Red Sea Shipping Houthi Impact
Red Sea shipping Houthi conflict has significantly impacted global trade. This disruption has forced a reevaluation of shipping routes and security protocols, highlighting the vulnerability of vital maritime trade lanes. The conflict’s effects ripple through various industries, impacting supply chains and potentially leading to long-term adjustments in global commerce.
This article delves into the complex issue of the Houthi conflict’s effect on Red Sea shipping, exploring historical context, current challenges, alternative routes, and future implications for global trade. We will examine the security measures in place, the economic consequences, and the potential long-term shifts in the shipping industry.
Overview of Red Sea Shipping
The Red Sea, a vital waterway connecting the Indian Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea, has played a critical role in global trade for centuries. Its strategic location and relatively shallow depth have historically attracted maritime activity. This route, though facing challenges, remains a significant conduit for goods and services, with ongoing efforts to enhance its capacity and safety.The Red Sea shipping lanes are characterized by a combination of natural advantages and logistical intricacies.
The sea’s narrow passage, coupled with its importance in international commerce, necessitates meticulous planning and execution of shipping operations. Understanding the history, significance, and operational aspects of this vital waterway is crucial for comprehending its role in the global economy.
Historical Significance of Red Sea Shipping Routes
The Red Sea’s maritime history stretches back millennia. Ancient civilizations recognized its importance as a trade route, utilizing it for the exchange of goods and ideas between Africa, Asia, and the Middle East. The spice trade, the movement of textiles, and the exchange of precious metals were all facilitated by the Red Sea. The Suez Canal’s opening in 1869 dramatically accelerated the importance of the Red Sea as a vital shipping lane.
Significance of the Red Sea to Global Trade
The Red Sea’s strategic location between Africa, Asia, and Europe makes it a crucial link in global trade. It offers a shorter alternative to routes around Africa, thereby reducing travel time and costs for goods shipped between these continents. This direct link is essential for transporting various commodities, including oil, minerals, and manufactured goods, contributing significantly to global supply chains.
Major Ports and Terminals along the Red Sea
The Red Sea boasts a cluster of important ports and terminals. These facilities handle a substantial volume of cargo, and their efficiency directly impacts global trade. Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, is a major port with substantial throughput. Port Sudan, Sudan, handles significant cargo volumes, particularly for the African continent. Other significant ports include Aqaba, Jordan, and Salalah, Oman, each serving specific trade needs and routes.
- Jeddah, Saudi Arabia: A major hub for container shipping, handling a vast range of commodities and serving as a crucial link for the Middle East and beyond. Its modern infrastructure and efficient operations are critical for the region’s trade.
- Port Sudan, Sudan: A key port for East Africa, providing access to the region’s resources and trade partners. Its strategic location facilitates trade with neighboring countries.
- Aqaba, Jordan: A significant port that serves as a vital link between the Red Sea and the Mediterranean, providing access to markets in Europe and beyond.
- Salalah, Oman: An important port focusing on bulk cargo, notably handling crude oil and other resources from the region. It plays a crucial role in the regional energy market.
Types of Cargo Transported Through the Red Sea
A diverse range of cargo transits through the Red Sea. This includes but is not limited to:
- Crude oil and petroleum products: The Red Sea plays a vital role in the movement of oil and related products between producing nations and consuming countries.
- Manufactured goods: A substantial amount of manufactured products are transported across the Red Sea, connecting manufacturers in Asia and the Middle East with markets worldwide.
- Minerals and raw materials: The Red Sea facilitates the movement of minerals and raw materials, vital components in manufacturing and construction.
- Consumer goods: Numerous consumer goods are transported across the Red Sea, connecting manufacturers with consumers across continents.
Typical Vessel Types Used for Red Sea Shipping
Various vessel types are used for shipping across the Red Sea, depending on the cargo being transported. These include:
- Container ships: These vessels are essential for transporting containers of goods, facilitating efficient handling of a broad spectrum of products.
- Bulk carriers: These ships are specialized in transporting large quantities of bulk materials, such as minerals and agricultural products.
- Tankers: Tankers, especially those carrying crude oil and petroleum products, are a prominent part of Red Sea shipping.
- Ro-Ro (roll-on/roll-off) vessels: These vessels are crucial for transporting vehicles and other cargo that can be driven or rolled onto the ship.
