Semiconductors Chips US Subsidies A Deep Dive
Semiconductors chips US subsidies are rapidly reshaping the global tech landscape. This in-depth look explores the intricate web of government support, its impact on domestic production, and the ripple effects across international relations and technological advancement. We’ll examine the history, rationale, and potential consequences of these subsidies, considering their effects on the environment, the economy, and public perception.
From the current global semiconductor industry landscape to the environmental considerations of manufacturing, this analysis will provide a comprehensive overview of the complex issue. Understanding the intricacies of these subsidies is crucial to grasping the future of the semiconductor industry.
Global Semiconductor Industry Landscape
The global semiconductor industry is a complex and dynamic ecosystem, crucial for powering countless technologies in our modern world. From smartphones to automobiles, and from medical devices to supercomputers, semiconductors are the invisible workhorses behind much of our technological advancement. Understanding the current landscape, including key players, market trends, and regional disparities, is essential for comprehending the industry’s evolving role in the global economy.The industry’s growth is intertwined with advancements in computing power, miniaturization, and the integration of diverse technologies.
This constant innovation, coupled with global demand, shapes the strategic decisions of companies and governments alike. Analyzing the distribution of production and consumption across different regions reveals crucial insights into the industry’s global interconnectedness.
Key Players and Market Trends
The semiconductor industry is dominated by a handful of large multinational corporations. These companies often leverage advanced manufacturing techniques and extensive research and development investments to maintain their competitive edge. The industry is characterized by rapid innovation, with new materials and processes constantly emerging, creating a challenging environment for smaller players. Market trends, such as the rise of artificial intelligence and the increasing demand for high-performance computing, significantly influence the industry’s trajectory.
These trends often drive the development of specialized chips tailored to meet specific needs.
Regional Production and Consumption
Semiconductor production is geographically dispersed, with significant hubs in Asia, particularly in Taiwan, South Korea, and China. These regions often boast advanced manufacturing capabilities and substantial government support. Consumption patterns vary across different regions, influenced by economic development, technological adoption, and local industry needs. The US, while historically a leader in semiconductor design, has witnessed a shift in manufacturing toward other parts of the world.
This shift has implications for national security, economic competitiveness, and the global supply chain.
US subsidies for semiconductor chip production are a hot topic, but the global geopolitical landscape is also deeply intertwined. Recent events, like the ongoing Gaza cease-fire negotiations involving Russia and NATO, gaza cease fire russia nato , highlight the complex interplay of economic and international factors. Ultimately, these subsidies are crucial for maintaining American technological dominance, but the ripple effects are felt far beyond the chip industry.
US Semiconductor Industry vs. Other Economies
The US semiconductor industry has historically been a leader in design and innovation. However, manufacturing capabilities have been challenged by increasing competition from other regions, particularly Asia. Government initiatives and policies are being implemented to bolster domestic manufacturing capacity and ensure the continued US leadership in the industry. This competition is shaping the global landscape, prompting nations to invest in their domestic semiconductor ecosystems.
The US and other advanced economies are recognizing the strategic importance of maintaining a robust semiconductor industry.
Top 5 Semiconductor Companies
Understanding the market leaders provides insight into the competitive dynamics within the industry. Financial strength, technological advancements, and global reach are crucial factors in their dominance.
| Rank | Company | Revenue (USD Billions) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Intel | ~150 |
| 2 | Samsung Electronics | ~250 |
| 3 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) | ~100 |
| 4 | Qualcomm | ~50 |
| 5 | Nvidia | ~30 |
Note: Revenue figures are approximate and may vary depending on the reporting period and source.
US Government Subsidies for Semiconductors
The US government’s recent focus on semiconductor subsidies reflects a strategic recognition of the crucial role these technologies play in national security and economic competitiveness. This initiative aims to bolster domestic production, reduce reliance on foreign suppliers, and foster innovation in a rapidly evolving technological landscape. The subsidies are designed to incentivize investment, attract talent, and ultimately enhance the US’s position in the global semiconductor industry.The rationale behind these subsidies stems from the understanding that a robust semiconductor industry is essential for a strong economy.
