PFAS Forever Chemicals North Carolina A Deep Dive
PFAS forever chemicals North Carolina are a serious concern, impacting communities and the environment. These persistent chemicals, found in various products, are now showing up in water sources and soil across the state, raising significant health and environmental questions. Understanding the sources, locations, and potential impacts of PFAS contamination is crucial for protecting public health and the natural environment.
This deep dive examines the pervasive issue of PFAS forever chemicals in North Carolina, exploring everything from contamination hotspots to potential long-term health effects. We’ll analyze the current regulations, community response, and future research needed to address this complex challenge.
Overview of PFAS in North Carolina: Pfas Forever Chemicals North Carolina
PFAS, or per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, are a group of man-made chemicals that have become ubiquitous in the environment and human bodies. These chemicals are known for their resistance to water, oil, and heat, making them useful in a wide range of products. Unfortunately, this very characteristic also makes them persistent in the environment, and their long-term effects on human health are still being studied.
North Carolina, like many other parts of the country, is facing the challenge of PFAS contamination.The presence of PFAS in North Carolina’s water sources, soil, and potentially other environmental mediums is a growing concern. Contamination has been linked to various industrial and manufacturing activities, and the lingering effects of past uses pose a significant environmental and public health issue.
Understanding the sources of PFAS, potential health risks, and the current regulatory landscape is crucial for effective mitigation and remediation strategies.
Sources of PFAS Contamination in North Carolina
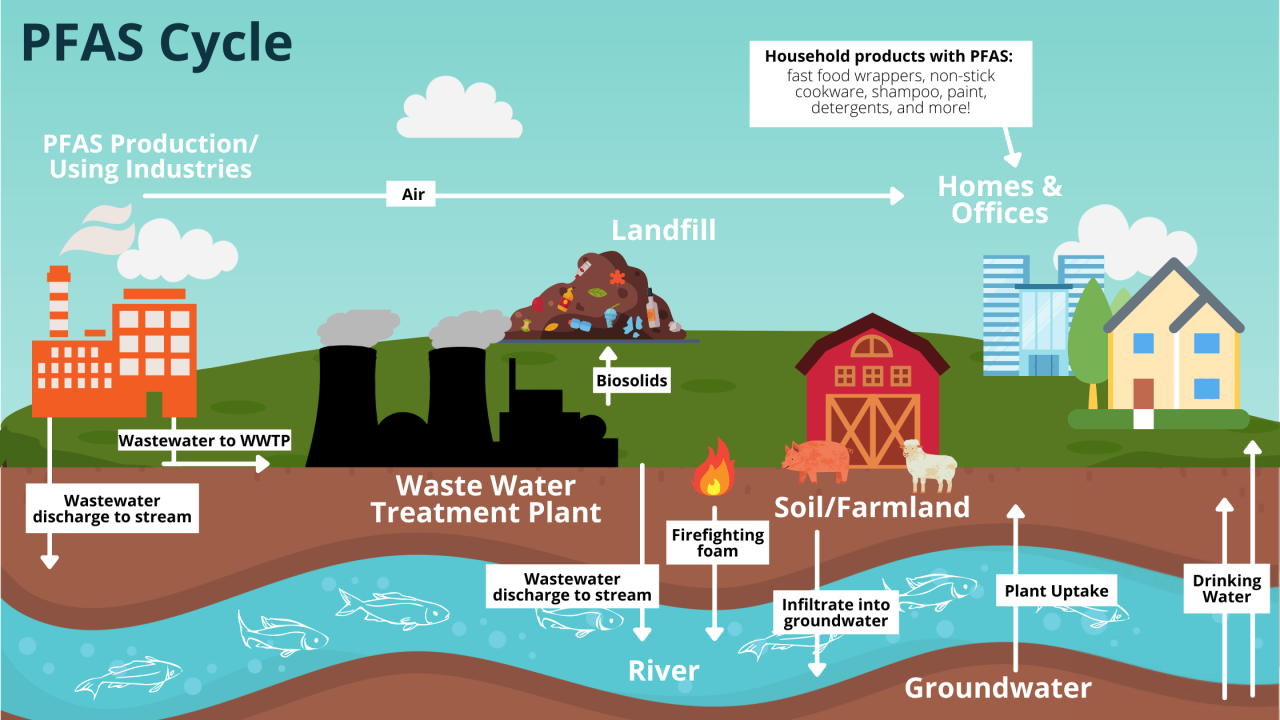
PFAS contamination stems from various sources. Industrial discharges, particularly from manufacturing facilities that use PFAS in their processes, are a primary concern. Fire-fighting foam, widely used for decades, is another significant contributor to PFAS contamination. The use of PFAS in products such as non-stick cookware, food packaging, and stain-resistant textiles, while prevalent, also contributes to the overall contamination load.
