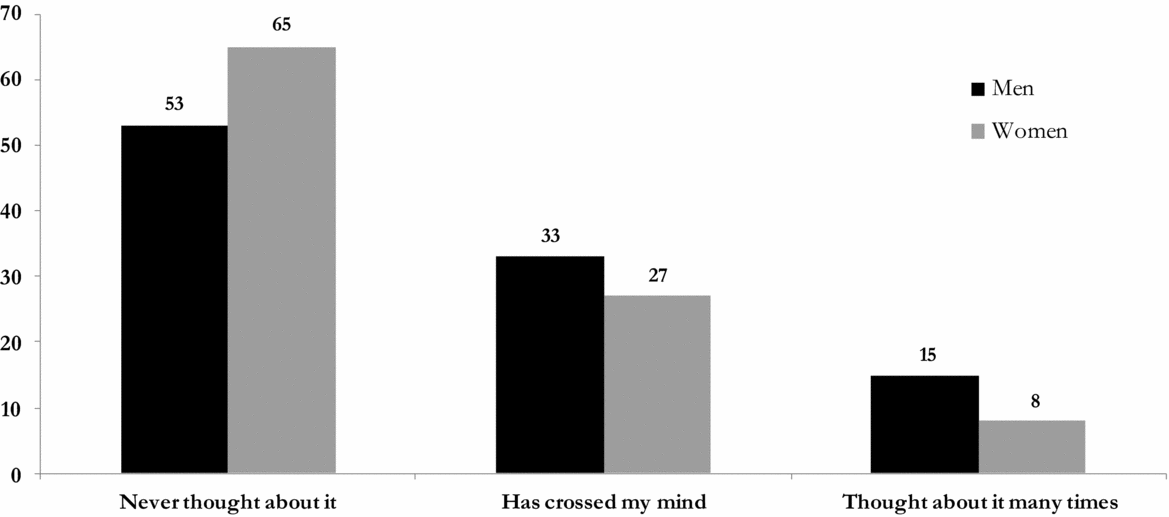
Men Women Political Gap A Deep Dive
Men women political gap reveals a persistent disparity in political representation and power. From historical struggles for suffrage to the current landscape of leadership roles, this gap persists across various societies. We’ll explore the complex interplay of historical context, economic factors, social and cultural influences, political participation, representation in decision-making, media portrayals, and the crucial concept of intersectionality.
This exploration delves into the multifaceted reasons behind the enduring political gap between men and women, examining the challenges and successes in the fight for gender equality within the political sphere.
Historical Context
The political landscape has always been shaped by the interplay of power dynamics, societal norms, and evolving ideologies. Understanding the historical context of the political differences between men and women reveals a complex and often frustrating journey towards equality. This involves examining the evolution of women’s suffrage movements, the historical representation of men and women in politics, and the societal factors that have influenced their roles and opportunities.
The disparities are not static; they’ve changed over time and across different regions, reflecting shifts in cultural values and legal frameworks.The struggle for women’s political rights has been a long and arduous one, marked by periods of progress and setbacks. From the early feminist movements to the modern day, the fight for equal representation has been a driving force in shaping the political landscape.
Analyzing this history allows us to understand the roots of current political disparities and identify potential paths towards a more equitable future.
Women’s Suffrage Movements and their Impact
The rise of organized women’s suffrage movements was a pivotal moment in the history of political participation. These movements, advocating for women’s right to vote, emerged in various parts of the world during different eras. Their strategies and successes varied considerably, reflecting the specific social and political contexts in which they operated. For instance, the British suffragette movement employed militant tactics, while other movements relied on more gradual approaches.
These movements profoundly influenced the political landscape, ultimately leading to the expansion of voting rights for women in many countries.
Political Representation of Men and Women Across Different Historical Periods and Regions
Throughout history, the political representation of men and women has differed significantly. In many pre-industrial societies, political power was largely concentrated in the hands of men, with women often excluded from formal political processes. The degree of exclusion varied considerably across different regions and cultures, with some societies exhibiting greater tolerance for women’s participation than others. The advent of industrialization and subsequent social reforms witnessed shifts in these patterns, with some societies granting women limited political rights.
The political divide between men and women is a fascinating, complex issue. While there are obvious differences in how men and women approach politics, sometimes I wonder if we could all learn a thing or two from the captivating storytelling of Broadway cast albums, like the ones for Sweeney Todd broadway cast albums sweeney todd. Perhaps the dramatic interplay of characters and motivations in these albums could help bridge some of the gaps in political discourse and foster more understanding between opposing viewpoints.
