Housing Market New vs. Existing
Housing market new existing is a complex landscape, where new construction battles with the established market. Interest rates, inflation, and supply and demand all play a crucial role in shaping the current conditions. Understanding the differences between purchasing a new home and an existing one is key to navigating this market effectively.
This exploration delves into the nuances of both new and existing home markets, examining factors influencing prices, financing options, and buyer demographics. We’ll also explore historical trends, local market analysis, and the impact of economic forces on this dynamic sector. Get ready to compare average sale prices, construction timelines, and typical features of new homes with the established features and maintenance considerations of existing homes.
Overview of the Housing Market
The housing market, a crucial component of the economy, continues to evolve in response to a complex interplay of factors. Recent trends in both new and existing home sales provide insights into the current state of the market and the forces shaping its trajectory. Understanding these dynamics is vital for both buyers and sellers, as well as investors and policymakers.The current housing market landscape is characterized by fluctuating conditions, influenced by interest rate adjustments, inflation, and the ever-present interplay of supply and demand.
Navigating these complexities requires a comprehensive understanding of the specific factors at play and their individual and collective impacts on the market.
Current State of New and Existing Home Sales
New home sales often reflect the current construction environment and the availability of financing options. Existing home sales, conversely, mirror the preferences of established homeowners and the prevailing conditions in the resale market. Together, these provide a comprehensive picture of the housing market’s current state.
Key Factors Influencing Market Conditions
Interest rates, inflation, and supply and demand dynamics significantly influence housing market conditions. Fluctuations in interest rates directly affect mortgage affordability, impacting both buyers and sellers. Inflation, a general increase in prices, can erode purchasing power and affect the overall cost of housing. Supply and demand, as with any market, play a pivotal role in pricing and availability.
If demand outstrips supply, prices typically rise. Conversely, an oversupply can lead to price decreases.
Buyer Demographics for New and Existing Homes
The demographics of homebuyers differ between new and existing homes. Buyers of new homes are frequently first-time buyers, young families, or individuals seeking modern amenities and designs. Existing home buyers may be more established, seeking specific features or locations, and may be looking to upgrade or relocate. These differences influence the characteristics of the housing market segments.
Historical Trends in New and Existing Home Markets
Historically, both new and existing home markets have experienced periods of growth and decline. Factors like economic downturns, shifts in interest rates, and demographic changes have consistently impacted market trends. The Great Recession, for example, led to a significant downturn in both markets, highlighting the susceptibility of the housing sector to broader economic conditions.
The housing market, with its fluctuating new and existing home sales, is always interesting to watch. It’s a complex dance of supply and demand, and lately, it’s been a bit of a rollercoaster. Speaking of rollercoasters, did you know that Adrian Beltre, a true Texas Rangers legend, is now in the Hall of Fame? Adrian Beltre hall of fame Texas Rangers His impressive career is a testament to dedication and hard work, qualities that often mirror the resilience of those navigating the current housing market.
This market, with its ups and downs, ultimately reflects the overall economic climate and the constant search for affordable and suitable housing.
Average Sale Prices of New and Existing Homes Across Regions
Regional variations in housing prices are substantial. The following table illustrates average sale prices for new and existing homes in various regions of the country.
| Region | Average Sale Price (New Homes) | Average Sale Price (Existing Homes) |
|---|---|---|
| Northeast | $650,000 | $580,000 |
| Midwest | $480,000 | $420,000 |
| South | $520,000 | $450,000 |
| West | $700,000 | $620,000 |
Note: Data in the table represents approximate averages and can vary based on specific location, size, and features of the property. These figures are not exhaustive and may not reflect all regional variations.
New Home Market

The new home market presents a unique set of considerations for potential buyers. From construction timelines and costs to financing options and regulations, navigating this sector requires a thorough understanding of the process. This in-depth look at the new home market will help you make informed decisions about building or purchasing a new home.Construction costs and timelines are significant factors influencing the final price and delivery date of a new home.
The housing market, new and existing, is definitely feeling the ripple effects of economic shifts. While the recent fluctuations in prices are interesting, it’s hard to ignore the broader political landscape, particularly the New Hampshire Democratic Primary results, which are generating quite a buzz. results new hampshire democratic primary are potentially influencing voter sentiment and, in turn, influencing the direction of the market.
Ultimately, the long-term trends in the housing market will be shaped by a combination of factors, from interest rates to overall consumer confidence.