Improper disposal of PFAS-containing products and wastewater further exacerbates the issue. Agricultural practices may also be a source of PFAS contamination, especially where fertilizers or pesticides containing these chemicals are used.
Potential Health Risks Associated with PFAS Exposure
Exposure to PFAS has raised serious concerns about potential health effects. Studies have linked PFAS exposure to various health issues, including immune system problems, liver damage, thyroid issues, and developmental problems in children. Moreover, there’s a concern regarding potential reproductive problems and some evidence of increased cancer risk. The long-term health effects of chronic exposure are still being actively researched, and more studies are needed to fully understand the implications.
While the exact thresholds of risk are not always clear, there is a growing consensus on the need for protective measures.
Current State Regulations and Policies Regarding PFAS in North Carolina
North Carolina’s regulatory framework for PFAS is still evolving. Currently, there are some standards in place for drinking water, but these may not cover all potential exposure routes or PFAS types. Ongoing efforts focus on developing more comprehensive regulations and policies. The state is working to improve monitoring and testing procedures to better understand the extent of PFAS contamination and to support remediation efforts.
Furthermore, there’s a growing emphasis on identifying and mitigating PFAS sources to prevent future contamination.
Contamination Locations and Impacts
PFAS contamination is a growing concern across North Carolina, impacting both the environment and human health. Understanding the specific locations affected, the extent of the contamination, and the resulting impacts is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies and protecting public health. This section delves into the geographical distribution of PFAS, its effects on various ecosystems, and its potential health risks in the affected areas.PFAS contamination is a complex issue, not easily solved.
It often involves a chain of events, starting with industrial discharge and ultimately impacting human health. The persistent nature of PFAS means that contaminated sites can continue to release these chemicals into the environment for extended periods, making long-term remediation a necessity.
Key Locations in North Carolina with PFAS Contamination
Several locations in North Carolina have been identified as having elevated levels of PFAS contamination. These areas frequently feature industrial activity or sites where PFAS-containing products were used or manufactured. Specific locations include, but are not limited to, areas near military bases, industrial facilities, and sites of past firefighting training exercises.
Impacts on the Environment
PFAS contamination poses significant threats to the environment. The chemicals can persist in water sources for years, affecting aquatic life. They can also accumulate in soil, impacting plant life and potentially entering the food chain.
North Carolina’s PFAS “forever chemicals” problem is a real heartbreaker. The ongoing contamination is causing immense stress and worry for residents, and it’s a heavy weight to bear. This situation reminds me a lot of the powerful emotional journey explored in the article “Grief is for People Sloane Crosley” grief is for people sloane crosley. It highlights how widespread pain can be, and how important it is to address these deeply personal struggles.
Ultimately, finding solutions to the PFAS crisis is crucial for the well-being of the entire community.
- Water Contamination: PFAS contaminates water sources such as rivers, lakes, and groundwater. This contamination can negatively affect aquatic life, disrupting ecosystems and potentially harming drinking water supplies. The long-term effects on the aquatic food chain are still being studied, but early indications suggest significant disruption.