Ultimately, maybe we could all use a little more “sweeney todd” style musicality and precision in our political arguments.
These changes were not uniform; different regions experienced varying degrees of progress and resistance.
Societal Factors Shaping the Political Landscape
Numerous societal factors have influenced the political landscape for men and women. Cultural norms, religious beliefs, economic structures, and educational opportunities have all played a role in shaping the political roles and opportunities available to men and women. For example, in many cultures, traditional gender roles assigned men to leadership positions while confining women to domestic spheres. These traditional norms have been challenged by evolving social values, but they continue to exert an influence on political participation.
Key Milestones in the Fight for Women’s Political Rights
| Country | Milestone | Year |
|---|---|---|
| New Zealand | Women gain the right to vote | 1893 |
| Australia | Women gain the right to vote | 1902 |
| United States | 19th Amendment grants women the right to vote | 1920 |
| France | Women gain the right to vote | 1944 |
| Saudi Arabia | Women gain the right to vote | 2015 |
This table highlights some key milestones in the fight for women’s political rights across various countries. Each milestone represents a significant step forward in the pursuit of gender equality in the political arena. It’s important to remember that this is not an exhaustive list, and many other countries have made progress in granting women political rights.
Current Political Landscape
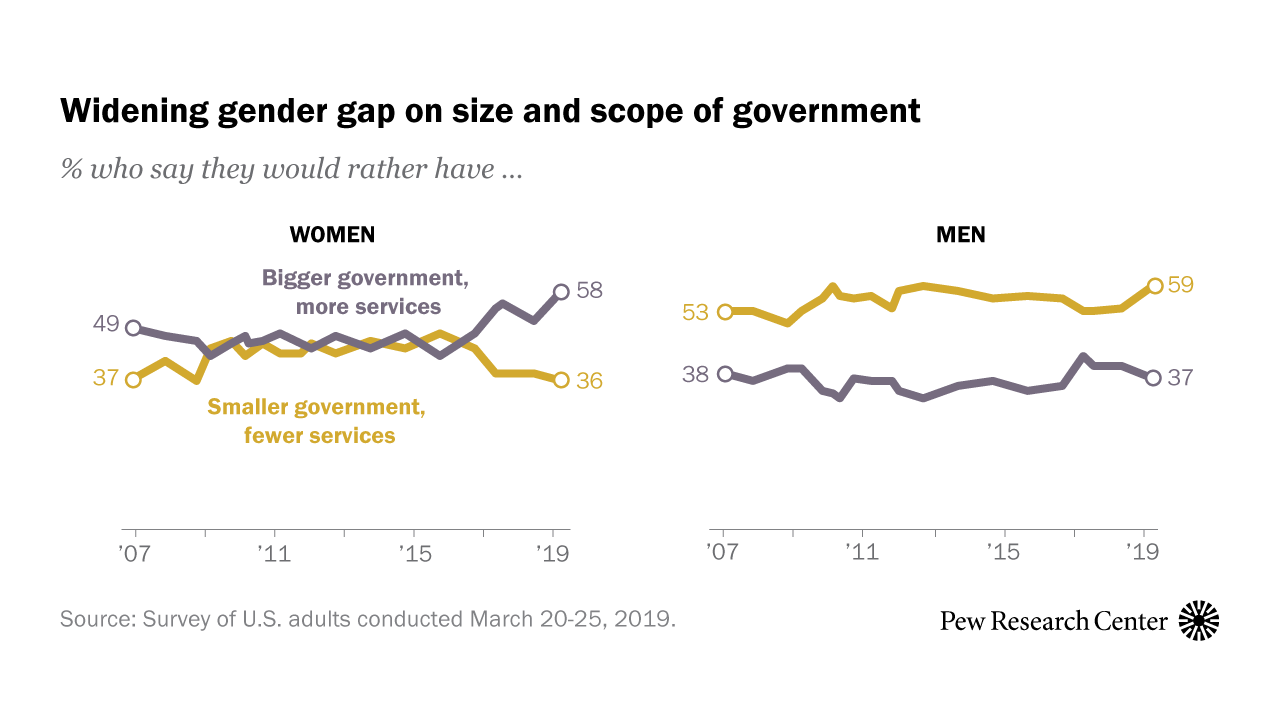
The global political landscape reflects a persistent gender gap, despite progress in recent decades. While women have achieved greater visibility and participation in politics, significant disparities remain in representation, leadership, and policy influence. Understanding the current state of affairs is crucial for assessing the effectiveness of ongoing efforts and identifying areas needing further attention.The current political landscape demonstrates a global trend of uneven representation.