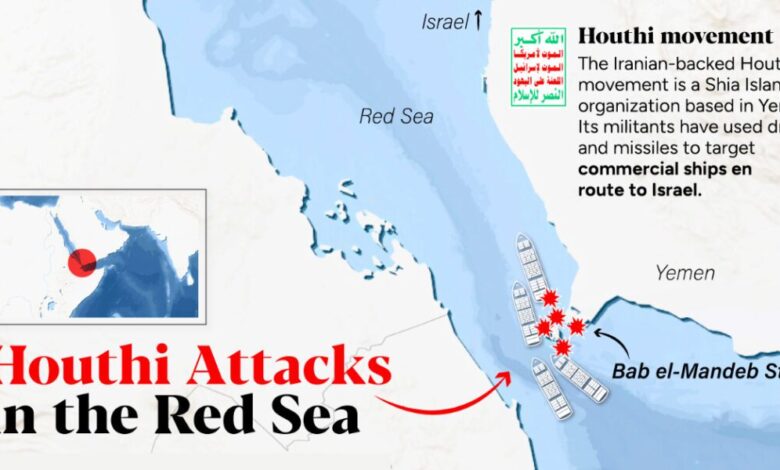
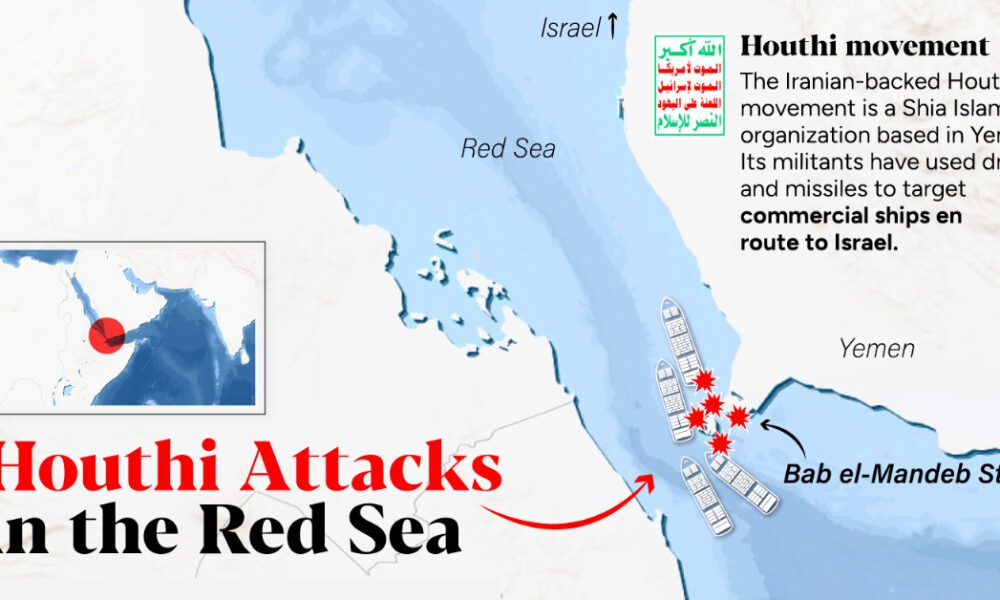
Impact of the Houthi Conflict
The Houthi conflict in Yemen has significantly disrupted the vital Red Sea shipping lanes, impacting global trade and regional stability. This conflict, ongoing for years, has created a complex security landscape, forcing vessels to navigate treacherous waters and leading to increased costs and delays. The consequences extend far beyond the immediate area, affecting supply chains and potentially stoking further geopolitical tensions.The conflict’s influence on the Red Sea’s maritime routes is multifaceted, with disruptions ranging from increased piracy attempts to the imposition of restrictions on navigation.
This necessitates the adoption of enhanced security measures by shipping companies, with substantial economic repercussions. The cumulative effect on international trade is substantial and underscores the need for diplomatic solutions to restore normalcy to the region.
Disruptions to Shipping Lanes
The Houthi conflict has led to numerous disruptions to shipping activity in the Red Sea. These disruptions manifest in various forms, including heightened piracy risks, the presence of armed groups, and restrictions on navigation imposed by certain parties. These factors combine to create a complex and unpredictable environment for vessels transiting the region. The resulting delays and increased security costs have significant economic repercussions.