- Soil Contamination: PFAS can accumulate in soil, potentially impacting plant growth and potentially transferring into the food chain. This poses a risk to agricultural activities and the overall soil health of the affected regions. The long-term effects on soil organisms and the soil structure are not yet fully understood.
- Wildlife Impacts: Studies indicate that PFAS can negatively affect wildlife populations. Animals consuming contaminated water or food can experience health problems, including reproductive issues, immune deficiencies, and developmental abnormalities. These effects can cascade through the food web, impacting the entire ecosystem.
Effects on Human Health
PFAS contamination in North Carolina presents potential health risks to humans who consume contaminated water, soil, or food. Studies are ongoing to determine the long-term health consequences of exposure.
- Potential Health Issues: Exposure to PFAS has been linked to various health issues, including immune system suppression, developmental problems, liver damage, and certain cancers. The specific effects and their severity often depend on the level of exposure and the specific type of PFAS present.
- Vulnerable Populations: Certain populations may be more susceptible to the negative impacts of PFAS exposure. Children, pregnant women, and individuals with pre-existing health conditions may experience more pronounced effects. Understanding these vulnerable groups is crucial for targeted interventions.
Comparing Contamination Severity Across Locations
The severity of PFAS contamination varies across different locations in North Carolina. Factors such as the history of industrial activity, the type of PFAS present, and the amount of contamination influence the level of risk.
| Region | Contamination Level (Estimated) | Affected Population | Potential Consequences |
|---|---|---|---|
| Region A | High | Significant | Increased risk of health issues, potential water restrictions |
| Region B | Moderate | Moderate | Monitoring required, potential remediation efforts |
| Region C | Low | Limited | Ongoing monitoring, precautionary measures |
Public Health Concerns
The presence of PFAS in North Carolina’s water supply raises serious public health concerns, demanding immediate attention and proactive measures. The potential for long-term health effects, particularly for vulnerable populations, necessitates a comprehensive understanding of the risks and a robust strategy for mitigation. The intricate nature of PFAS and the complexities of tracking exposure highlight the urgent need for transparent communication and ongoing research.PFAS exposure can lead to a range of potential health consequences, and the long-term effects are still being studied.
Early research suggests that exposure can impact various bodily systems, and the cumulative effect of exposure over time is a critical area of concern. Understanding the diverse health impacts and vulnerabilities within different populations is crucial for effective preventative measures. This includes focusing on potential long-term health impacts and specific concerns for vulnerable populations.
Potential Long-Term Health Effects of PFAS Exposure
The potential long-term health effects of PFAS exposure are diverse and complex. Research continues to uncover new connections between PFAS and various health conditions. Scientific studies have established correlations between PFAS exposure and specific health outcomes, although causality is not always definitively proven. Understanding the potential impacts is essential for implementing appropriate public health interventions.
- Immunological Effects: PFAS exposure can disrupt the immune system, potentially leading to an increased susceptibility to infections. This effect can be particularly concerning for children, whose immune systems are still developing.
- Reproductive Effects: There’s evidence suggesting that PFAS can negatively affect reproductive health, potentially impacting fertility and embryonic development. Studies on pregnant women and their offspring are crucial to understanding the risks.
- Endocrine Disruption: Some PFAS compounds are suspected to interfere with the endocrine system, which regulates hormone production. This can have far-reaching consequences for growth, development, and overall health, especially in children.
- Developmental Effects: Research suggests a potential link between PFAS exposure and developmental issues in children, including neurodevelopmental problems and impaired cognitive function. The long-term consequences of these impacts can be significant.
- Cardiovascular Effects: Some studies indicate a potential connection between PFAS exposure and cardiovascular issues, including high blood pressure and other related problems. The impact on long-term cardiovascular health is an area of ongoing investigation.
- Cancer Risk: A number of studies have shown a possible association between PFAS exposure and certain types of cancer, such as kidney cancer. More research is needed to determine the strength and nature of this link.