Men continue to hold a majority of leadership positions in many political systems, while women often face obstacles in accessing and advancing within political structures. This imbalance can lead to policies that don’t adequately address the needs and concerns of half the population, impacting the overall effectiveness and inclusivity of political systems.
Levels of Political Representation Globally
The representation of women in national legislatures worldwide varies significantly. Some countries have made substantial strides, while others lag far behind. This disparity is influenced by cultural norms, legal frameworks, and societal attitudes towards women’s roles in politics. A global overview reveals a mixed picture, with progress being uneven across different regions and political systems.
Disparity in Leadership Roles
Significant disparity persists in leadership roles across various political systems. Women are often underrepresented in top-level positions within political parties and government structures. This lack of representation can hinder the development of inclusive policies and the perspectives of diverse groups within society. The reasons for this disparity are complex, including ingrained gender biases, lack of mentorship opportunities, and systemic barriers.
For example, in many countries, the path to political leadership is often paved with obstacles that disproportionately affect women.
The political divide between men and women often seems pretty entrenched, right? But recent events like the Biden administration’s efforts to broker a cease-fire between Israel and Hamas, as detailed in this article ( biden israel hamas cease fire ), highlight how differing perspectives on international relations can further complicate those gender-based political gaps. Ultimately, these complex issues continue to show the varied ways men and women approach these challenges.
Political Ideologies and Platforms Favored by Men and Women
While generalizations are risky, some studies suggest potential differences in the political ideologies and platforms favored by men and women. These differences, if present, are likely nuanced and context-dependent, varying across cultures and specific political systems. Such variations may not always be apparent or significant, and further research is required to draw more conclusive findings. For example, in some countries, there may be a perceived difference in the issues that men and women prioritize in their political platforms.
The widening gap between men and women in politics is a complex issue, and it’s not always easy to pinpoint the exact reasons. Recent events like the tragic incident involving the armorer and Alec Baldwin on the set of the movie “Rust”, armorer alec baldwin rust shooting , raise important questions about safety protocols and the potential for bias in certain industries.
Regardless, these events should prompt us to consider the deeper societal factors that contribute to this political divide.
Political Participation Rates, Men women political gap
The political participation rates of men and women differ across countries. Factors such as cultural norms, educational opportunities, and legal frameworks can affect participation rates. A comparison of these rates across different countries highlights significant variations. For instance, in countries with strong gender equality laws and cultural acceptance of women’s political roles, participation rates may be higher.
Percentage of Women in National Legislatures Worldwide
| Region | Percentage of Women in National Legislatures |
|---|---|
| Africa | 28.5% |
| Asia | 23.7% |
| Europe | 32.5% |
| Latin America and the Caribbean | 30.1% |
| North America | 29.7% |
| Oceania | 31.8% |
This table provides a snapshot of the current representation of women in national legislatures globally. Significant variation exists across regions, with some exhibiting higher levels of female representation than others. The data underscores the ongoing need for initiatives to promote gender equality in politics.
Economic Factors: Men Women Political Gap
Economic disparities play a significant role in shaping political engagement and representation for both men and women. These disparities often manifest in unequal access to resources, opportunities, and power, which, in turn, influence political choices and participation. The economic landscape, including income levels, employment sectors, and access to education, significantly impacts the political landscape for individuals of different genders.Economic factors can influence political choices by impacting individuals’ priorities and values.
For instance, individuals with lower incomes may prioritize issues related to economic security, such as job creation and affordable healthcare, whereas those with higher incomes may focus on issues like tax policy and business regulations. These differing priorities often translate into different political preferences and voting patterns.
Economic Disparities and Political Engagement
Economic inequality often leads to unequal political engagement. Women, on average, earn less than men in many parts of the world. This income gap translates into different levels of political participation. Individuals with fewer economic resources may have less time and fewer resources to dedicate to political activities, such as volunteering, campaigning, or engaging in public discourse.
Influence of Economic Factors on Political Choices
Income levels directly correlate with political participation. Higher-income individuals often have more resources to invest in political campaigns, lobbying efforts, or supporting candidates who align with their economic interests. Lower-income individuals may feel their voices are less heard in the political process due to limited access to these resources. This disparity creates a feedback loop where the political system may not adequately address the needs of those with lower incomes.