Semiconductors power everything from smartphones to automobiles to medical devices. A domestic supply chain ensures greater resilience against global disruptions and protects critical infrastructure. These subsidies, therefore, represent an investment in the future of the US economy and its technological leadership.
History and Rationale of US Semiconductor Subsidies
The US government’s intervention in the semiconductor industry isn’t entirely new. Historically, various government programs, though not specifically focused on subsidies, have supported research and development, particularly during the Cold War and the early days of the microchip era. However, the recent emphasis on direct subsidies signifies a shift towards more proactive and targeted interventions. This approach is motivated by concerns about the increasing dominance of foreign competitors and the potential vulnerability of the US to disruptions in the global supply chain.
Types of Subsidies and Targets
Various types of financial incentives are offered to support semiconductor production, research, and development. These include tax credits, grants, loan guarantees, and direct funding for specific projects. Specific targets of these subsidies are diverse, encompassing the development of new fabrication facilities (fabs), research and development of advanced semiconductor technologies, and the expansion of domestic semiconductor manufacturing capacity. The aim is to stimulate innovation and encourage the creation of a resilient and competitive domestic semiconductor ecosystem.
Economic Impacts of Subsidies
The potential economic impacts of these subsidies are multifaceted and complex. Increased domestic manufacturing is expected to create jobs and boost economic activity in the targeted areas. This will also increase the availability of skilled labor in the semiconductor industry. Moreover, a robust domestic industry can enhance the nation’s technological leadership and reduce dependence on foreign sources, improving national security.
The long-term impact will depend on the effective implementation of the subsidies, the level of private sector investment, and the ability of US companies to compete in the global market.
Funding Amounts for Semiconductor Projects
The table below Artikels the funding amounts for various semiconductor-related projects, though precise figures may be subject to change and vary across programs. Funding is often allocated based on project scope, anticipated impact, and feasibility assessments.
| Project Category | Estimated Funding (USD) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Chip Fabrication Facilities | $20-50 billion | Funding for the construction and operation of cutting-edge semiconductor fabrication plants. |
| Research and Development of Advanced Technologies | $10-20 billion | Supporting research and development of next-generation semiconductor technologies like quantum computing and new materials. |
| Expansion of Domestic Manufacturing Capacity | $5-10 billion | Facilitating the expansion of existing semiconductor manufacturing facilities to increase production capacity. |
Impact on Domestic Semiconductor Production
US government subsidies for semiconductor manufacturing are poised to significantly reshape the domestic landscape. These incentives are driving substantial investment in new facilities and research, aiming to bolster the nation’s technological independence and competitiveness. The implications extend beyond the semiconductor industry itself, impacting related sectors and potentially fostering substantial economic growth.
Influence on Domestic Production
The subsidies are designed to incentivize the construction of advanced semiconductor fabrication plants (fabs) in the US. Financial incentives, tax credits, and grants are attracting substantial investment from both established players and new entrants. These investments translate into the creation of advanced manufacturing capabilities, expanding the nation’s capacity to produce cutting-edge chips. This move away from reliance on foreign manufacturers strengthens the domestic supply chain and enhances national security.
Existing US semiconductor companies are also expected to increase their domestic production, potentially moving their manufacturing operations to reduce their reliance on foreign facilities.
Effects on the Supply Chain
The revitalization of domestic semiconductor production has a ripple effect across the supply chain. This includes the creation of new jobs in related industries, such as equipment manufacturing, material supply, and engineering. Companies involved in the production of raw materials and components crucial to chip manufacturing will experience increased demand. For example, the growth of domestic wafer production facilities will lead to greater demand for high-purity silicon and other essential materials.
This increased demand translates into economic growth and job creation in the supporting industries. This heightened domestic presence is expected to reduce reliance on overseas suppliers, enhancing the resilience of the overall supply chain.
