US News College Rankings A Deep Dive
College rankings US News have long shaped the college application landscape. From shaping student choices to influencing institutional strategies, understanding their impact is crucial. This exploration delves into the history, methodology, and impact of these rankings, highlighting the factors that drive them and examining the potential biases within the system.
This in-depth look at US News college rankings examines the evolution of the methodology, exploring the different metrics and factors used to compile these influential lists. We’ll also analyze the specific ranking categories, revealing how institutions excel in various areas. Furthermore, we’ll discuss the impact of these rankings on institutions and students, considering alternative ranking systems, and finally, visualizing the data to offer a comprehensive perspective.
Overview of US News & World Report College Rankings
US News & World Report’s college rankings have become a significant factor in the college application process, influencing both students and institutions. Understanding the evolution of these rankings, their methodology, and the associated criticisms is crucial for making informed decisions. This analysis delves into the history, methodology, and impact of these influential rankings.The rankings have evolved considerably since their inception, adapting to changing educational landscapes and reflecting evolving societal values.
Initial rankings focused primarily on academic reputation and resources, while later iterations incorporated a broader array of factors to provide a more comprehensive assessment.
History of the Rankings
The US News & World Report college rankings first appeared in the 1980s, emerging as a response to the growing need for objective criteria in the college selection process. Initially, they were based on limited data points, primarily relying on faculty resources and institutional characteristics. Over time, the methodology expanded to include student outcomes and other factors.
Methodology of the Rankings
The US News & World Report methodology employs a complex scoring system, incorporating various factors to produce a composite ranking. The weighting assigned to each factor is a key element in understanding the relative importance placed on different aspects of a college. The process involves gathering data from institutions, analyzing them using specific formulas, and assigning numerical scores based on the analysis.
Metrics and Factors Considered
A wide array of metrics and factors are considered in the rankings, reflecting the multifaceted nature of a college’s performance. These include academic reputation, faculty resources, student selectivity, financial resources, and graduation rates. Different metrics are weighted differently, creating a complex system that reflects the multifaceted nature of a college.
US News college rankings are always a hot topic, right? But lately, I’ve been more focused on the political landscape, like how Biden is taking on Trump’s policies, particularly with the infrastructure push in Wisconsin. Taking on Trump, Biden promotes an infrastructure decade in Wisconsin is definitely shaping the narrative. Ultimately, though, college rankings still have me wondering about the best fit for me, especially with so many great universities to consider.
- Academic Reputation: This metric assesses the perceived quality of a college’s faculty and programs. It’s often derived from surveys of other academics and institutions, reflecting the overall prestige and standing of the college within the academic community.
- Faculty Resources: This factor considers the ratio of faculty members to students. A higher ratio often correlates with more individual attention and potentially enhanced learning opportunities.
- Student Selectivity: This metric assesses the competitiveness of admission standards. A higher selectivity rate suggests a more rigorous application process, potentially attracting students with higher academic achievement.
- Graduation Rates: This factor reflects the success of the college in graduating students. Higher graduation rates often suggest better academic support and resources, fostering student success.
- Financial Resources: This factor considers the financial stability of the institution, including endowments and funding. Adequate financial resources are often linked to the ability to provide students with quality educational opportunities.
Criticisms and Debates Surrounding the Rankings
The US News & World Report college rankings have faced considerable criticism for their potential to oversimplify the complex realities of higher education. These rankings are frequently criticized for their limitations and biases, impacting the decision-making process of prospective students and institutions.
- Oversimplification of Complex Factors: The rankings are often criticized for reducing the complexities of higher education to a single numerical value, neglecting the various aspects of a college experience, such as its social environment, campus life, and career services.
- Bias and Limitations of Data Collection: The reliance on self-reported data and limited surveys may introduce biases into the rankings. This limitation can result in inaccurate or incomplete portrayals of a college’s true value proposition.
- Impact on Prospective Students: The rankings can significantly influence prospective students’ choices, potentially leading them to focus on institutions with high rankings and neglect other factors that might better suit their needs and interests.
Impact on Prospective Students and Institutions, College rankings us news
The rankings can influence the decisions of prospective students and the strategies of institutions. Understanding this impact is crucial for making informed decisions. Prospective students often use rankings to narrow their choices, while institutions often adjust their practices to improve their rankings.