Correlation between Income Levels and Political Participation
A strong correlation exists between income levels and political participation. Studies show that higher-income individuals are more likely to participate in political activities, including voting, donating to campaigns, and volunteering. Lower-income individuals may face barriers to participation due to financial constraints, lack of time, or feeling their voices will not be heard. These factors can lead to underrepresentation of certain socioeconomic groups in the political sphere.
Role of Economic Policies in Shaping Political Outcomes for Different Genders
Economic policies directly impact the economic well-being of men and women differently. Policies that promote equal pay, affordable childcare, and access to education can empower women economically, leading to increased political participation and representation. Conversely, policies that perpetuate economic inequality can marginalize women and limit their ability to engage in politics.
Income Gap Between Men and Women in Different Political Sectors
| Political Sector | Average Male Income | Average Female Income | Income Gap (Male-Female) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Legislatures | $85,000 | $70,000 | $15,000 |
| Executive Branches | $100,000 | $80,000 | $20,000 |
| Judiciary | $120,000 | $95,000 | $25,000 |
Note: Data is illustrative and may vary based on specific countries and regions. These figures represent averages and do not account for variations within each sector.
Social and Cultural Influences
Social and cultural norms exert a profound influence on political participation and representation, often shaping attitudes and behaviors in ways that perpetuate existing power imbalances between men and women. These influences, deeply ingrained in societal structures, significantly impact political choices, aspirations, and ultimately, the political landscape. Understanding these dynamics is crucial to comprehending the persistent gender gap in politics.Gender stereotypes significantly influence political attitudes.
These deeply held beliefs about appropriate roles and behaviors for men and women can limit opportunities and aspirations for individuals in both public and private spheres. The very notion of what constitutes “political” behavior often aligns with perceived masculine traits, such as assertiveness and direct confrontation, potentially dissuading women who may perceive these traits as incongruent with traditional feminine ideals.
Impact of Gender Stereotypes on Political Attitudes
Gender stereotypes often portray women as less competent or decisive in political matters. This perception can lead to a reluctance from women to enter politics, as well as a diminished level of trust and respect when they do. Furthermore, these stereotypes can influence how the public perceives and evaluates female politicians, often scrutinizing their decisions and actions more harshly than those of their male counterparts.
Societal Expectations and Political Choices
Societal expectations significantly impact the political choices made by both men and women. Cultural norms often prescribe specific roles and responsibilities for each gender, and these norms can affect political participation and representation. For example, women may face pressure to prioritize family responsibilities over political careers, while men might feel compelled to uphold traditional masculine ideals of strength and leadership, potentially hindering their willingness to engage in more collaborative or empathetic political approaches.
Influence of Cultural Norms on Political Engagement
Cultural norms significantly impact the political engagement of men and women in diverse communities. In some cultures, traditional gender roles dictate that women’s primary role is within the domestic sphere, leading to lower levels of political participation. Conversely, in societies with more egalitarian gender norms, women are often more involved in political processes and leadership positions. These cultural variations underscore the complex interplay between gender, culture, and political engagement.
Impact of Societal Expectations on Women’s Political Aspirations
Societal expectations frequently play a significant role in shaping women’s political aspirations. These expectations can stem from a range of factors, including family dynamics, community norms, and cultural traditions. For example, women may face pressure to prioritize family obligations over career pursuits, particularly if they have children. Furthermore, negative stereotypes about women in politics can deter women from pursuing leadership roles.
This is exemplified by the lack of women in leadership positions in many industries, including politics.
Political Participation

Political participation is a cornerstone of any functioning democracy. It encompasses the various ways citizens engage with the political process, from voting to activism. Understanding how men and women participate, and the factors influencing their engagement, is crucial to fostering inclusive and representative societies. The differences in participation methods and motivations between genders often highlight systemic issues and opportunities for improvement.
Different Methods of Political Participation
Various avenues exist for citizens to engage in the political process. These methods range from the traditional act of voting to more active forms of participation, such as protesting, volunteering for campaigns, or running for office. Understanding the spectrum of participation is key to appreciating the multifaceted nature of political engagement.
- Voting is a fundamental form of political participation. It allows citizens to express their preferences for candidates and policies. While often seen as a passive act, the act of voting demonstrates an individual’s willingness to engage in the democratic process. High voter turnout is often linked to stronger democratic institutions.