Potential for Job Creation and Economic Growth
The expansion of domestic semiconductor manufacturing is projected to generate significant employment opportunities. Construction and operation of new fabs will require a large workforce, spanning engineering, construction, and maintenance roles. The development and production of supporting technologies will create more jobs, boosting overall employment. The resulting economic activity will likely lead to higher wages, increased consumer spending, and overall economic growth.
The growth in the semiconductor sector will also attract further investment in research and development, leading to innovation and technological advancements.
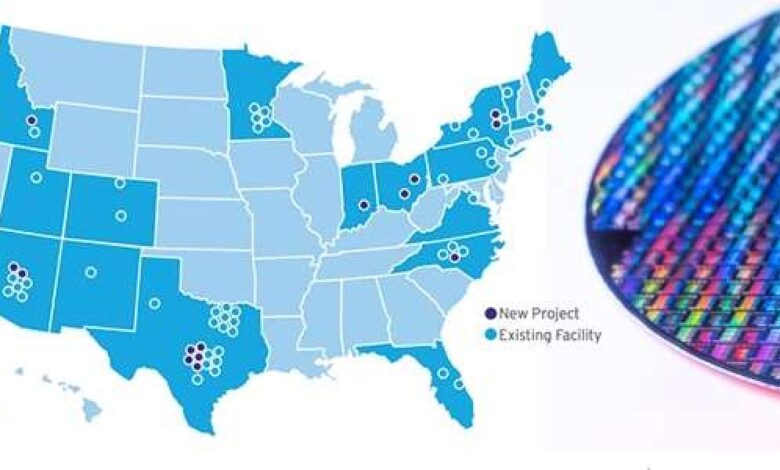
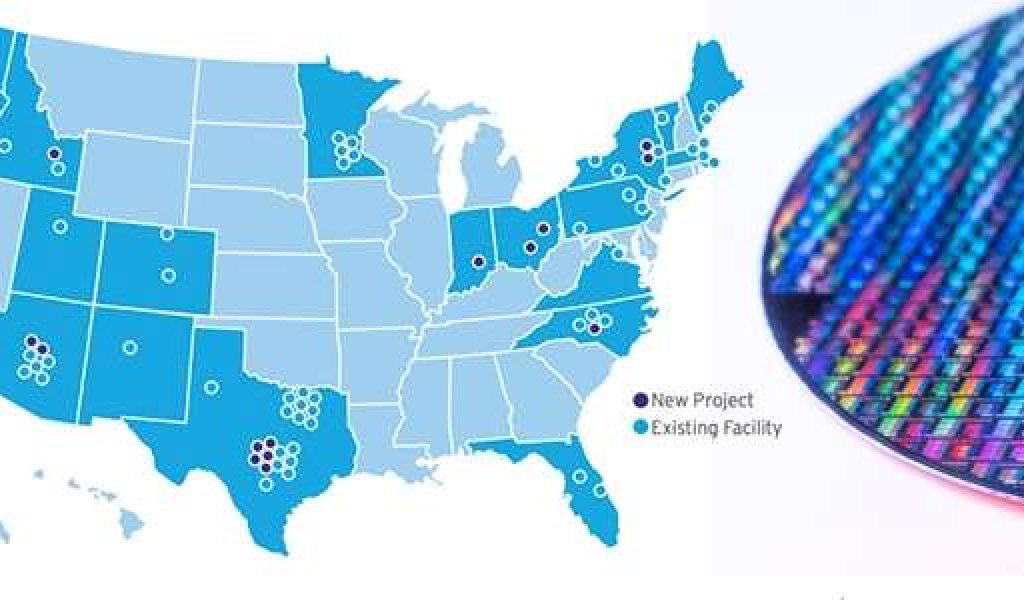
Projected Increase in Semiconductor Manufacturing Facilities
The projected increase in semiconductor manufacturing facilities in the US is expected to be substantial. Several companies have already announced plans to build new fabs, and the incentives are attracting additional investment.
| Year | Projected Number of New Facilities | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 3 | Initial wave of investment, driven by early subsidies. |
| 2025-2027 | 5-7 | Expansion driven by growing demand and positive feedback loop. |
| 2028-2030 | 8-12 | Further expansion and maturation of the domestic industry. |
Note: These projections are based on current announcements and anticipated government support. Actual numbers may vary based on various factors, including regulatory approvals, market conditions, and unexpected delays. The growth will be uneven, but the overall trend points towards a significant increase in the number of semiconductor fabrication plants within the United States.