Types of Disruptions
- Increased Piracy Attempts: The conflict has created an environment ripe for opportunistic piracy attempts, as armed groups exploit the volatile situation to target merchant vessels. These groups may seek to seize cargo or demand ransom payments, impacting the safety of crews and the smooth flow of goods. For example, in 2022, several incidents were reported involving armed groups attempting to intercept vessels, leading to disruptions and delays.
- Imposed Navigation Restrictions: Certain parties involved in the conflict may impose restrictions on navigation, such as closing certain ports or restricting access to specific areas. These restrictions can create bottlenecks and force vessels to alter their routes, leading to delays and increased costs.
- Presence of Armed Groups: The presence of armed groups operating in the Red Sea poses a constant threat to shipping activity. These groups may be involved in armed clashes, creating unsafe conditions for vessels navigating the area. This also impacts the frequency and timing of shipping schedules.
Security Measures Implemented
To mitigate the risks associated with the Houthi conflict, various security measures have been implemented. These include enhanced vessel protection, increased security personnel, and collaboration among shipping companies and navies. These measures aim to reduce the likelihood of attacks and improve the safety of vessels and their crews.
Examples of Incidents Impacting Shipping Activity
- Specific Incidents: Numerous incidents have been reported throughout the conflict, impacting shipping activity. These incidents vary in severity and impact, ranging from minor disruptions to significant delays. For instance, the blockade of certain ports has resulted in significant delays for cargo shipments, while attacks on vessels have led to the diversion of routes and the temporary suspension of operations.
- Specific Impacts: These incidents have tangible impacts on shipping companies and cargo owners. Increased security costs, vessel delays, and cargo losses are common consequences. These impacts ripple through supply chains, impacting businesses worldwide.
Economic Consequences of Disruptions
The Houthi conflict’s disruptions have significant economic consequences. Increased insurance premiums, delays in cargo delivery, and higher operational costs all contribute to increased expenses for shipping companies. The cost of these disruptions can be substantial, affecting businesses relying on these routes for imports and exports. This ultimately translates to higher prices for consumers and reduced profitability for companies involved in the trade.
Analysis of Alternative Routes

The ongoing conflict in the Red Sea, specifically the Houthi blockade, has significantly impacted global shipping. This disruption necessitates a reassessment of traditional trade routes and an exploration of viable alternatives. Finding suitable replacements requires a careful balancing act between efficiency, cost, and security. The repercussions of choosing the wrong alternative can be substantial, affecting not only individual companies but also global supply chains.Alternative routes offer a crucial contingency plan for maintaining global trade flow.
Understanding the advantages and disadvantages, along with the logistical and cost implications, is essential for navigating this new landscape. This analysis delves into the potential impact of these alternative routes, highlighting the critical considerations for a smooth transition.
Comparison of Alternative Routes
Different alternative routes exist, each with its own set of characteristics. The Suez Canal, while crucial, has become unreliable due to the ongoing conflict. Therefore, shipping companies are exploring alternative routes like the Cape of Good Hope route around Africa, or the Northern Sea Route (NSR) through the Arctic. The choice of route depends on several factors, including the destination, cargo type, and ship size.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Alternative Routes
- Cape of Good Hope Route: This traditional route offers a reliable, established path. However, it significantly increases transit time, leading to higher fuel consumption and potential delays. This can result in higher transportation costs, which ultimately affect consumer prices. The extended journey also raises security concerns, especially if the route is less frequently used. An example of this is the rise in piracy along certain stretches of the sea, which was historically less of a concern for the Suez route.
- Northern Sea Route (NSR): This route, primarily accessible during the summer months when the Arctic ice melts, is relatively faster than the Cape route. It offers a shorter distance for certain destinations, reducing transportation time and costs. However, the unpredictable nature of Arctic ice conditions, coupled with the logistical challenges of navigating this region, makes the NSR a less reliable option.
This is evident in the limited number of vessels equipped to navigate these icy waters, and the need for specialized support infrastructure.