Vulnerable Populations and PFAS
Certain populations are more susceptible to the adverse health effects of PFAS exposure due to factors like their physiological development and overall health. Children and pregnant women are particularly vulnerable.
North Carolina’s PFAS forever chemicals are a serious environmental concern, and while the latest fashion trends at saint laurent dior paris fashion week are captivating, the impact of these persistent chemicals on the state’s ecosystem and public health demands attention. We need to prioritize solutions and effective regulations to address this critical issue.
- Children: Children are more susceptible to PFAS exposure because their bodies are still developing. Exposure can impact their growth, development, and immune systems. Their consumption of water and food, especially breast milk, can be affected, leading to higher concentrations in their bodies.
- Pregnant Women: Pregnant women are also vulnerable to PFAS exposure due to the potential for the chemicals to pass through the placenta and affect the developing fetus. This can lead to long-term health consequences for the child.
Challenges in Monitoring and Tracking PFAS Exposure
Monitoring and tracking PFAS exposure present considerable challenges. The complex nature of PFAS contamination, its widespread presence, and the long-term effects make comprehensive monitoring a demanding task.
- Complexity of PFAS compounds: The diverse range of PFAS compounds adds complexity to monitoring efforts. Different compounds may have different impacts on health.
- Variability of exposure levels: Exposure levels vary significantly depending on factors like location, water sources, and individual habits. This makes it difficult to establish clear exposure-effect relationships.
- Long latency periods: The long latency periods between PFAS exposure and health effects make it challenging to establish clear cause-and-effect relationships. It requires extensive longitudinal studies.
- Cost of testing: PFAS testing can be expensive, which can limit the scope of monitoring efforts and impact the frequency of testing.
Need for Public Awareness Campaigns
Public awareness campaigns are essential to educate the public about PFAS and the potential health risks. Understanding the risks and taking preventive measures are vital to protect public health.Public awareness campaigns can help educate residents about the potential risks of PFAS exposure, promoting safer practices and encouraging individuals to seek medical advice if they have concerns.
Environmental Impacts
PFAS contamination poses a significant threat to North Carolina’s environment, impacting water quality, ecosystems, and long-term remediation efforts. These “forever chemicals” persist in the environment for extended periods, accumulating in various components of the ecosystem and disrupting natural processes. The effects are widespread and complex, demanding careful attention and coordinated action to mitigate damage.PFAS contamination affects water sources by leaching into groundwater and surface water bodies.
This contamination can lead to the accumulation of PFAS in drinking water supplies, posing a significant threat to human health and the overall environment. The impact extends to the delicate balance of ecosystems, with profound consequences for plant and animal life. Addressing this issue requires a multi-faceted approach that considers the long-term challenges in cleaning up PFAS and ensuring sustainable environmental remediation.
Impact on Water Quality
PFAS contamination in water sources is a serious concern. These chemicals are persistent and can accumulate in the water column, potentially affecting both surface and groundwater. PFAS can persist in the environment for an extremely long time, leading to ongoing contamination of water bodies. The contamination can affect the quality and usability of water for various purposes, including drinking water, agricultural irrigation, and industrial processes.
This necessitates careful monitoring and stringent cleanup strategies to mitigate the risks associated with long-term exposure.
North Carolina’s PFAS forever chemicals problem is a serious one, impacting water sources and public health. It’s a complex issue, but recent news about the tragic armorer Alec Baldwin’s Rust shooting incident armorer alec baldwin rust shooting highlights the need for responsible handling of potentially hazardous materials in various industries. We need to keep focusing on finding solutions for PFAS contamination in North Carolina, as this issue demands urgent attention.
Impact on Local Ecosystems
The presence of PFAS in the environment has a detrimental effect on local ecosystems. The accumulation of these chemicals in the soil and water can disrupt the natural processes that support plant and animal life. For example, PFAS contamination can alter nutrient cycling, impacting plant growth and development. Furthermore, the uptake of PFAS by plants and animals can lead to bioaccumulation, potentially reaching toxic levels in higher trophic levels of the food chain.