International Relations and Trade Implications: Semiconductors Chips Us Subsidies
US government subsidies for semiconductor manufacturing are likely to reshape the global landscape of the industry. This intervention, while intended to bolster domestic production, has the potential to spark a domino effect, impacting international trade relationships and global supply chains. The potential for trade disputes and retaliatory measures cannot be ignored, demanding careful navigation to avoid significant disruptions.The introduction of substantial financial incentives for semiconductor production in the US is poised to attract significant investment and production to American shores.
This shift could disrupt existing global supply chains, as companies re-evaluate their production strategies in response to the altered economic environment.
Potential for Trade Disputes
The US subsidies, if perceived as unfair trade practices by other nations, could trigger retaliatory measures. Other countries might introduce similar subsidies or tariffs to protect their own industries, potentially escalating the conflict and harming the global economy. For example, if China were to retaliate against the US semiconductor subsidies with tariffs or its own subsidies, it could disrupt the flow of semiconductors across the globe, leading to shortages and increased prices.
Existing trade agreements might be challenged or renegotiated.
Impact on Global Semiconductor Supply Chains
US subsidies could lead to a fragmentation of the global semiconductor supply chain. Companies might prioritize domestic production over international partnerships, seeking to insulate themselves from potential trade disputes or political pressures. This fragmentation could result in higher costs for semiconductors and slower innovation as companies may struggle to access the full range of specialized expertise and materials necessary to maintain efficient production.
The “reshoring” of semiconductor manufacturing to the US might create regional imbalances, creating a more fragmented and potentially less efficient global system.
Comparison of US Subsidy Programs with Other Nations
| Country | Key Subsidy Programs | Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|
| United States | CHIPS Act, incentives for domestic production | Boosting domestic manufacturing, enhancing national security, fostering innovation |
| South Korea | Government funding for research and development, subsidies for chip fabrication | Supporting advanced semiconductor technology, maintaining global competitiveness |
| Taiwan | Subsidies for chip manufacturing and research, tax incentives | Sustaining its leading role in the semiconductor industry, fostering innovation |
| Netherlands | Investment incentives for chip manufacturing facilities | Attracting foreign investment, bolstering semiconductor capabilities |
The table highlights the varying approaches to semiconductor industry support among major players. These programs reflect the specific national priorities and goals of each country. Comparing these initiatives provides valuable insights into the evolving global semiconductor landscape and the competitive pressures driving the industry’s evolution.
Technological Advancements and Innovation
US government subsidies for semiconductors are poised to significantly impact the trajectory of technological advancement in the industry. These financial incentives, focused on bolstering domestic production, are not just about building factories; they’re about creating a fertile ground for innovation and breakthroughs. The hope is that this concentrated investment will lead to a cascade effect, driving improvements across the entire semiconductor value chain.The subsidies are expected to accelerate the development and deployment of cutting-edge technologies, from materials science to manufacturing processes.
US subsidies for semiconductor chips are a hot topic right now, but hey, sometimes you just need a break from the tech world. Speaking of breaks, have you checked out the subway weekend festivities in Jose Lasalle? Subway weekend Jose Lasalle is a great way to unwind and appreciate local culture. While these events are fun, the importance of US government support for semiconductor manufacturing remains critical for the future of technology innovation.
This targeted support could lead to breakthroughs in areas like faster processing speeds, improved energy efficiency, and enhanced integration capabilities in chips. This will ultimately benefit various sectors reliant on semiconductor technology, such as computing, communication, and healthcare.
Link Between Subsidies and Technological Advancements
The US semiconductor industry is incentivized by these subsidies to focus on cutting-edge research and development. The financial backing fosters innovation by enabling companies to invest in pioneering research projects, experimental manufacturing processes, and the development of novel materials. This investment fuels a virtuous cycle, pushing the boundaries of semiconductor technology and driving the development of next-generation products.