Fluctuations in material costs, labor shortages, and unforeseen challenges during the building process can impact these elements. Furthermore, the complexity of the building process, from initial design to final inspections, contributes to the duration of construction.
Construction Costs and Timelines
Construction costs for new homes vary significantly depending on location, size, and features. Factors such as labor rates, material prices, and local regulations all influence the overall cost. For example, a custom home in a high-demand area will typically command a higher price point than a standard model home in a less populated area. Timelines for construction can range from several months to over a year, depending on the complexity of the project and the availability of resources.
Delays can occur due to unforeseen circumstances, material shortages, or permitting issues. Building permits are crucial to ensure compliance with local codes and regulations. A thorough understanding of the local building codes and regulations is critical.
Financing Options
Financing options for new homes differ slightly from those for existing homes. Lenders often assess the value of the property based on its estimated construction costs. Typically, new construction loans involve a larger upfront investment and potentially higher interest rates, depending on the market and the individual borrower’s creditworthiness. The availability of government-backed loans like FHA loans can ease the process for certain buyers.
Additionally, incentives such as tax deductions for mortgage interest payments and potential rebates may apply.
Regulations and Permitting Processes
Regulations and permitting processes are crucial to ensuring the quality and safety of new construction. Local building codes and regulations dictate aspects like structural integrity, energy efficiency, and accessibility standards. The permitting process typically involves several stages, including plan review, inspections at various stages of construction, and final approval. Strict adherence to regulations is critical to avoiding delays or issues with the final product.
Incentives and Programs
Various incentives and programs exist to encourage new home purchases. These can include tax credits, rebates, or grants for energy-efficient features. State and local governments may offer specific programs targeting new construction in certain areas. Researching these programs and incentives can potentially lower the overall cost of the home and make it more affordable.
Typical Features and Amenities
New homes often feature modern amenities and energy-efficient designs. Buyers frequently have choices regarding customization of the interior and exterior of the home. Advanced technologies, such as smart home features and high-efficiency appliances, are increasingly common in new construction. Sustainability and eco-friendliness are also important considerations for many new home buyers.
Pros and Cons of Buying New Homes vs. Existing Homes
| Feature | New Home | Existing Home |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Higher initial cost, but potentially lower long-term maintenance | Lower initial cost, but potential for higher long-term maintenance |
| Customization | Greater opportunity to personalize the home | Limited customization options |
| Condition | New and in excellent condition | May require repairs or renovations |
| Warranty | Builder warranties on materials and workmanship | Limited warranties, if any |
| Energy Efficiency | Often more energy-efficient | Potentially less energy-efficient |
| Location | May have more limited or new community development | Greater variety of established neighborhoods |
Existing Home Market
The existing home market presents a unique set of considerations compared to the new construction market. Factors like age, previous ownership, and existing conditions play a crucial role in determining value and pricing. Understanding these nuances is essential for both buyers and sellers navigating this segment of the real estate landscape.
Factors Influencing Existing Home Prices
Location remains a paramount factor in determining existing home values. Proximity to amenities, schools, and employment centers directly impacts desirability and price. The condition of the home itself is equally critical. Upgrades, repairs, and maintenance history all contribute to the overall value proposition. Size and layout, while important, are often weighed against the other factors, as well as current market trends.
The new housing market is buzzing, but what’s driving the demand? Perhaps it’s the burgeoning electric vehicle (EV) industry in Hefei, China, a city rapidly becoming a hub for innovation in the sector. China’s Hefei EV city economy is experiencing remarkable growth, which in turn could be influencing housing market trends. Ultimately, though, the fluctuating dynamics of the new and existing housing markets remain a complex mix of factors.
For example, a well-maintained, spacious home in a desirable neighborhood will generally command a higher price than a comparable home in a less desirable area or one with significant maintenance needs.
Types of Existing Homes
A variety of existing home types are available for purchase. Single-family homes remain the most common, offering individual living spaces. Condominiums and townhouses represent alternatives with shared amenities and potentially lower maintenance responsibilities. Each type presents its own set of benefits and drawbacks, affecting the overall cost and the level of ownership responsibilities.
Home Renovation Costs and Return on Investment
Renovation costs for existing homes can vary significantly depending on the scope of the project. Kitchen and bathroom upgrades are frequently undertaken and can represent a substantial investment. Knowing the potential return on investment (ROI) for specific renovations is crucial. For example, a well-executed kitchen remodel in a competitive market could recoup a substantial portion of the investment, while less strategic renovations might not yield a comparable return.