Challenges in Cleaning Up PFAS Contamination
Removing PFAS from the environment is a complex and expensive undertaking. The persistence of PFAS in the environment makes traditional cleanup methods less effective. The high cost of remediation is a significant challenge. Furthermore, the extensive nature of PFAS contamination can make cleanup efforts time-consuming and require substantial resources. Innovative technologies and strategies are necessary to overcome these obstacles and effectively address PFAS contamination.
Challenges in Long-Term Environmental Remediation of PFAS
Long-term environmental remediation of PFAS contamination requires a comprehensive and sustained approach. The persistence of PFAS in the environment means that remediation efforts need to be ongoing and adaptable to evolving scientific understanding. Finding effective and cost-effective methods to remove PFAS from contaminated sites is a continuous challenge. The long-term monitoring of PFAS levels in the environment is essential to ensure that remediation efforts are successful and sustainable.
Summary of PFAS Impacts on North Carolina Ecosystems
| Ecosystem Component | Impact of PFAS |
|---|---|
| Water | Contamination of drinking water sources, disruption of aquatic ecosystems, bioaccumulation in fish and other aquatic life. |
| Soil | Reduced plant growth, altered nutrient cycling, bioaccumulation in plant life. |
| Plants | Reduced growth and yield, potential uptake of PFAS and transfer to consumers. |
| Animals | Bioaccumulation in tissues, potential reproductive and developmental issues, disruption of food webs. |
Regulations and Response

North Carolina’s response to the pervasive issue of PFAS contamination is a complex and evolving process. Initial responses have focused on identifying affected areas and investigating potential sources. Now, the state is actively implementing regulations and working to mitigate the impact on public health and the environment. The journey is far from over, but the commitment to addressing this challenge is clear.
Current Regulations in North Carolina
North Carolina has begun to implement regulations concerning PFAS, although these are still relatively new and developing. The state is using a phased approach, likely due to the varied and extensive nature of the contamination, and the evolving scientific understanding of PFAS. These regulations, while a step in the right direction, are constantly being reviewed and revised as more data becomes available and new technologies are developed.
Effectiveness of Existing Regulations
Assessing the effectiveness of existing regulations is difficult at this early stage. The impact on contamination levels and public health outcomes will take time to fully evaluate. Monitoring and reporting programs are crucial for understanding the efficacy of the implemented regulations. The long-term health impacts of PFAS exposure are still being studied, so a complete picture of the regulations’ effectiveness will require years of data collection and analysis.
It’s essential to understand that any immediate assessments are likely to be incomplete and preliminary.
Timeline of PFAS Contamination Events
The timeline of PFAS contamination events in North Carolina is characterized by gradual discoveries and growing awareness. Initial findings from testing and investigations have revealed the extent of the contamination, with the locations and levels varying greatly. Understanding the historical patterns of contamination is crucial for future prevention and remediation strategies. This knowledge is key to developing targeted prevention measures in the future.
The specific timeline is not yet fully documented in public records. This includes the precise dates when contamination was first detected in specific locations.
Role of Government Agencies
Government agencies play a critical role in addressing PFAS contamination. The Environmental Protection Division (EPD) and the Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS) are likely leading the charge in North Carolina, working closely with local authorities. Their role includes overseeing regulatory compliance, funding remediation efforts, and communicating with the public about the risks and mitigation strategies. The coordination between these agencies is vital for a comprehensive response.
Furthermore, ongoing collaboration with federal agencies is also essential for accessing additional resources and expertise.