US subsidies for semiconductor chip manufacturing are a hot topic right now, but it’s important to remember that global health initiatives are equally crucial. Protecting public health, like preventing the spread of HIV/AIDS through proper safe sex practices, is vital. Condom use in preventing HIV/AIDS is a critical aspect of this, and it’s something that needs sustained global attention.
Ultimately, focusing on both semiconductor chip advancements and public health initiatives is essential for a balanced and healthy future, and these US subsidies will likely play a key role in the global tech race.
Potential for Innovation and Breakthroughs
The potential for innovation in semiconductor technology is vast. The subsidies can drive breakthroughs in several key areas. These include novel materials with superior electrical properties, new architectures for chip design, and more efficient manufacturing techniques. These advancements can lead to faster, more energy-efficient, and more powerful semiconductor devices. Examples of this include creating chips with integrated photonic circuits for faster data transmission, or developing novel materials for higher thermal conductivity to reduce chip overheating.
Specific Technologies Fostered by Subsidies
The subsidies can significantly impact the development of several key technologies.
US subsidies for semiconductor chip production are a hot topic right now, but did you know that sometimes, the most fascinating parallels can be found in unexpected places? For instance, the intricate world of Broadway cast albums, like the haunting melodies of Sweeney Todd, broadway cast albums sweeney todd , offer a similar kind of meticulous craftsmanship and dedication to detail.
Ultimately, both the intricate chip manufacturing process and the creation of these captivating soundtracks highlight the dedication and innovation needed to bring something extraordinary to life. This all comes back to the intricate web of US semiconductor chip subsidies.
- Advanced Packaging Technologies: Subsidies can encourage research and development in innovative packaging techniques that reduce chip size and improve heat dissipation. This could result in smaller, more efficient devices. These advanced packaging techniques could integrate various components onto a single chip, enabling more complex and integrated functionalities.
- New Materials for Semiconductor Fabrication: The subsidies could stimulate the development and utilization of novel materials, such as gallium nitride or graphene, which possess superior electrical and thermal properties. This could lead to more efficient and powerful chips, potentially for applications requiring high-frequency operation or high-power handling.
- Quantum Computing: Subsidies could foster research and development in quantum computing, potentially leading to the creation of quantum-based semiconductor devices. This is a long-term vision, but the support could be a crucial factor in pushing the field forward.
Influence on Next-Generation Semiconductors
The subsidies are expected to have a profound influence on the development of next-generation semiconductors. These include:
- Increased Processing Power: Advancements in chip design and materials science could result in exponentially higher processing speeds and greater computing power.
- Enhanced Energy Efficiency: The development of new materials and architectures can lead to more energy-efficient chips, crucial for sustainable technological advancement.
- Improved Integration Capabilities: More advanced packaging and integration techniques could lead to denser chips, enabling more complex functionalities in smaller spaces.
Environmental Considerations
The semiconductor industry, while crucial for technological advancement, carries a significant environmental footprint. From the extraction of raw materials to the complex manufacturing processes, the industry consumes substantial energy and generates considerable waste. This chapter examines the environmental impact of semiconductor manufacturing, highlighting the potential of subsidies to drive sustainable practices and reduce the industry’s ecological burden.The growing demand for semiconductors fuels the need for more efficient and sustainable production methods.
Environmental regulations and a global shift towards sustainability provide a critical framework for the industry’s future. Subsidies can play a vital role in incentivizing companies to adopt these environmentally friendly practices, potentially leading to significant improvements in the industry’s overall ecological performance.
Environmental Impact of Semiconductor Manufacturing
Semiconductor manufacturing encompasses a broad range of processes, each contributing to the overall environmental impact. The extraction and processing of raw materials, like silicon and rare earth elements, often involve significant energy consumption and generate substantial waste. Manufacturing facilities themselves consume vast amounts of energy, from the initial heating and cooling processes to the intricate lithography and etching stages.