Researching local market trends and consulting with professionals is key to understanding potential ROI.
Financing Options for Existing Homes
Various financing options are available for purchasing existing homes, including mortgages. Different lenders offer varying interest rates, loan terms, and eligibility criteria. Understanding the specifics of each option is critical for making informed decisions. A fixed-rate mortgage provides predictability, while an adjustable-rate mortgage may offer lower initial rates but could change over time. The choice depends on individual financial situations and market expectations.
Condition and Maintenance Needs
Existing homes, by definition, have a history. This history can include previous repairs, maintenance, and potential deferred maintenance issues. New homes, on the other hand, typically offer the benefit of a warranty and a lack of deferred maintenance. Buyers of existing homes should be prepared for the possibility of unexpected repairs or maintenance tasks. This should be considered when evaluating the property’s overall condition and budget.
Common Repairs and Maintenance Tasks
| Repair/Maintenance Task | Description | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Roof Inspection | Checking for leaks, damage, and wear | Annually or as needed |
| Plumbing Checks | Inspecting pipes, fixtures, and water usage | Biannually or as needed |
| Electrical System Inspection | Checking for worn wiring, faulty outlets, and tripping breakers | Annually or as needed |
| HVAC Maintenance | Cleaning and servicing the heating, ventilation, and air conditioning system | Annually |
| Exterior Inspections | Inspecting siding, paint, gutters, and foundation | Annually or as needed |
This table provides a starting point for understanding common maintenance tasks. The frequency and extent of these tasks will depend on the specific home’s condition and location. Regular maintenance can prevent larger, more expensive problems down the line.
Market Trends and Forecasts
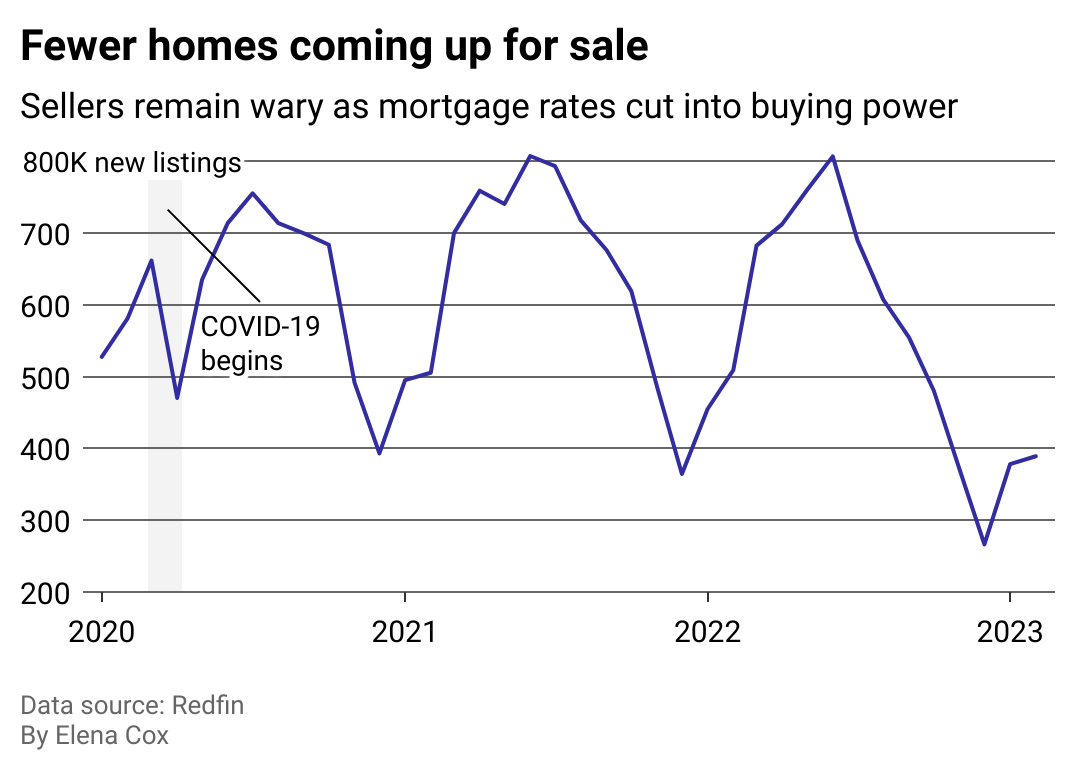
The housing market, a cornerstone of the economy, is constantly evolving. Understanding current trends and anticipating future directions is crucial for both buyers and sellers. This section delves into the dynamic nature of the new and existing home markets, examining the factors shaping their trajectory. We will explore potential economic impacts and offer a glimpse into the predicted price changes for the next two years.The interplay of interest rates, inflation, and consumer confidence significantly influences housing market dynamics.