Comparison of PFAS Regulations in North Carolina and Other States
| Feature | North Carolina | California | Massachusetts | New York |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Contaminant Levels (MCLs) | Currently in development, with specific levels yet to be determined. | Has established MCLs for certain PFAS. | Has established MCLs for certain PFAS. | Has established MCLs for certain PFAS. |
| Remediation Standards | Standards are being developed and implemented. | Strict standards for remediation. | Rigorous standards for remediation, particularly in heavily affected areas. | Standards vary based on the specific contamination site. |
| Monitoring Programs | Ongoing monitoring programs are being implemented. | Extensive monitoring programs to track PFAS levels. | Monitoring is actively conducted in impacted areas. | Comprehensive monitoring is carried out in various locations. |
Note: This table provides a general comparison. Specific details and regulations are subject to change and vary depending on the particular site. The data presented is a simplified overview of the current situation. More detailed and specific information is available through official state government websites.
Community Engagement and Advocacy
Addressing PFAS contamination requires a strong, unified effort from communities, government agencies, and scientists. Community engagement is crucial for understanding the specific concerns of affected residents, fostering trust, and developing effective solutions. Active participation from residents allows for the identification of localized needs and empowers them to advocate for their rights and well-being.Community engagement isn’t just a good idea; it’s essential for the success of any PFAS remediation effort.
By involving residents in the process, we can ensure that solutions are tailored to their specific needs and concerns, ultimately leading to more effective and sustainable outcomes. This participatory approach builds trust, fosters cooperation, and strengthens the community’s resilience in the face of environmental challenges.
Importance of Community Engagement
PFAS contamination impacts individuals and families at a very personal level. Understanding the anxieties, concerns, and potential health impacts of these chemicals is vital. Community engagement provides a platform for open dialogue and fosters a sense of shared responsibility in addressing the issue.
North Carolina’s PFAS forever chemicals are a serious concern, impacting the environment and public health. While the issue is undeniably complex, exploring creative solutions is key. Listening to a Broadway cast album, like broadway cast albums sweeney todd , can offer a welcome distraction, but ultimately, the focus must remain on finding lasting solutions for these dangerous chemicals in our state.
Examples of Community Initiatives and Advocacy Groups
Numerous community initiatives and advocacy groups have emerged in response to PFAS contamination. These groups play a critical role in educating residents, organizing meetings, and advocating for policy changes. For instance, some groups are actively involved in collecting and analyzing water samples, conducting community forums, and organizing town halls to discuss potential health risks.
Strategies for Raising Awareness Among Residents
Effective communication strategies are essential for raising awareness among residents about PFAS issues. Utilizing clear and accessible language, utilizing local media outlets, and creating educational materials specifically tailored to the community are critical steps. Organizing workshops, presentations, and community events can empower residents with knowledge and encourage participation in the response.
Transparency in Communication Between Government Agencies and Affected Communities
Transparency is paramount in the communication between government agencies and affected communities. Openly sharing information about testing results, remediation plans, and potential health risks builds trust and fosters collaboration. Regular meetings, public forums, and accessible online resources can facilitate clear communication and address concerns.
Successful Community Engagement Strategies
Communities facing PFAS contamination have demonstrated successful engagement strategies. For example, some communities have established task forces comprised of residents, scientists, and government representatives. These task forces facilitate a coordinated approach to problem-solving, ensuring the voice of the community is heard and addressed. Another example includes community-led data collection efforts, such as the creation of volunteer-based monitoring programs to track PFAS levels in local water sources.
These initiatives show how community involvement can be vital in driving the process forward.
North Carolina’s ongoing struggle with PFAS “forever chemicals” is a serious issue, impacting water supplies and public health. Recent news regarding Felicia Snoop Pearson and Ed Burns’s wiretap case, felicia snoop pearson ed burns wire , highlights the complex web of legal and environmental challenges surrounding these harmful substances. The contamination continues to be a pressing concern, demanding attention and solutions.
Future Research and Mitigation
The ongoing PFAS contamination crisis demands a proactive approach to future research and mitigation strategies. Understanding the long-term health impacts and developing effective remediation methods are crucial for protecting North Carolina’s environment and public health. This requires a multi-faceted effort involving scientific investigation, technological innovation, and community engagement.