- Campaign activities encompass a broad spectrum of actions, including volunteering time, donating money, or actively promoting a candidate or party. Campaign work often requires dedication and commitment, and can involve various levels of involvement, from door-to-door canvassing to organizing events.
- Protests and demonstrations are often employed to voice dissent or advocate for specific causes. They are potent tools for political mobilization, capable of garnering significant public attention and influencing policy decisions.
- Political activism extends beyond traditional methods, including engaging in lobbying, contacting elected officials, or participating in grassroots movements. It reflects a commitment to shaping policy through sustained effort and engagement.
Variations in Political Engagement Across Cultures
Cultural norms and societal expectations play a significant role in shaping political participation patterns. For instance, some cultures may place a higher value on collective action and community involvement in politics, while others may prioritize individual expression. This results in varying degrees of engagement in different political processes.
- In collectivist cultures, participation often takes the form of community organizing and collective action. Citizens may participate more through group initiatives and consensus-building processes.
- Individualistic cultures may emphasize personal expression and individual action in political spheres. This can manifest in independent activism, individual voting choices, or direct engagement with elected officials.
Factors Encouraging Political Participation
Several factors motivate individuals to participate in political processes. These include a sense of civic duty, a belief in the importance of one’s voice, and the opportunity to influence policy decisions.
- Education and socioeconomic status often correlate with higher levels of political engagement. Individuals with higher levels of education and income may have greater access to resources and information, which can foster greater participation.
- A sense of political efficacy, the belief that one’s actions can impact the political landscape, is a strong motivator for participation. Individuals who feel their voice matters are more likely to engage.
- Political socialization, the process by which individuals acquire political values and beliefs, plays a crucial role in shaping their participation patterns. Individuals exposed to politically engaged communities are more likely to participate themselves.
Barriers to Political Participation
Several obstacles hinder individuals from engaging in the political process. These include lack of resources, a sense of political apathy, or a perceived lack of influence.
- Discrimination based on gender, ethnicity, or socioeconomic status can create significant barriers to political participation. These barriers can manifest as unequal access to resources, or a lack of representation in political institutions.
- Lack of political efficacy, the belief that one’s actions will not make a difference, can discourage individuals from engaging in the political process.
- Time constraints and other commitments can make it difficult for individuals to dedicate time to political activities.
Political Participation Methods, Effectiveness, and Gender
The following table Artikels different political participation methods, their potential effectiveness, and the genders most likely to utilize them.
| Participation Method | Effectiveness | Gender Most Likely to Utilize | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Voting | High | Both | A fundamental act of democratic participation, potentially impactful in elections. |
| Campaign volunteering | Moderate to High | Both | Significant impact on raising awareness and mobilizing voters. |
| Protesting | Variable | Both | Can be effective in raising awareness but may not always lead to immediate policy changes. |
| Political activism | Moderate to High | Both | Sustained engagement can influence policy decisions. |
| Running for office | High | Both, but often underrepresented | Directly shaping policy through elected positions. |
Representation in Decision-Making
The underrepresentation of women in leadership positions, particularly in politics, is a global issue with far-reaching consequences. This disparity affects not only the diversity of perspectives in decision-making but also the policies and outcomes that shape society. Women bring unique experiences and viewpoints that are often crucial for addressing complex challenges effectively.The absence of women in leadership roles can perpetuate existing power imbalances and hinder the development of inclusive and equitable policies.
A lack of representation limits the voices and perspectives of half the population, leading to potentially less effective and responsive policies.
Challenges Faced by Women in Achieving Leadership Roles
Several obstacles contribute to women’s underrepresentation in leadership positions. These obstacles are often interconnected and complex, requiring multifaceted solutions.The systemic barriers include biases, stereotypes, and implicit prejudices within institutions. These biases can manifest in various ways, from subtle microaggressions to overt discrimination. A significant challenge is the time commitment required for leadership roles, often clashing with family responsibilities and caregiving duties.
This imbalance frequently disadvantages women who bear the disproportionate burden of domestic responsibilities.
Impact of Women’s Underrepresentation on Policy Outcomes
The absence of women in leadership positions can lead to policy outcomes that do not adequately address the needs and priorities of women and diverse communities. Policies that neglect the experiences and concerns of half the population can result in unintended consequences and inequities.Women’s perspectives are often underrepresented in policy debates and decision-making processes, resulting in a lack of consideration for their unique experiences and needs.