- Student Decisions: Prospective students often rely on these rankings to narrow down their options, potentially overlooking other critical factors such as the specific programs offered or the overall campus culture.
- Institutional Strategies: Institutions often strategize to enhance their ranking, which may lead to a focus on quantifiable metrics at the expense of other important aspects of a holistic education.
Factors Influencing College Rankings
US News & World Report’s college rankings are a significant factor in prospective students’ decision-making process. Understanding the factors driving these rankings is crucial for interpreting the results and recognizing their limitations. These rankings, while influential, should not be the sole determinant in choosing a college. A holistic approach, considering individual needs and aspirations, is essential.The methodology behind these rankings is complex, with a multitude of factors contributing to a college’s overall score.
While the exact weighting of each factor is proprietary, the general categories and their impact on the final ranking are readily apparent.
Key Factors Impacting College Rankings
The US News & World Report rankings consider a broad spectrum of factors to assess the quality of a college. These factors are crucial in determining a college’s position and influence a prospective student’s decision-making.
| Factor Category | Description | Weighting (Approximate) | Example Colleges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Academics | This encompasses factors like faculty credentials, student-to-faculty ratios, graduation rates, and standardized test scores of admitted students. | High | Harvard, MIT, Caltech |
| Research | The amount and quality of research conducted by faculty and student involvement in research initiatives are considered. | Medium-High | Stanford, University of California, Berkeley, Johns Hopkins |
| Student Life | This category encompasses aspects like campus environment, student diversity, extracurricular activities, and overall student satisfaction. | Medium | University of Michigan, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, University of Texas at Austin |
| Financial Resources | Resources available for student support, facilities, and faculty compensation. | Medium-Low | Large public universities, state-funded institutions |
| Graduation and Retention Rates | The proportion of students who successfully complete their degrees and remain enrolled in the institution. | High | Top universities and colleges with rigorous academic programs |
Limitations and Potential Biases in the Ranking Methodology
The US News & World Report rankings, despite their perceived objectivity, have inherent limitations and potential biases. These factors can influence the rankings and should be considered when evaluating a college.
- Focus on Quantifiable Metrics: The rankings heavily rely on quantitative data, which may not fully capture the qualitative aspects of a college’s educational experience, such as a strong sense of community or innovative teaching methods.
- Geographic Variation: The rankings may not adequately reflect the diverse educational environments found across different regions of the United States. A highly-regarded institution in a rural area might not receive the same recognition as a similar institution in a major metropolitan area. The differences in student demographics and regional resources can skew results.
- Financial Resources and Institutional Size: The relative importance of factors like financial resources and institutional size can influence rankings, potentially creating an imbalance between institutions with varying resources.
- Potential for Bias: The selection of factors and their weighting may reflect certain biases, potentially overlooking important aspects of a college’s overall strengths.
The inherent limitations and potential biases associated with these rankings should not be overlooked by prospective students. While the US News & World Report rankings provide valuable insights, prospective students should conduct thorough research, consider their personal preferences, and evaluate colleges beyond the ranking system. The most important factor in choosing a college is a student’s individual fit and long-term goals.
Analysis of Specific Ranking Categories: College Rankings Us News
US News & World Report college rankings are a complex system, evaluating institutions across a wide range of criteria. Understanding the specific categories and how they are measured provides a more nuanced perspective on the rankings. This analysis delves into the key components, illustrating how different institutions excel in various areas.Understanding the specific criteria used to assess colleges provides valuable insight into the ranking process.
US News college rankings are always a hot topic, but lately, other things have been grabbing headlines. For example, the recent flooding at Eton College, causing problems in the restrooms, as reported by eton college flooding toilets , is definitely overshadowing the usual college ranking chatter. Still, when the dust settles, the prestige of US college rankings will undoubtedly remain a major factor for prospective students and their families.
Different institutions often prioritize different aspects, leading to a diverse range of strengths and weaknesses across the various factors.
Undergraduate Academics
This category assesses the quality of undergraduate education. It considers several crucial aspects of the educational experience. The rigor of coursework, faculty qualifications, and student-to-faculty ratios are significant indicators of academic strength. These metrics, when combined, provide a comprehensive view of the academic program.