PFAS Impact on Human Health: Long-Term Studies
Further research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects of PFAS exposure on human health. Existing studies often focus on short-term exposure or specific populations. More comprehensive longitudinal studies, encompassing various demographic groups and exposure levels, are essential to establish clear links between PFAS exposure and specific health outcomes. This includes the development of biomarkers to detect and quantify PFAS exposure in human tissues and fluids, enabling the monitoring of individuals over extended periods.
For example, the long-term health impacts of PFAS exposure in children and the developing fetus require further investigation. Tracking and monitoring these vulnerable populations are critical for understanding the cumulative effects of PFAS.
PFAS Remediation Technologies: Innovation and Efficiency
Innovative technologies are crucial for effective PFAS removal and cleanup. Existing methods, such as activated carbon filtration and membrane bioreactors, often have limitations in terms of efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Research should focus on developing more efficient and cost-effective technologies, such as advanced oxidation processes, nanofiltration, and bioaugmentation techniques. For instance, the use of advanced oxidation processes, like electrochemical oxidation, may prove effective in degrading PFAS in contaminated water sources.
These methods offer potential solutions for treating large volumes of contaminated water.
Long-Term Costs of PFAS Mitigation, Pfas forever chemicals north carolina
The costs associated with PFAS mitigation are significant and multifaceted. These include not only the upfront costs of implementing remediation technologies but also the long-term monitoring and maintenance costs. The long-term cost of PFAS mitigation will vary depending on the extent of contamination, the chosen remediation method, and the regulatory requirements. For example, the cleanup of a large-scale industrial site contaminated with PFAS may involve substantial financial investments over several years.
This requires a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis for different remediation strategies, considering the potential long-term economic impact on affected communities.
Summary Table: Future Research and Mitigation Strategies
| Research Area | Proposed Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|
| Long-term health effects of PFAS exposure in specific populations (e.g., children, pregnant women) | Longitudinal studies tracking health outcomes, biomarker development, and epidemiological investigations. |
| Development of more efficient and cost-effective PFAS remediation technologies | Research into advanced oxidation processes, nanofiltration, and bioaugmentation. Pilot-scale testing of innovative technologies in real-world contaminated sites. |
| Comprehensive cost-benefit analysis of various PFAS remediation strategies | Detailed cost estimations for different technologies, considering long-term maintenance and monitoring requirements. Risk assessment for different mitigation strategies, taking into account potential environmental impacts. |
| Community engagement and public awareness campaigns | Educational programs to raise awareness about PFAS contamination and health risks, community involvement in research design and data interpretation. Public forums to discuss mitigation strategies and potential impacts on affected communities. |
Last Recap
In conclusion, the PFAS forever chemicals crisis in North Carolina is a multifaceted problem demanding immediate attention and collaborative action. From contaminated water sources to potential health risks, the impact of these chemicals is far-reaching. We’ve examined the complex interplay of contamination, public health concerns, and environmental impacts. Addressing this challenge requires a multifaceted approach that includes stricter regulations, robust community engagement, and continued research.
Ultimately, the future health and well-being of North Carolina residents and the environment depend on effective mitigation and remediation strategies.
FAQ Explained
What are the most common sources of PFAS contamination in North Carolina?
PFAS can be found in various sources, including industrial discharges, firefighting foam, and certain consumer products. Tracing the specific sources in different North Carolina locations is an ongoing process.
What are the short-term health effects of PFAS exposure?
Short-term effects can include skin irritation, nausea, and vomiting. However, the long-term effects are of more concern.
How can I get involved in the fight against PFAS contamination in my community?
Contact your local environmental agencies and support community groups working to raise awareness and advocate for change. Follow the news and stay informed.
What is the current status of PFAS remediation efforts in North Carolina?
Remediation efforts are underway in several areas, but there is still a significant need for further funding, research, and community support to address the contamination completely.