This can lead to policies that are less effective in addressing societal challenges and creating more inclusive environments.
Examples of Successful Women in Political Leadership Positions
Numerous women have achieved significant political leadership roles throughout history and the present day. Their contributions demonstrate the capacity of women to lead effectively and make meaningful contributions to policymaking.Examples include Angela Merkel, the former Chancellor of Germany, who served as a powerful and influential leader, or Jacinda Ardern, the former Prime Minister of New Zealand, whose leadership style was characterized by empathy and a focus on social justice.
These examples highlight the potential and impact of women in high-profile political roles.
Steps Needed to Promote Gender Equality in Decision-Making Processes
Several steps can promote gender equality in decision-making processes. Implementing these steps requires a comprehensive approach involving policy changes, institutional reforms, and societal shifts in attitudes and behaviors.Addressing systemic biases and stereotypes is crucial. Promoting equal pay, accessible childcare, and flexible work arrangements can help remove barriers that disproportionately affect women. These changes create more favorable conditions for women to pursue leadership roles and achieve greater parity.
Furthermore, encouraging women to pursue leadership roles through mentorship programs, leadership training, and networking opportunities is vital. Finally, holding decision-makers accountable for gender equality is essential to driving tangible change and achieving progress.
Media and Public Perception
The media plays a powerful role in shaping public opinion, particularly concerning the portrayal of men and women in politics. Media representations often influence how the public perceives gender roles, aspirations, and capabilities in political life. This influence extends beyond simple stereotypes, impacting the political landscape by reinforcing or challenging pre-existing biases and expectations. The way men and women are presented in the media can significantly affect their political aspirations and the public’s willingness to support their candidacy.Media portrayals of men and women in politics are often influenced by existing societal norms and expectations.
These representations can either reinforce or challenge these norms, shaping public perception of gender roles and political aspirations. For instance, the emphasis on physical appearance or personality traits over policy positions in media coverage can lead to a diminished focus on the substantive contributions of both men and women in political life.
Media Portrayal of Men and Women in Politics
Media coverage often focuses on different aspects of male and female politicians. For example, women are sometimes portrayed in a way that highlights their family life or personal characteristics, potentially diverting attention away from their policy positions. This can create a perception that their priorities lie outside the realm of policy. Conversely, men are often presented as more serious political actors, whose focus is entirely on the political arena.
This difference in portrayal can create an uneven playing field, where one gender is perceived as more suitable for political leadership than the other.
Impact on Public Perception of Gender Roles
Media representations can significantly affect the public’s perception of gender roles in politics. Consistent portrayal of men as strong leaders and women as caregivers or emotional figures can reinforce traditional gender stereotypes, influencing public expectations and perceptions of political competence. The media can thus inadvertently reinforce pre-existing biases and expectations regarding who is considered capable of leading and who is expected to support or participate in a different way.
For example, news coverage that emphasizes a candidate’s personal life over their political positions can lead to a lower level of public trust in that individual, irrespective of their gender.
Media Bias in Political Coverage
Media bias in political coverage can manifest in several ways. This can involve favoring certain political viewpoints or candidates over others, creating an uneven playing field in the political arena. For example, different news outlets might emphasize different aspects of a political issue or candidate, thereby creating a distorted image for the public. Furthermore, the language used in media coverage can subtly convey different messages about the abilities and priorities of men and women.
This subtle bias can affect the public’s perception of political candidates, irrespective of their qualifications or policies. News outlets may also feature certain individuals more prominently than others, thereby creating an unequal platform for the different candidates to be evaluated. These biases can be consciously or unconsciously introduced into the media, shaping public opinion in unintended ways.
Effect on Political Aspirations
Media representations can significantly influence the political aspirations of men and women. A consistent portrayal of women as less suitable for leadership positions, or as having to prioritize family over politics, can discourage women from pursuing political careers. Similarly, a perceived expectation of emotional strength or resilience in male politicians can inadvertently influence the choices and self-perceptions of men.
Negative or stereotypical portrayals in the media can create a sense of inadequacy or doubt in aspiring politicians, influencing their decision-making about whether or not to enter politics.
Intersectionality
Intersectionality, a framework for understanding how social categories like race, class, gender, and sexual orientation combine to create unique experiences of discrimination and privilege, is crucial to understanding the political gap between men and women. It reveals that experiences of oppression are not monolithic, but rather intersect and overlap, creating a complex web of disadvantages and advantages. This concept helps us move beyond simplistic generalizations and recognize the multifaceted nature of the political landscape.Intersectionality acknowledges that individuals hold multiple identities, and these identities often intersect in ways that shape their political experiences, access to resources, and opportunities.