- Panama Canal: This route provides a shorter alternative to the Cape route for certain destinations in the Americas and Asia. However, its capacity is limited, and congestion could occur during peak shipping seasons. Additionally, the Panama Canal has faced challenges with dredging and maintenance, which can impact efficiency and reliability.
Impact on Global Trade
The shift towards alternative routes will reshape global trade patterns. Businesses will need to adapt their supply chains to accommodate longer transit times and potentially higher costs. This adaptation could lead to increased warehousing costs and inventory management. The resulting changes could affect pricing models and consumer purchasing patterns, leading to increased prices for some goods. Examples of this are the current price increases of goods that have seen supply chain disruptions, due to the global impact of these disruptions.
Logistical Considerations for Switching
Switching to alternative routes requires careful planning and preparation. Companies need to evaluate the capabilities of their vessels and ensure they can navigate the new routes. They must also assess the availability of ports and infrastructure along the new routes. This includes considering factors like port security, loading/unloading facilities, and customs procedures. Furthermore, companies must address any regulatory changes or requirements specific to the new routes.
For example, there may be different documentation requirements, security checks, and permits that must be followed.
Cost Implications of Using Alternative Routes
The cost implications of using alternative routes vary depending on the specific route and the duration of the transit. The most significant factor influencing cost is the increase in transit time, leading to higher fuel consumption and potential demurrage fees. Other factors, such as port fees and handling charges, can also increase the overall cost. Companies will need to analyze the total cost of ownership to determine the most economical route.
For instance, a significant price increase could be seen if a shipping company is using the Cape route instead of the Suez route. This is because of the significantly longer transit times.
Effects on Global Trade
The ongoing conflict in the Red Sea, particularly the Houthi-related disruptions, casts a long shadow over global trade. The strategic importance of the waterway, a crucial artery for international shipping, is now significantly compromised. This disruption reverberates throughout global supply chains, affecting everything from consumer goods to industrial materials.The flow of goods across the Red Sea is experiencing substantial bottlenecks.
This is not just a localized issue; it’s a global challenge. The effects are felt acutely by businesses and consumers alike, leading to a cascade of consequences that ripple through economies worldwide.
Impact on the Flow of Goods
The Houthi attacks on shipping vessels in the Red Sea have created a significant hurdle for the movement of goods. This disruption is causing delays in delivery times, impacting the timely arrival of essential products and raw materials. The uncertainty and volatility surrounding the situation make it difficult for businesses to plan and manage their logistics effectively. Shipping companies are forced to adopt alternative routes, which can increase transit times and costs.
Potential Delays and Increased Costs
Importers and exporters face substantial challenges due to the conflict. Delays in shipments lead to increased inventory costs and disruptions in production schedules. The need to utilize alternative routes adds to the overall expense, as shipping costs are typically higher through longer, less direct routes. This financial burden is ultimately passed on to consumers, resulting in higher prices for goods.
For example, the recent Suez Canal blockage highlighted the vulnerability of global trade to disruptions, and this situation has similar repercussions.
Industries Affected by Shipping Disruptions
Numerous industries are directly impacted by the Red Sea shipping disruptions. The automotive industry, heavily reliant on the import of raw materials and finished goods, faces significant challenges in maintaining production schedules. Similarly, the electronics industry, which relies on the timely transport of components and finished products, is experiencing substantial delays and increased costs. The agricultural sector is also affected, as the transport of agricultural products is essential for food security and international trade.
Red Sea shipping has been a hot topic lately, with the Houthis’ actions causing significant disruption. Their recent activities in the Red Sea, as detailed in this article on houthis ships red sea , have raised serious concerns about the safety of maritime traffic. This ultimately impacts global trade and necessitates careful diplomatic solutions to ensure the free flow of goods through the vital shipping lanes.
The overall impact on Red Sea shipping houthi is substantial.
Furthermore, the pharmaceutical industry, which relies on the efficient delivery of medicine and medical supplies, is vulnerable to delays.
Implications for Global Supply Chains
The disruptions in the Red Sea shipping lanes have profound implications for global supply chains. The uncertainty and instability in the region create vulnerabilities in the entire system. Businesses are forced to reassess their logistics strategies and explore alternative routes. This process can be costly and time-consuming, potentially impacting the reliability and resilience of global trade networks.
For instance, the COVID-19 pandemic demonstrated how fragile supply chains can be, and this situation presents another significant challenge.