- Coursework Rigor: This evaluates the depth and breadth of the curriculum. A demanding curriculum, incorporating challenging courses and advanced topics, is indicative of a rigorous academic environment. Institutions may utilize course descriptions and syllabi to determine the level of academic challenge.
- Faculty Qualifications: The qualifications of the faculty are crucial in shaping the educational experience. A high percentage of tenured or tenure-track faculty often signifies a commitment to long-term academic excellence and advanced research. Institutions often publicize faculty credentials and expertise.
- Student-to-Faculty Ratio: This metric reflects the level of individual attention students receive. A lower student-to-faculty ratio suggests more opportunities for interaction and individualized support from professors.
Different institutions demonstrate varied strengths in these areas. For example, some universities might excel in research-oriented programs with demanding coursework, while others may emphasize a more hands-on learning environment with a lower student-to-faculty ratio. Recognizing these diverse approaches is crucial for understanding the nuances of the rankings.
| Institution | Coursework Rigor | Faculty Qualifications | Student-to-Faculty Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| University A | High (Challenging upper-level courses) | High (High percentage of tenured faculty) | Low (10:1) |
| University B | Medium (Balanced mix of introductory and advanced courses) | Medium (Mix of tenure-track and adjunct faculty) | Medium (15:1) |
| University C | Low (Mostly introductory courses) | Low (High percentage of adjunct faculty) | High (20:1) |
Faculty Resources
This category focuses on the resources available to support faculty research and development. It includes funding opportunities, access to advanced technologies, and the overall research environment. The quality and quantity of research conducted by faculty members often reflect the institution’s commitment to academic excellence.
- Research Funding: The amount of research funding awarded to faculty members can indicate the university’s investment in academic pursuits. This is often measured by the amount of grants and research contracts received by faculty.
- Advanced Technology Access: The availability of high-quality equipment and software directly affects faculty research capabilities. This is often assessed based on the university’s investment in modern facilities and resources.
- Research Environment: The presence of collaborative research opportunities, seminars, and conferences fosters a vibrant and stimulating academic atmosphere.
A strong faculty resource profile supports the development and advancement of faculty members, directly impacting the quality of education and research.
Student Selectivity
Student selectivity reflects the competitiveness of admission standards. A higher selectivity rate often indicates a stronger academic reputation and a more demanding admissions process.
- Acceptance Rate: The percentage of applicants admitted is a key metric. A low acceptance rate indicates a highly selective institution.
- GPA and Test Scores of Entering Class: The average GPA and standardized test scores of admitted students provide insight into the academic profile of the incoming class.
- Application Volume: The volume of applications received provides context regarding the demand for admission.
These metrics, when combined, provide a clear picture of the institution’s reputation and the strength of its academic program. High selectivity often indicates a strong emphasis on academic excellence.
Impact of Rankings on Institutions and Students
US News & World Report college rankings have a significant impact on both the institutions themselves and the students seeking higher education. These rankings, while often lauded for their perceived objectivity, are complex tools that influence decisions at all levels of the educational process. Understanding the dynamics of this influence is crucial for prospective students and institutions alike.The prestige associated with high rankings translates directly into increased applications.
Institutions often use rankings as a key marketing tool to attract top students and faculty. A favorable ranking can position an institution as a desirable choice, leading to higher enrollment rates and a more competitive applicant pool. Conversely, lower rankings can make it harder to attract talented students and faculty, potentially leading to a cycle of declining reputation.
How Institutions Use Rankings to Attract Students and Faculty
Institutions leverage rankings to enhance their public image and attract desirable applicants. They often highlight their strong performance in specific ranking categories, such as academics, research, or financial aid, to prospective students and their families. Strategic marketing campaigns often feature these ranking data to promote the institution’s strengths. Furthermore, the reputation of highly-ranked institutions can influence faculty recruitment, attracting professors seeking to work at prestigious universities.
In addition to marketing, institutions may also adjust their programs and initiatives to improve their standing in the rankings.
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks for Students
Rankings can be a valuable tool for students navigating the college application process. A high ranking can signal a strong academic environment and reputable faculty, making the institution a more appealing choice. Students can use rankings to narrow their search and identify schools that align with their academic goals and preferences. However, relying solely on rankings can be problematic.
