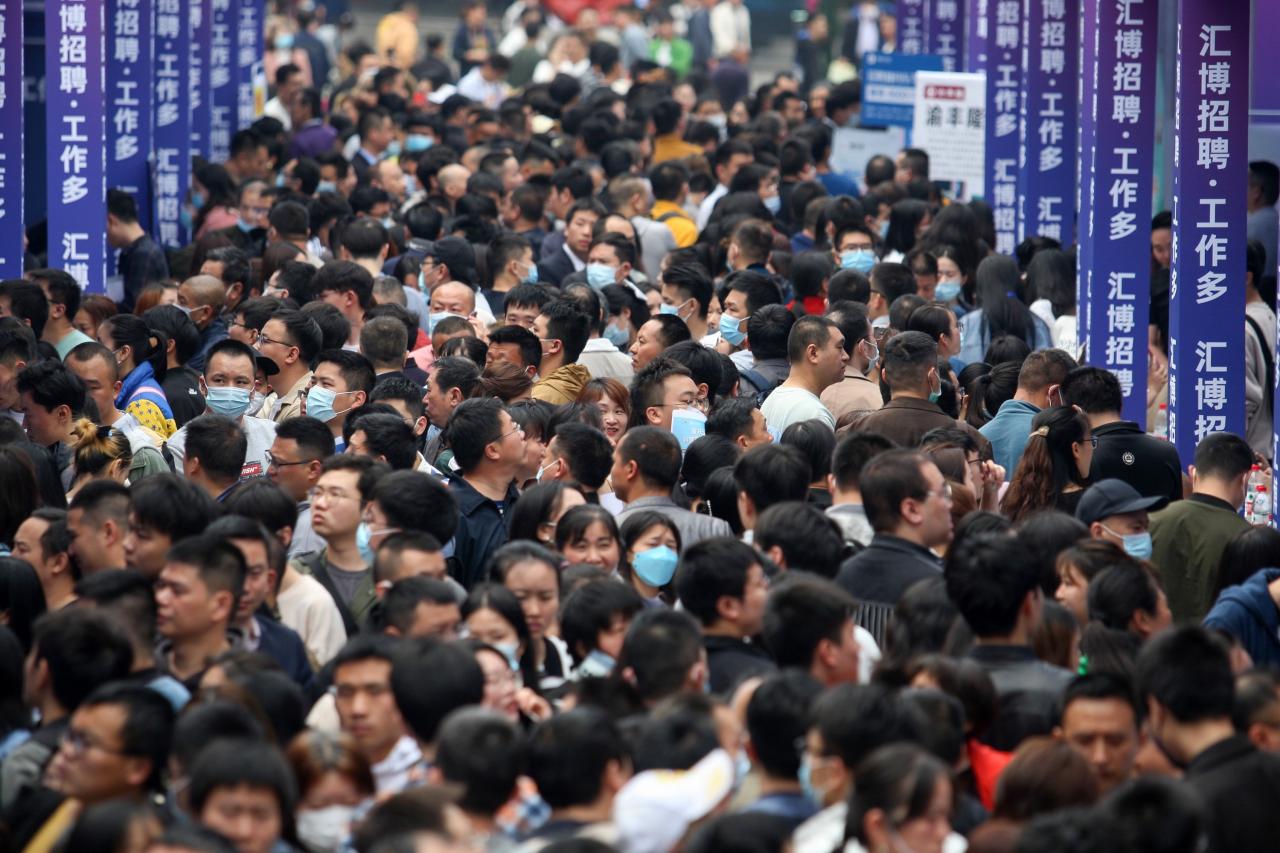

In conclusion, the Chinese economy job market for young adults presents a dynamic mix of challenges and opportunities. While navigating a competitive landscape and adapting to technological advancements is crucial, supportive government policies and emerging industries offer potential pathways to success. The future of the Chinese economy hinges on the success of its young workforce, and understanding the current realities and future projections is essential for both individuals and policymakers alike.
FAQ Summary
What are the most common career paths for young adults in China?
While traditional professions like engineering and medicine remain popular, the rise of technology has created new opportunities in fields like software development, data science, and e-commerce. The specific choices depend heavily on individual skills and educational background.
How does education affect job prospects for young adults in China?
Higher education levels are often associated with better job prospects. However, specialized skills and practical experience are increasingly important for securing competitive roles, especially in tech-driven industries.
What are the biggest challenges faced by young adults in China’s job market?
Competition for jobs is fierce, particularly in urban areas. Skills gaps, a lack of practical experience, and navigating a rapidly changing economic landscape are common hurdles.
How effective are government policies in addressing youth unemployment?
Government initiatives vary in their effectiveness. While some programs focus on skills development, their reach and impact differ across regions and industries. Further evaluation and targeted measures are needed to enhance their efficacy.