Overall Impact on International Commerce
The conflict in the Red Sea is having a significant and far-reaching impact on international commerce. The delays and increased costs associated with shipping disruptions are causing a decline in trade volume. Businesses are losing revenue, and consumers are facing higher prices for goods. The uncertainty surrounding the situation is creating a climate of apprehension, making it more difficult for businesses to invest and expand.
The implications for international relations and economic stability are also significant.
Security and Safety Measures
The ongoing conflict in the Red Sea, particularly the actions of the Houthis, has significantly impacted the safety and security of maritime traffic. This necessitates a robust response to protect vessels and crews, and ensure the free flow of goods vital for global trade. This section examines the enhanced security measures, international cooperation, and potential risks associated with navigating the region.The heightened risk to shipping necessitates comprehensive security measures.
The Red Sea shipping situation with the Houthis is definitely a major concern, impacting global trade routes. It’s a complex issue with far-reaching consequences, and the political maneuvering surrounding it is significant. Recent developments related to Guatemalan President Giammattei’s visit to the United States ( giammattei estados unidos guatemala ) might offer some clues to the broader geopolitical picture, potentially influencing how the international community tackles the Red Sea shipping crisis.
This is an evolving situation, so we’ll need to watch closely to see how it plays out.
These involve increased surveillance, enhanced vessel protection, and strengthened collaboration between navies and shipping companies. International efforts to maintain stability in the region are crucial to mitigate the impact of the conflict on global trade.
Enhanced Security Measures for Red Sea Shipping
Numerous measures have been implemented to bolster the security of vessels transiting the Red Sea. These include increased surveillance by naval forces, providing real-time information on potential threats, and coordinating patrols to deter attacks.
- Enhanced Vessel Protection: Shipowners are advised to implement enhanced security protocols on their vessels. This includes using advanced technologies like radar systems and employing security personnel onboard to monitor and respond to potential threats. The inclusion of specialized security equipment, such as reinforced hull plating and improved alarm systems, can further enhance the resilience of vessels to attacks.
- International Cooperation Efforts: International cooperation plays a pivotal role in securing the Red Sea shipping lanes. Collaborative efforts between navies, coastal states, and shipping companies are essential to share intelligence, coordinate patrols, and deter potential attacks. The sharing of real-time information on threats, coupled with joint patrols, contributes significantly to maritime security.
Role of Maritime Security Forces
Maritime security forces play a crucial role in safeguarding shipping lanes. Their presence acts as a deterrent to potential attacks and provides protection to vessels. Naval patrols, surveillance, and swift response capabilities are vital elements of these forces.
- Naval Patrols: Increased naval patrols and surveillance are employed to deter potential attacks and monitor the region. This continuous presence helps to identify and respond to threats quickly. This can involve the use of maritime surveillance assets and the coordination of forces across multiple nations.
- Swift Response Capabilities: Naval forces must be prepared to respond swiftly to any security threat. This includes the deployment of naval assets, the coordination of rescue operations, and the provision of assistance to vessels in distress. The speed of response is critical in mitigating damage and ensuring the safety of crews and cargo.
Potential Risks to Shipping Vessels
Several risks are associated with transiting the Red Sea, particularly during periods of heightened conflict. These include the potential for piracy, armed attacks, and the disruption of navigation. The unpredictable nature of the conflict zone demands continuous vigilance and adaptation.
- Piracy and Armed Attacks: The possibility of piracy and armed attacks remains a significant concern for vessels navigating the Red Sea. The region’s proximity to conflict zones and the presence of armed groups can create a volatile environment. The potential for hijacking, looting, or even direct attacks on vessels cannot be overlooked.
- Disruption of Navigation: Disruptions to navigation can occur due to the unpredictable nature of the conflict. These disruptions could range from localized blockades to broader restrictions on navigation. The need for flexibility and adaptation is critical to ensure the smooth and continuous movement of cargo.
Examples of Successful Security Measures
Several instances demonstrate the effectiveness of enhanced security measures. These examples showcase the importance of international cooperation and the adoption of proactive security protocols.
- Joint patrols by naval forces: Joint patrols by navies from multiple countries are proving effective in deterring attacks and providing a visible presence. This collaborative effort demonstrates the importance of international cooperation in maintaining maritime security.