A school with a high overall ranking may not be the best fit for every student. Students should carefully consider other factors, such as campus culture, extracurricular activities, and specific program offerings, alongside ranking data. Furthermore, a school with a lower ranking may offer a more personalized and intimate learning experience that is superior to the large-scale, impersonal learning environment of a top-ranked institution.
How Students Might Use Rankings to Narrow Their College Search
Students can use rankings to filter potential colleges, identifying schools that match their academic interests. For example, a student interested in engineering might focus on schools highly ranked for engineering programs. Rankings can be a useful starting point, but students should not limit their search to just highly ranked schools. Students should also consider factors like the specific programs offered, the location of the college, and the overall atmosphere of the campus.
US News college rankings are always a hot topic, right? But with the New Hampshire Democratic primary results just out, results new hampshire democratic primary are definitely grabbing headlines. It’s fascinating to see how these events might influence future college applications, even if indirectly. Still, the core issue remains the same: how these rankings affect students and institutions in the long run.
They should also delve deeper into the methodology of the rankings to understand how certain factors are weighted.
How Rankings May Influence College Admissions Decisions
Rankings are often considered in the admissions process, though their influence varies from institution to institution. Highly ranked schools often have more selective admissions criteria, potentially accepting a smaller percentage of applicants. Colleges may prioritize students who attend high-ranking high schools or have strong academic records, even if they are not in the top percentiles of their class.
Students should understand that rankings are one factor among many in the admissions process. Ultimately, admissions decisions are made based on a holistic review of each applicant’s profile, including academic performance, extracurricular activities, letters of recommendation, and personal essays.
Alternative Ranking Systems and Perspectives

College rankings, while popular, often present a limited view of an institution’s strengths. The traditional US News & World Report methodology, with its focus on metrics like faculty resources and graduation rates, doesn’t capture the full spectrum of a college’s value proposition. Recognizing this limitation, alternative ranking systems have emerged, offering different perspectives and highlighting various aspects of higher education.Alternative ranking systems provide valuable insights into specific aspects of a college’s offerings, moving beyond the generalized metrics often employed in broader rankings.
They allow for a more nuanced understanding of an institution’s strengths and weaknesses, empowering prospective students and researchers with more comprehensive data.
Examples of Alternative Ranking Systems
Various alternative ranking systems have emerged, targeting different aspects of higher education. These systems often focus on specific academic fields, student outcomes, or institutional values. For instance, some rankings focus exclusively on engineering programs, while others prioritize career placement statistics. This targeted approach allows for a deeper dive into particular niches, providing more tailored insights for students with specific career goals.
Comparing and Contrasting Ranking Methods
| Ranking System | Focus | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| US News & World Report | General academic performance across disciplines | Broad overview; widely recognized; established methodology | Limited to quantifiable metrics; may not reflect specialized programs; potential for bias |
| Princeton Review | Student experience, campus environment | Emphasizes student life; offers qualitative insights | Subjective; relies on student feedback; may not accurately represent all student experiences |
| Washington Monthly | Social impact and public service | Highlights colleges contributing to society | Difficult to quantify social impact; may not appeal to students focused solely on career advancement |
| PayScale | Career outcomes and salary potential | Directly addresses career prospects | Limited to career outcomes; may not reflect other valuable aspects of education; data dependent on accurate employment reporting |
The table above demonstrates a variety of ranking systems, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Choosing the right ranking system depends heavily on the specific criteria that are important to the individual or institution being evaluated. A student seeking a strong engineering program would benefit from rankings specifically focused on that field, while someone prioritizing campus life would find rankings based on student experiences more useful.
Varying Perspectives on the Value of College Rankings
The value of college rankings is a subject of ongoing debate. Some view rankings as valuable tools for guiding prospective students and informing institutional improvement efforts. They argue that rankings can provide transparency and comparison across institutions. Others view rankings as overly simplistic and potentially misleading. They argue that a single ranking system cannot capture the multifaceted nature of a college’s value proposition and that focusing solely on quantitative metrics can obscure important qualitative aspects.
Limitations of a Single Ranking System
A significant limitation of any single ranking system is its inability to capture the diverse experiences and outcomes associated with a college education. Rankings often rely on limited data points, potentially overlooking important factors such as a school’s commitment to diversity, faculty expertise in specific fields, or the quality of its mentorship programs. The nuanced and personal value of a college education often transcends the metrics measured by a single ranking system.