Recent shifts in these factors have already been observed in market activity. Analyzing these influences will provide valuable insights into the potential future path of the market.
Current Market Trends
The current housing market displays a mix of contrasting trends in new and existing home sectors. Existing home sales have shown a slight deceleration, possibly indicating a cooling effect following a period of brisk activity. New home construction, however, has remained relatively stable, reflecting ongoing demand. These observations suggest a market adapting to shifting economic conditions.
Predicted Future Directions
Several factors point towards a potentially more moderate pace for both new and existing home sales in the coming years. Rising interest rates, while potentially impacting affordability, may also stabilize market growth, preventing a sudden surge or collapse. Consumer confidence, a crucial element in the market, is expected to fluctuate. Inflation, although currently a concern, is expected to moderate, influencing purchasing power and thus demand.
The housing market, with its new and existing homes, has been a hot topic lately. While things are generally stable, recent news about Chris Young’s charges being dropped has me thinking about the potential impact on the economy, and specifically how it might affect the market in the long run. Chris Young’s charges dropped could potentially shift consumer confidence, leading to either a surge or a lull in the demand for new and existing properties.
All in all, the housing market’s trajectory remains a fascinating area to watch.
Factors Influencing Future Trends
Several factors are poised to influence the housing market’s trajectory. Interest rates, as mentioned earlier, will continue to play a pivotal role. Supply chain disruptions, although less pronounced than in recent years, could still impact construction costs and availability. Government policies, such as changes in tax laws or incentives, could also shift market dynamics.
Potential Impacts of Economic Changes
Economic downturns often correlate with a slowdown in the housing market. Increased unemployment or decreased consumer spending can reduce demand and put downward pressure on prices. Conversely, economic growth typically fuels demand and can lead to price increases. The current economic climate, with its combination of factors, suggests a market adapting to a new equilibrium.
Predicted Price Changes (2-Year Forecast)
| Market Segment | Predicted Price Change (Year 1) | Predicted Price Change (Year 2) |
|---|---|---|
| New Homes | +2% to +5% | +1% to +4% |
| Existing Homes | +1% to +4% | 0% to +3% |
Note: These figures are estimates and should not be considered financial advice. Market fluctuations can significantly alter these predictions.
Buyer and Seller Perspectives
Navigating the housing market, whether buying a new or existing home, requires understanding the motivations, strategies, and challenges faced by both buyers and sellers. This section delves into the nuances of each side, exploring their perspectives and highlighting key factors influencing transactions. From the excitement of a new home purchase to the meticulous planning of a seller’s strategy, this analysis will reveal the intricacies of the market.
Motivations of Buyers
Buyers in both new and existing home markets are driven by various factors. For new homes, the allure of modern amenities, customizability, and often, a sense of starting fresh are key motivators. Existing home buyers, conversely, are frequently drawn to established neighborhoods, proximity to schools and amenities, and often, lower price points. The desirability of a particular location or lifestyle plays a significant role in both markets.
Potential buyers meticulously research neighborhoods, schools, and community features, weighing them against their budget and personal preferences.
Strategies of Sellers
Sellers in both markets employ different strategies. New home builders often focus on showcasing the unique features and benefits of their models. They might emphasize the quality of construction, the latest energy-efficient technologies, or the home’s location relative to amenities. Existing home sellers often leverage the appeal of established neighborhoods, the home’s condition, and the current market value.
Marketing strategies are crucial for successful sales in both scenarios.
Negotiation Processes
The negotiation processes in new and existing home markets differ significantly. New home purchases often involve less negotiation over price, as the agreed-upon price is usually set during the initial sales process. Existing home sales, however, typically involve more negotiation. Understanding market values, competing offers, and the seller’s willingness to compromise are critical components of successful negotiation in the existing home market.
Challenges and Opportunities
Buyers and sellers face diverse challenges and opportunities in both markets. Buyers in a competitive market might find themselves outbid or face difficulty securing financing. Sellers might encounter challenges in pricing their homes accurately, or attracting sufficient buyer interest. Opportunities, however, abound. The new home market offers buyers the potential to design and customize a home, while existing home buyers benefit from established infrastructure and community connections.