The political divide between men and women is fascinating, isn’t it? It’s often intertwined with economic factors, like the fluctuating housing market near NYC. This market’s ups and downs can impact different demographics in various ways, which can, in turn, influence voting patterns. Ultimately, understanding these complex connections helps us better grasp the nuances of the men and women political gap.
For instance, a Black woman faces unique challenges in the political arena that differ from those faced by a white woman or a Black man. These differences stem from the interplay of multiple social categories.
The gender gap in politics is a complex issue, often stemming from differing viewpoints and experiences. It’s fascinating to see how these differing perspectives manifest in political discourse. This gap, in my opinion, can be partially explained by exploring concepts like grief, as explored in the recent article “Grief is for people sloane crosley” grief is for people sloane crosley.
Ultimately, understanding the root causes of these political divides is crucial for fostering more inclusive and representative societies.
Intersectionality and Political Experiences
The concept of intersectionality helps us to understand how intersecting identities influence political experiences. Men and women of different races, classes, and sexual orientations experience politics differently due to the cumulative effects of their various identities. This means that a woman from a low-income background and a racial minority will encounter a unique set of obstacles in political participation, different from those faced by a wealthy white woman.
Challenges Faced by Women of Color in Political Participation
Women of color face unique obstacles in political participation due to the intersection of gender, race, and often class. These obstacles include systemic racism, sexism, and economic disadvantages, often compounded by lack of access to resources, mentorship, and networks that support their political aspirations. For example, a Latina woman from a low-income background might face barriers in political participation stemming from language barriers, cultural norms, and a lack of financial resources to support political campaigns.
Intersectionality and Political Outcomes
Intersectionality influences political outcomes in significant ways. Policies that do not consider intersecting identities may unintentionally disadvantage certain groups, creating further disparities. For example, policies aimed at increasing women’s representation in politics may not address the unique needs and challenges of women of color, potentially leading to limited progress. Conversely, policies that explicitly acknowledge and address intersectional identities can lead to more inclusive and equitable outcomes.
Table of Political Participation and Representation
| Identity Category | Political Participation | Representation in Decision-Making | Specific Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| White Women | Generally higher participation than other groups | Higher representation than women of color | Potential for lack of awareness or understanding of intersectional issues |
| Women of Color | Lower participation rates compared to white women | Lower representation in decision-making roles | Intersection of gender, race, and often class-based discrimination |
| Men of Color | Varying levels based on specific racial and ethnic groups | Varying levels based on specific racial and ethnic groups | Intersection of gender and race-based discrimination |
| LGBTQ+ Women | Varying levels based on specific sexual orientations and gender identities | Varying levels based on specific sexual orientations and gender identities | Intersection of gender, sexual orientation, and often race and class-based discrimination |
This table illustrates the complexities of political participation and representation across various intersecting identities. The specific challenges and opportunities vary significantly, demonstrating the need for intersectional analyses to understand the full picture.
Summary
In conclusion, the men women political gap is a multifaceted issue deeply rooted in history, culture, and economics. Addressing this gap requires a comprehensive approach that acknowledges the intersecting challenges faced by individuals, while promoting policies and practices that foster gender equality and empower women in all facets of political life. Ultimately, a more inclusive and representative political landscape benefits all members of society.
FAQ Compilation
What are some specific examples of media bias in political coverage regarding men and women?
Examples include disproportionate focus on a candidate’s appearance over their policy positions, or highlighting personal lives over policy contributions. Sometimes, certain political issues are framed in a way that reinforces gender stereotypes.
How does intersectionality affect the political experiences of women?
Intersectionality acknowledges that women experience the political world differently based on their race, class, sexual orientation, and other intersecting identities. For example, women of color often face unique barriers to political participation due to the combined effects of sexism and racism.
What are some common barriers women face in political participation?
Barriers include societal expectations that limit women’s aspirations, lack of access to resources and networks, and gender bias within political institutions.
What specific economic factors influence political engagement and representation for women?
The wage gap, lack of affordable childcare, and unequal access to economic opportunities all limit women’s ability to participate in and succeed in politics. Economic hardship often impacts a woman’s ability to dedicate time and resources to political activities.