Visual Representation of Data
Visualizing US News & World Report college rankings is crucial for understanding the complexities and nuances of the data. Effective visualizations can quickly convey the distribution of rankings across different institution types and highlight correlations between factors and placement. This allows for a deeper, more intuitive grasp of the ranking system’s intricacies and its implications for both institutions and prospective students.
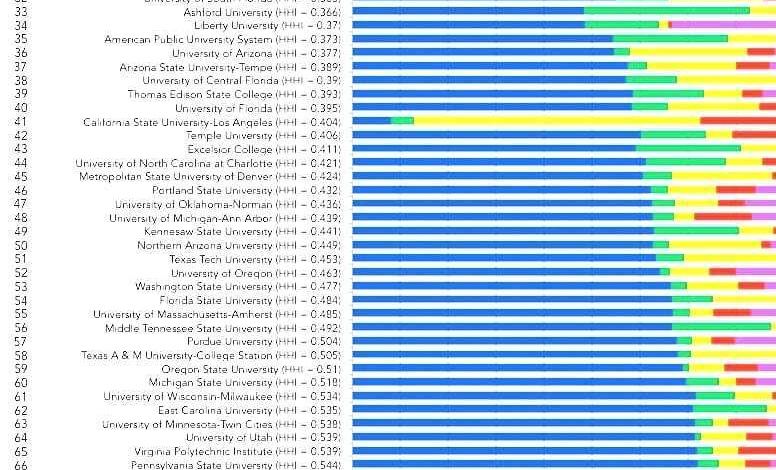
Distribution of Rankings Across Institution Types
Understanding how various institution types fare in the rankings is vital. A pie chart, for example, could clearly display the percentage of top-ranked institutions that are public universities, private non-profit colleges, or for-profit institutions. This visualization would immediately reveal whether certain types of institutions are disproportionately represented at the top of the rankings. Further, a stacked bar chart could compare the average ranking position of each institution type across different years.
This would visually illustrate any trends or shifts in the representation of institution types within the top ranks.
Correlation Between Factors and Ranking Position
Visualizing the correlation between specific ranking factors and a college’s overall rank is essential for understanding the relative importance of each factor. A scatter plot, for example, could depict the relationship between a college’s graduation rate and its overall ranking. Points on the plot would represent individual colleges, with the x-axis representing the graduation rate and the y-axis representing the overall ranking.
A positive correlation would be visually apparent with points clustered along a rising diagonal line. This allows a quick assessment of the relationship’s strength and direction.
Checking out US News college rankings is always a fun way to see how things are shaping up. While that’s happening, it’s also interesting to see how coaching changes, like the recent hiring of Arthur Smith as the Steelers’ offensive coordinator ( arthur smith hired steelers offensive coordinator ), might impact future rankings. Ultimately, though, the long-term success of any program is still going to depend heavily on the students and their individual abilities.
So, rankings are just one piece of the puzzle.
Key Takeaways from Visualizations
Visualizations of US News & World Report college rankings offer key insights into the data. The pie chart showing the distribution of rankings across different institution types would help in understanding the dominance of specific institution types at the top. The stacked bar chart highlighting the trend in average ranking position over years would reveal if there’s a change in the representation of institution types in the top ranks.
Similarly, a scatter plot displaying the correlation between factors and ranking position will visually reveal if a higher graduation rate is correlated with a higher overall ranking, for example.
Detailed Description of Visualizations
The pie chart, representing the distribution of rankings across institution types, will display slices corresponding to each type of institution (e.g., public, private non-profit, for-profit). The size of each slice corresponds to the percentage of institutions of that type within the top ranks. A stacked bar chart, comparing average ranking positions of different institution types over time, will show separate bars for each institution type, with the height of each section representing the average ranking in a specific year.
A scatter plot illustrating the correlation between factors and ranking position will show each college as a data point, with the x-axis representing the value of a specific factor (e.g., graduation rate) and the y-axis representing the overall ranking. The clustering of points will indicate the correlation strength and direction.
Future Trends in College Rankings
College rankings, while controversial, remain a significant factor in the higher education landscape. Understanding the potential evolution of these rankings is crucial for institutions and prospective students alike. These predictions are not crystal ball gazing, but rather analyses of current trends and potential impacts of emerging factors.The methodologies and criteria behind college rankings are likely to undergo substantial transformations in the coming years.