- Implementation of advanced security technologies: The integration of advanced surveillance technologies, like real-time tracking systems, helps to identify and monitor potential threats. This proactive approach to monitoring enhances the security of shipping lanes.
Future Implications

The ongoing conflict in the Red Sea, impacting vital shipping lanes, necessitates a careful examination of future implications for global trade and maritime security. Adapting to these disruptions requires a nuanced understanding of potential shifts in shipping routes, technological advancements, and the long-term consequences of the current geopolitical instability.
Scenario for Future Red Sea Shipping Routes, Red sea shipping houthi
The Houthi conflict has significantly altered the Red Sea shipping landscape. Alternative routes, like the Suez Canal, have seen increased traffic, while some vessels are forced to use longer, more circuitous paths around Africa. This necessitates a reevaluation of transit times, costs, and potential risks associated with different routes. Predicting future routes requires a dynamic model that considers factors like security concerns, political developments, and the economic pressures on shippers.
The Red Sea shipping situation with the Houthis is definitely a tricky one, impacting global trade routes. Meanwhile, it’s fascinating to see how the fashion world is celebrating milestones like the 50th anniversary of couture designer Didier Ludot in Paris, couture didier ludot 50th anniversary paris. Hopefully, these creative endeavors, like those in the fashion world, can inspire solutions to ease the tensions and get those shipping lanes moving smoothly again.
Potential Adjustments to Shipping Practices
Shippers will likely adopt more stringent security protocols, increasing the use of advanced tracking systems and enhanced crew training. Insurance premiums for vessels transiting the Red Sea are expected to rise, influencing pricing structures and cargo allocation decisions. This will incentivize the use of alternative transport modes like rail or road for certain commodities, potentially impacting global supply chains.
Shippers may also explore the possibility of dedicated security escorts for vessels navigating the region.
The Red Sea shipping situation with the Houthis is definitely a major headache, impacting global trade routes. It’s fascinating to see how seemingly unrelated events, like the recent flooding issues at Eton College, which saw toilets overflowing ( eton college flooding toilets ), can highlight the unexpected ripple effects of these kinds of conflicts. The ongoing disruption to Red Sea shipping, however, continues to be a serious concern for international commerce.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on Red Sea Trade
Autonomous vessels and AI-powered navigation systems are likely to become increasingly important in the Red Sea. These technologies can enhance safety, optimize fuel consumption, and potentially mitigate some risks associated with human error. Furthermore, satellite communication advancements will improve vessel tracking and communication in challenging environments. This will allow for real-time data analysis and improved disaster response.
The development of sophisticated maritime security systems using AI could also enhance the defense of vessels.
Summary of Possible Future Disruptions
Geopolitical tensions and armed conflicts are unpredictable, potentially leading to further disruptions in the Red Sea shipping lanes. The region’s fragile security environment could lead to port closures or transit restrictions. Natural disasters, such as storms or tsunamis, can also disrupt shipping activities. The interplay of these factors could cause significant volatility in global trade, impacting the availability and cost of goods.
Predictions for Long-Term Implications
The Red Sea shipping crisis is likely to have lasting effects on global trade patterns. The current disruption may incentivize the development of more diversified shipping routes and the expansion of alternative transportation networks. This diversification may lead to a rebalancing of trade flows, potentially benefiting regions outside the traditional maritime hubs. Furthermore, the crisis highlights the vulnerabilities of global supply chains and the need for resilience and adaptability in the face of geopolitical uncertainties.
Illustrative Information
The Red Sea shipping lane, a vital artery for global trade, has faced significant disruptions due to the Houthi conflict. Understanding the specifics of this crucial shipping route, including its cargo types, frequency, security measures, and alternative routes, is essential for evaluating the impact and potential solutions. This section provides illustrative data to highlight the complexity and consequences of the current situation.