Successful sellers in either market must effectively showcase their property’s strengths and appeal to a broad range of buyers.
Successful Marketing Strategies
Effective marketing strategies are paramount for both new and existing home sellers. New home builders often utilize virtual tours, showcasing the community amenities, and highlighting model homes. Existing home sellers can leverage professional photography, detailed property descriptions, and targeted online advertising to reach potential buyers. Utilizing social media, open houses, and staging can significantly impact the success of a sale in either market.
Example of Successful Marketing Strategies
A new home builder, for example, might use virtual reality tours to showcase the homes’ designs, floor plans, and the neighborhood’s amenities. They might offer incentives, such as closing costs assistance or extended warranties, to attract buyers. An existing home seller might use professional photography, highlighting the home’s features, such as a spacious backyard or updated kitchen, to attract interest.
Table of Negotiation Tactics and Strategies
| Characteristic | New Home Market | Existing Home Market |
|---|---|---|
| Pricing | Generally less negotiable; price often set during initial sales process. | Highly negotiable; market value, competing offers, and seller’s willingness to compromise are critical. |
| Negotiation Tactics | Focus on incentives, upgrades, and closing cost assistance. | Negotiating price, closing date, and contingencies. |
| Contingencies | May include appraisal, financing, or inspection contingencies. | May include appraisal, financing, inspection, or home sale contingencies. |
| Market Conditions | Often influenced by builder inventory and pricing. | Driven by overall market conditions, buyer demand, and competing properties. |
Local Market Analysis: Housing Market New Existing
Understanding the nuances of specific regional housing markets is crucial for navigating the complexities of real estate. Local factors significantly impact pricing, inventory, and overall market health. This section delves into the unique characteristics of different regions, exploring the interplay of economic forces, demographic shifts, and regulatory environments that shape the local housing landscape.Regional variations in housing markets are influenced by a complex interplay of economic, social, and environmental factors.
These factors range from local job markets and wage levels to the availability of amenities and transportation options, and even the prevalence of natural disasters.
Factors Affecting Housing Markets in Specific Regions
Local economic conditions, including employment rates, income levels, and industry trends, are fundamental drivers of regional housing markets. Strong job growth in a particular sector can lead to increased demand and higher home prices, while economic downturns can suppress demand and cause price reductions. For example, a region with a burgeoning tech sector often sees a corresponding rise in housing prices as young professionals flock to the area.
Unique Characteristics of Housing Markets in Different Regions
Regional differences in housing preferences, demographics, and available amenities also significantly influence market dynamics. Coastal areas, for instance, often command higher prices due to their desirability and limited land availability. Conversely, rural areas might experience slower price growth but offer more affordable options for homebuyers. The availability of schools, parks, and other amenities also impacts demand and influences the pricing of properties in those areas.
Consider a suburban area with top-rated schools, where families are willing to pay a premium for that educational advantage.
Local Economic Factors Influencing the Housing Market, Housing market new existing
Local economic factors, like unemployment rates, interest rates, and the prevalence of local industries, are essential to understanding regional housing market trends. For example, a region heavily reliant on a single industry (e.g., agriculture) may see fluctuations in home prices corresponding to the ups and downs of that industry. The presence of government incentives, such as tax breaks for first-time homebuyers, also plays a role.
Areas with robust industrial sectors tend to experience more stable housing markets.
Comparison of Housing Market Trends Between Different Regions
Comparing trends across regions reveals valuable insights. A region experiencing consistent job growth might see steady price increases, while another with stagnant or declining employment could face slower price appreciation or even price corrections. For instance, a comparison of the housing markets in California’s Silicon Valley versus a rural area in the Midwest might show significant differences in price trends and buyer demographics.
Housing Availability in Different Regions
Housing availability is a critical factor in any regional market analysis. Supply and demand dynamics heavily influence prices and market competitiveness. Areas with limited land availability and stringent zoning regulations often have lower housing inventory, driving up prices. A shortage of affordable housing options in a densely populated urban area can create significant pressure on the housing market.
Areas with abundant land and looser regulations can have more readily available housing, often with slower price growth.