Adapting to technological advancements, evolving student needs, and changing social trends will be critical for rankings to maintain relevance. This shift in approach will be necessary for providing a more accurate and comprehensive view of an institution’s strengths and weaknesses.
Potential Changes in Ranking Methodology
Current ranking systems often rely on quantitative metrics like graduation rates and standardized test scores. However, there’s a growing recognition that these metrics don’t fully capture the nuanced experience of a college education. Future rankings might incorporate qualitative data, such as faculty research output, student satisfaction surveys, and alumni success stories. This broadened approach could provide a more holistic evaluation of institutions.
For example, a ranking system that considers the impact of a college’s research on the broader community, alongside traditional metrics, would offer a more comprehensive view.
Evolving Role of Rankings in Higher Education
Rankings have historically influenced admissions decisions, funding allocations, and public perception of institutions. Their influence on institutional strategies and student choices will continue. However, the future role of rankings may shift towards a more supportive and less prescriptive function. Instead of dictating the path for institutions, rankings might serve as tools for institutions to showcase their unique strengths and cater to student needs in a more individualized manner.
US News college rankings are always a hot topic, right? But lately, a different kind of controversy is swirling around Indiana University, specifically regarding the cancellation of the Samia Halaby exhibition. This incident raises some interesting questions about how institutions handle sensitive topics and potentially impacts future college rankings, especially when it comes to curating exhibitions that are culturally relevant and inclusive.
The controversy surrounding the canceled exhibition could be a factor in how institutions are evaluated in the future in US News college rankings. indiana university samia halaby exhibition canceled
Colleges might use rankings as a marketing tool to attract students with specific interests, rather than simply aiming for the top spot.
Impact of Technology on Future Rankings
Technological advancements are transforming higher education, from online learning platforms to AI-powered tutoring systems. Future rankings might incorporate metrics reflecting institutions’ adoption and utilization of technology in their educational models. This could include the integration of data analytics for personalized learning, the quality of online course offerings, and the institution’s digital infrastructure. The growing use of online learning platforms and virtual labs is likely to be reflected in future ranking criteria.
Adapting to Evolving Student Needs
Students are increasingly seeking more personalized and flexible educational experiences. Future rankings may consider factors such as the availability of co-curricular activities, support for diverse learning styles, and career counseling services. These factors might be reflected in metrics related to student success, not just in traditional academic measures, but also in career preparation. Rankings might also focus on the college’s ability to adapt to diverse student needs.
Social Trends and College Rankings
Social trends, such as a growing emphasis on social justice and environmental sustainability, will likely influence future ranking criteria. Colleges demonstrating commitment to these values might see a corresponding increase in their rankings. This could involve considering the institution’s efforts in promoting diversity, its engagement with local communities, and its commitment to environmental responsibility. The growing emphasis on social responsibility and sustainability is likely to be a significant factor influencing the way colleges are evaluated in the future.
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, US News college rankings remain a powerful force in the higher education landscape. While offering valuable insights, they also come with limitations and biases. Students and institutions alike need to approach these rankings with a critical eye, considering multiple perspectives and factors beyond numerical scores. The future of these rankings likely lies in evolving to incorporate a broader range of student needs and experiences.
Key Questions Answered
What are the main criticisms of US News college rankings?
Critics often point to the potential for bias in the methodology, highlighting the emphasis on certain factors like prestige and selectivity over other important aspects like affordability and student support. The complexity of quantifying various aspects of a college’s performance also raises concerns about the accuracy and fairness of the rankings.
How do students use these rankings to narrow their college search?
Students often use rankings as a starting point, helping to filter potential institutions based on their desired profile. However, it’s crucial for students to go beyond the rankings and conduct further research into the specific programs, faculty, and campus environment that best suit their needs.
Are there any alternative ranking systems available?
Yes, there are alternative ranking systems that focus on different aspects of higher education, such as specific academic fields or student outcomes. These systems often provide a more nuanced view of an institution’s strengths and weaknesses, but they don’t always enjoy the same level of widespread recognition as the US News rankings.
How do institutions use rankings to attract students and faculty?
High rankings often correlate with increased visibility and reputation, which can attract a larger pool of qualified applicants and faculty. Institutions may invest in areas that are highly weighted in the rankings to boost their position.