Port, Cargo Type, Frequency, and Security Measures
The Red Sea is a crucial maritime route, connecting several important ports and carrying various cargo types. The frequency of shipping, combined with the vulnerability to security threats, necessitates robust security measures.
| Port | Cargo Type | Frequency of Shipping | Security Measures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Port Sudan | Petroleum products, food, and general cargo | High | Increased naval presence, port security patrols, and enhanced surveillance. |
| Djibouti | Containerized goods, bulk cargo, and humanitarian aid | Moderate | Collaboration with regional navies, enhanced port security, and information sharing. |
| Eilat | General cargo, petroleum products, and specialized goods | High | Increased security patrols, surveillance, and close coordination with regional partners. |
Comparison of Red Sea Shipping Costs with Alternative Routes
The Houthi conflict has led to higher insurance premiums and increased operational costs for shipping companies using the Red Sea route. Alternative routes, while potentially longer, can offer more secure transit and, in some cases, lower costs. It is important to consider both the direct financial impact and the potential disruptions to schedules.
| Route | Estimated Cost (per container) | Transit Time (Days) | Security Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Red Sea Route | $1,000 – $1,500 | 7-10 | High risk of piracy and attacks |
| Cape of Good Hope Route | $1,200 – $2,000 | 25-30 | Lower risk of attacks, longer transit time |
| Suez Canal (Alternative) | $800 – $1,200 | 3-5 | Moderate risk, but potentially higher congestion during peak seasons |
Illustrative Scenario: Security Threat in the Red Sea
A container ship, carrying a large volume of electronics, is transiting the Red Sea. Unidentified small craft rapidly approach the vessel, displaying weaponry and flags indicative of a potential armed group. The ship’s security team initiates a high alert protocol, activating defensive systems and contacting regional navies for assistance. The situation escalates, leading to a brief standoff, and ultimately resolves with the intervention of naval forces from a regional partner.
The Red Sea shipping situation with the Houthis is really complex. It’s causing major headaches for global trade, and the ripple effects are being felt everywhere. Meanwhile, the political maneuvering between DeSantis, Trump, and Iowa Republicans is fascinating to watch, especially given the potential impact on future political landscapes, as discussed in desantis trump iowa republicans.
Ultimately, the global shipping crisis needs a solution, and the Houthis’ actions are a significant factor in the ongoing problem.
This illustrative scenario highlights the real-world challenges of navigating the Red Sea in the current security climate.
Key Commodities Transported Through the Red Sea
The Red Sea is a vital link in global supply chains, facilitating the movement of various commodities.
| Commodity | Description |
|---|---|
| Petroleum products | Crude oil, refined products, and associated materials. |
| Foodstuffs | Grain, rice, and other agricultural products. |
| Consumer goods | Electronics, textiles, and other manufactured products. |
| Raw materials | Minerals, metals, and other raw materials. |
Key Players in Red Sea Shipping
Several international players have significant involvement in shipping through the Red Sea. Their roles in navigation, security, and logistics influence the overall operations of the route.
| Player | Role |
|---|---|
| Shipping Companies | Transporting goods, managing logistics, and ensuring vessel safety. |
| Maritime Security Agencies | Maintaining security and countering threats, providing surveillance, and support to vessels. |
| Regional Governments | Supporting maritime security and navigation, ensuring stability in the region. |
| International Organizations | Facilitating communication and coordination between stakeholders, promoting peace and security. |
Summary: Red Sea Shipping Houthi
In conclusion, the Houthi conflict’s impact on Red Sea shipping is multifaceted and far-reaching. From the immediate disruptions to the long-term potential for altered trade patterns, the situation underscores the importance of robust security measures, alternative route planning, and international cooperation. The future of Red Sea shipping will undoubtedly reflect these challenges and adaptations. The tables provide a tangible representation of the diverse issues at play, while the FAQs offer additional insights for those seeking more clarification.
FAQ Insights
What are the key commodities transported through the Red Sea?
Major commodities include oil, gas, containerized goods, and various manufactured products. The Red Sea is a vital artery for international trade, connecting numerous Asian and African nations.
What are the typical vessel types used for Red Sea shipping?
Container ships, bulk carriers, tankers, and specialized cargo vessels frequently navigate the Red Sea. The size and type of vessel often depend on the cargo being transported.
How has the Houthi conflict impacted the cost of shipping?
The conflict has led to increased insurance premiums, security costs, and potentially longer transit times, all contributing to higher shipping costs for importers and exporters.
What alternative routes exist to the Red Sea?
Alternative routes include the Suez Canal and the Cape of Good Hope route, although these options might present varying logistical and cost implications.