Furthermore, the disposal of hazardous chemicals and byproducts poses a significant challenge.
Environmental Regulations Related to Semiconductor Manufacturing, Semiconductors chips us subsidies
Environmental regulations play a crucial role in mitigating the environmental impact of semiconductor manufacturing. Governments worldwide are enacting stricter regulations on emissions, waste disposal, and water usage. These regulations aim to reduce the industry’s negative footprint and promote sustainable practices. Specific regulations may vary by region, but the overarching goal is to minimize the environmental damage associated with semiconductor production.
Examples include stricter limits on the release of harmful chemicals into the atmosphere and stricter guidelines for wastewater treatment.
Potential of Subsidies to Encourage Eco-Friendly Technologies
Subsidies can significantly incentivize the adoption of eco-friendly technologies in semiconductor production. Financial support can be directed towards research and development of sustainable materials, processes, and technologies. This could include funding for alternative energy sources within semiconductor facilities, the development of closed-loop recycling systems, and the implementation of innovative waste management strategies. By lowering the cost of adopting eco-friendly solutions, subsidies can encourage widespread adoption, thus driving a transition towards a more sustainable semiconductor industry.
Environmental Impact of Different Semiconductor Materials
The choice of materials used in semiconductor production significantly impacts the environmental footprint. Silicon, the primary material, requires significant energy for its extraction and purification. Rare earth elements, often crucial components in advanced semiconductors, are often mined in environmentally sensitive regions, potentially causing habitat destruction and contamination. The environmental impact of these materials varies, and careful consideration is needed during material selection.
Research into alternative materials with a lower environmental footprint is crucial. For example, exploring the use of more readily available and sustainably sourced materials could reduce the overall environmental burden. A detailed analysis of the life cycle assessment of different materials is essential to inform material selection decisions.
Sustainable Practices in Semiconductor Manufacturing
Sustainable practices in semiconductor manufacturing involve a multifaceted approach. Strategies include optimizing energy consumption through the use of renewable energy sources, implementing closed-loop recycling systems to minimize waste, and developing innovative water management techniques to reduce water usage. Developing robust recycling systems is essential to minimize the environmental impact of semiconductor waste. Furthermore, stricter regulations and enforcement mechanisms will be crucial to promote sustainable practices across the industry.
Economic Considerations Beyond Manufacturing
The US semiconductor industry subsidies aren’t just about building new factories; they represent a significant economic intervention with ripple effects throughout the entire economy. Understanding these wider implications is crucial to evaluating the long-term benefits and potential challenges. These subsidies aim to bolster the entire ecosystem surrounding semiconductor production, from material suppliers to software developers.This economic intervention, while potentially boosting the US semiconductor sector, also necessitates a comprehensive understanding of its influence on related industries and the broader economy.
The subsidies are intended to create a more robust and competitive domestic semiconductor industry, but their impact extends beyond the manufacturing floor, influencing innovation, technology development, and the overall economic landscape.
Potential Effects on the Wider US Economy
The US semiconductor industry is deeply interwoven with other sectors. Increased domestic production of semiconductors will create new jobs and stimulate economic activity in associated industries, including material science, engineering, and logistics. Furthermore, the availability of domestically produced semiconductors will lower the cost of electronics for consumers and businesses, potentially stimulating demand and economic growth in various sectors.
For example, the automotive industry’s reliance on semiconductors for vehicle electronics is undeniable; a stronger US semiconductor sector could lead to cost reductions and improved vehicle technology.
Influence on Supporting Industries and Technologies
The subsidies will likely encourage the development of supporting industries and technologies, creating a virtuous cycle. These include materials science for semiconductor production, specialized equipment manufacturing, and advanced design software. The availability of high-quality, competitively priced US-made semiconductors will drive innovation in downstream industries, pushing them to adopt new technologies and enhance their own production processes. For example, the development of advanced packaging techniques for semiconductors is a crucial aspect of the semiconductor ecosystem, and increased domestic production will likely drive research and development in this area.