Housing Inventory Levels and Pricing Trends
A table summarizing housing inventory and pricing trends for selected cities can provide a clear visual representation of market conditions.
| City | Housing Inventory (Units) | Average Home Price (USD) | Year-over-Year Price Change (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| San Francisco | 1,500 | $2,500,000 | +5% |
| Austin | 2,800 | $500,000 | +8% |
| Denver | 3,200 | $550,000 | +4% |
| Kansas City | 4,500 | $250,000 | +2% |
*Note: Data in the table is illustrative and based on hypothetical figures. Actual figures should be obtained from reliable real estate market analysis reports.*
Impact of Economic Factors
The housing market is a complex ecosystem intricately intertwined with the broader economy. Understanding the interplay between economic factors and housing market performance is crucial for both buyers and sellers. From interest rate fluctuations to government policies, numerous forces shape the trajectory of home sales and values. This section delves into the key economic influences impacting the new and existing home markets.
The new and existing housing market is always a hot topic, with fluctuations depending on various factors. But, President Biden’s push for a decade of infrastructure improvements, as detailed in taking on trump biden promotes infrastructure decade in wisconsin , could potentially impact the market in interesting ways. Ultimately, the long-term effect on new and existing home sales remains to be seen.
Interest Rates and Home Sales
Interest rates directly impact the affordability of mortgages. Lower interest rates typically lead to increased borrowing power, stimulating demand for both new and existing homes. Conversely, higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive, reducing affordability and potentially dampening sales. For example, historically low rates in the early 2020s spurred significant housing market activity, while recent increases have cooled the market.
Inflation and Housing Prices
Inflation, the sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services, often correlates with housing price appreciation. When inflation rises, the purchasing power of money decreases, potentially leading to higher demand for housing as an asset class. However, rapid inflation can also erode affordability and create uncertainty in the market. Examples from recent years show how rising inflation has influenced home prices, sometimes leading to significant price increases and other times to market stagnation.
Unemployment Rates and the Housing Market
Unemployment rates significantly affect housing market activity. A high unemployment rate generally translates to lower consumer confidence and reduced purchasing power, impacting both new and existing home sales. During periods of high unemployment, there’s less disposable income available for major purchases like homes, leading to decreased demand and potentially a downturn in the market.
Government Policies and Housing Markets
Government policies, such as tax incentives, zoning regulations, and mortgage programs, have a profound influence on the housing market. Tax incentives can encourage homeownership, while regulations can impact supply and affordability. For instance, government programs that support first-time homebuyers or provide subsidies for affordable housing can stimulate the market, while stricter lending requirements can have the opposite effect.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Housing Market Fluctuations
Supply chain disruptions, such as those seen during the COVID-19 pandemic, can significantly affect the housing market. These disruptions impact the availability of building materials and labor, increasing construction costs and potentially lengthening the time it takes to build new homes. This can affect both new home sales and the overall price dynamics of the market.
Correlation Between Economic Factors and Housing Market Performance
| Economic Factor | Impact on Housing Market Performance |
|---|---|
| Interest Rates | Lower rates increase affordability, boosting demand. Higher rates reduce affordability, decreasing demand. |
| Inflation | Rising inflation can increase demand for housing as an asset, but rapid inflation can also erode affordability. |
| Unemployment Rates | High unemployment reduces purchasing power, impacting demand. |
| Government Policies | Incentives stimulate market; regulations affect supply and affordability. |
| Supply Chain Disruptions | Disruptions increase construction costs and time, potentially impacting new home sales and overall price dynamics. |
End of Discussion
In conclusion, the housing market new existing presents a multifaceted picture. While new homes offer modern features and construction timelines, existing homes provide established value and potentially lower upfront costs. Ultimately, the best choice depends on individual circumstances and priorities. The economic forces at play continue to reshape the market, so staying informed is crucial. Whether you’re a buyer or seller, understanding the intricacies of each market is essential for success.
FAQ Corner
What are the common repairs and maintenance tasks for existing homes?
Common repairs and maintenance tasks for existing homes can vary greatly depending on the age, condition, and type of home. These can include plumbing repairs, roof maintenance, HVAC system checks, and general home upkeep.
How do interest rates affect new and existing home sales?
Interest rates significantly impact both new and existing home sales. Higher interest rates typically cool the market as borrowing costs increase. Conversely, lower rates often boost demand.
What are the typical financing options for purchasing new homes?
Financing options for new homes often include traditional mortgages, FHA loans, and VA loans. Additionally, some builders may offer in-house financing options.
What are the key differences in buyer demographics for new and existing homes?
Demographics of buyers differ. First-time buyers often gravitate toward existing homes, while those seeking newer construction and amenities are more likely to consider new homes.