Downstream Effects on Related Industries
The effects will extend beyond the direct semiconductor supply chain. A stronger US semiconductor sector will boost related industries, such as consumer electronics, automotive, and medical devices, enabling them to innovate more rapidly and reduce costs. This could translate into higher productivity, improved efficiency, and enhanced competitiveness for these sectors in the global market. A good example of this is the use of advanced semiconductors in medical imaging equipment.
Long-Term Economic Benefits
The long-term benefits of these subsidies extend beyond immediate job creation. They include the potential for a more resilient and innovative US economy, increased technological leadership, and a reduced dependence on foreign suppliers. This will create a more competitive and technologically advanced nation, potentially impacting global trade dynamics and influencing international relations. For instance, the US could become a leader in the development of cutting-edge semiconductor technologies, potentially creating new industries and employment opportunities in the future.
Public Perception and Societal Impact
US semiconductor subsidies have ignited a complex discussion, not just within the industry but also in the public sphere. The potential for boosting domestic production and technological advancement is undeniable, but public perception is often shaped by concerns about fairness, economic impact, and the potential for unintended consequences. Understanding these perspectives is crucial to navigating the evolving landscape of semiconductor policy.Public perception of these subsidies is varied and often influenced by factors such as political leanings, economic anxieties, and perceived trade implications.
Some view the subsidies as necessary investments in national security and technological leadership, while others express concerns about their fairness and potential impact on global trade relations. This complex interplay of opinions requires careful consideration of both the potential benefits and drawbacks.
Public Discourse and Concerns
Public discourse surrounding US semiconductor subsidies often centers on questions of fairness and competitiveness. Concerns are raised about the potential for “unfair” advantages in the global market, prompting anxieties about retaliatory measures from other nations. These concerns highlight the delicate balance between fostering domestic innovation and maintaining a level playing field in international trade. Examples of such public discourse include online forums, social media discussions, and op-eds published in various news outlets.
Potential Societal Impacts
The societal impacts of semiconductor subsidies extend beyond the manufacturing sector. Positive impacts could include the creation of high-skilled jobs, increased technological advancement, and improved national security. However, potential negative impacts include job displacement in other sectors, particularly if the subsidies lead to a shift in manufacturing focus. The overall societal impact will depend on how effectively the government addresses the potential downsides.
For example, retraining programs for workers affected by the shift to semiconductor production could mitigate negative impacts.
Impact on Job Displacement and Other Societal Concerns
While semiconductor subsidies aim to boost domestic production, they may also lead to job displacement in other sectors. The shift in investment and production towards semiconductor-related industries could potentially leave workers in other sectors without employment opportunities. Government initiatives to mitigate these risks, such as workforce retraining programs and investments in affected industries, are crucial. In a similar vein, the potential for wage stagnation in sectors unaffected by the shift in production should also be considered.
US subsidies for semiconductor chips are a hot topic right now, but the ripple effects are felt far beyond the tech world. The booming demand for these chips is impacting the housing market near NYC, housing market near nyc , as construction costs rise and materials become scarce. Ultimately, these subsidies are likely to influence the broader economy, impacting everything from home prices to the availability of new tech products.
Examples of Public Discourse and Concerns
Public discourse regarding semiconductor subsidies often revolves around the perception of fairness in international trade. Some critics argue that these subsidies give US companies an unfair advantage, potentially triggering retaliatory measures from other countries. Concerns about the potential for trade wars and the disruption of established global supply chains are prominent. Furthermore, discussions around the environmental impact of semiconductor manufacturing are also emerging, prompting public discourse regarding the sustainability of these investments.
These concerns are vital to understand the nuances of public perception and the potential societal impact.
Comparative Analysis of Alternative Strategies
The US approach to semiconductor subsidies, while generating considerable debate, represents just one strategy among many for fostering technological advancement in the sector. Understanding alternative approaches is crucial for evaluating the US strategy’s effectiveness and potential unintended consequences. Different countries have adopted diverse models, ranging from direct government investment to fostering a supportive ecosystem through research and development initiatives.
This analysis explores these alternatives, highlighting their potential benefits and drawbacks.The effectiveness of any approach depends heavily on a nation’s specific context, including existing industrial infrastructure, research capabilities, and the overall investment climate. A tailored strategy, rather than a one-size-fits-all model, is likely to yield the most favorable outcomes.
Alternative Strategies for Semiconductor Development
Various approaches exist for promoting semiconductor development, each with unique characteristics and implications. These strategies often overlap and can be combined to create a comprehensive national semiconductor development plan.
Government-Led Investment
Some nations prioritize direct government investment in semiconductor research and development, manufacturing facilities, and workforce training programs. This approach can be rapid and focused, but it often carries significant financial risks and can lead to concerns about government overreach and potential inefficiencies. Examples include South Korea’s heavy investment in semiconductor manufacturing capacity, aimed at achieving global leadership.
Public-Private Partnerships
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) combine government funding with private sector participation. These partnerships can leverage the expertise and resources of both sectors, potentially reducing risks and maximizing efficiency. Examples include collaborative research initiatives between governments and semiconductor companies, as seen in several European nations, aimed at developing cutting-edge technologies.
Ecosystem Development
Focusing on building a robust semiconductor ecosystem—encompassing research institutions, universities, skilled labor pools, and supportive regulatory frameworks—is another strategy. This approach often takes longer to yield significant results but can create a sustainable environment for long-term innovation and competitiveness. Taiwan’s emphasis on cultivating a strong ecosystem of research and development institutions has been instrumental in its success in the semiconductor industry.
Tax Incentives and Subsidies
Tax incentives and subsidies can provide financial support to semiconductor companies, encouraging investment in research, development, and manufacturing within a nation’s borders. These policies, while potentially effective, can be susceptible to lobbying pressures and may not always lead to the desired outcomes.
Comparison of Costs and Effectiveness
A comparative analysis of the costs and effectiveness of different approaches is complex. The return on investment (ROI) for each strategy varies depending on the specific circumstances and the degree to which it aligns with national objectives. Factors like technological advancements, economic conditions, and global market dynamics all play a role.
| Strategy | Potential Benefits | Potential Drawbacks | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Government-Led Investment | Rapid development, targeted support | Financial risk, potential inefficiency | South Korea |
| Public-Private Partnerships | Leveraging expertise, shared risk | Potential for bureaucracy, negotiation challenges | European nations |
| Ecosystem Development | Sustainable innovation, long-term competitiveness | Slower return on investment, need for sustained commitment | Taiwan |
| Tax Incentives and Subsidies | Attracting investment, promoting domestic production | Potential for distortionary effects, lobbying pressures | Various countries |
Final Review
In conclusion, US semiconductor subsidies are a powerful tool with the potential to significantly reshape the global semiconductor industry. While offering opportunities for domestic production growth, technological innovation, and job creation, they also present complex challenges regarding international relations, trade implications, and environmental sustainability. The long-term effects remain to be seen, but one thing is clear: these subsidies will play a major role in shaping the future of technology.
Q&A
What are the different types of US semiconductor subsidies?
US semiconductor subsidies encompass various forms, including direct grants for research and development, tax incentives for investments in manufacturing facilities, and loan programs to support startup companies. The specific types and targets of these subsidies are continuously evolving.
How do these subsidies impact international trade relations?
The implementation of US semiconductor subsidies could trigger retaliatory measures from other nations, leading to trade disputes and potentially disrupting global semiconductor supply chains. This can have significant implications for businesses and consumers worldwide.
What are the potential environmental concerns related to semiconductor manufacturing?
Semiconductor manufacturing processes can generate significant environmental concerns, including water pollution and the use of hazardous materials. The subsidies may influence the adoption of sustainable practices, but the environmental impact needs careful consideration.
What are the potential job creation effects of these subsidies?
The subsidies have the potential to stimulate job creation in the semiconductor sector and related industries. However, the precise number of jobs created depends on various factors such as the efficiency of the programs and the responsiveness of the private sector.

