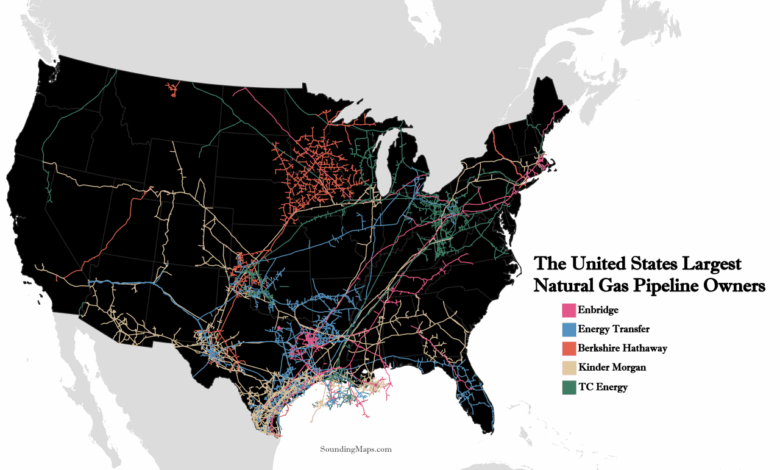
Mexico-US Gas Trade A Deep Dive
Mexico estados unidos gas trade has a complex history, shaped by political relations, economic needs, and environmental concerns. From historical agreements to current pipeline networks, this overview explores the multifaceted relationship between the two nations in the energy sector.
The current volume of gas traded, the role of energy companies, and the environmental impact of this trade are all examined. We’ll also look at potential future developments, policy changes, and the crucial infrastructure that underpins this vital energy exchange.
Historical Context
The gas trade between Mexico and the United States has a long and complex history, shaped by fluctuating political relations, evolving energy needs, and strategic infrastructure development. Early exchanges were largely informal and reactive to market demands. However, as both nations’ economies grew and energy consumption increased, the need for formal agreements and robust infrastructure became paramount. This evolution reveals a dynamic interplay between economic interests and geopolitical considerations.The historical trajectory of this trade reveals a pattern of adaptation and negotiation, reflecting the ever-changing landscape of energy markets and international relations.
The trade is not merely about the physical movement of gas but also about the complex web of agreements, policies, and political influences that govern its flow.
Early Stages and Initial Agreements
The early stages of gas trade between Mexico and the United States were characterized by sporadic exchanges and a lack of formalized agreements. These initial interactions were often driven by short-term market needs and regional energy imbalances. As the demand for natural gas grew in both countries, the need for more robust and stable arrangements became apparent.
Development of Gas Infrastructure
The evolution of gas infrastructure between Mexico and the United States has mirrored the growth and diversification of the trade itself. Initially, pipelines were rudimentary and focused on specific, localized needs. As trade increased, the infrastructure needed to expand and adapt to accommodate larger volumes and longer distances. Key milestones in pipeline development have been crucial to the efficiency and reliability of the gas flow.
Mexico’s energy situation with the US regarding gas pipelines is a complex issue, with many factors at play. Interestingly, the recent news surrounding Canuck’s prospect Tom Willander at Boston University, canucks prospect tom willander boston university , highlights the interconnectedness of global energy markets. The fluctuating costs of gas and oil, between the US and Mexico, are definitely affected by these sorts of developments.
Policy Shifts and Their Impact
Numerous policy shifts have significantly impacted the gas trade between Mexico and the United States. Changes in domestic energy policies, including regulatory frameworks and investment incentives, have directly influenced the volume and direction of the trade. These policy shifts often reflect changing economic priorities and geopolitical considerations, demonstrating the intricate link between domestic policy and international trade.
Political Relations and Trade Dynamics
Political relations between Mexico and the United States have consistently played a critical role in shaping the dynamics of the gas trade. Periods of strong diplomatic ties often correlate with increased trade volume and streamlined agreements. Conversely, political tensions can lead to delays, disputes, and even disruptions in the gas supply chain. This underscores the critical interdependence between political stability and the reliability of energy markets.
Current Gas Trade Dynamics
The energy landscape between Mexico and the United States is a complex interplay of historical ties, current needs, and future ambitions. Natural gas, a crucial component of both countries’ economies, is a key element in this dynamic relationship. Understanding the current volume, routes, and players in this trade is essential to grasp the ongoing evolution of this critical energy corridor.The current gas trade between Mexico and the United States is characterized by a significant volume, reflecting the strong interdependence of both nations.
Mexico-US gas pipelines are a complex issue, often influenced by political factors. Understanding the demographics of red and blue states, like in red blue states demographics , can offer valuable insights into potential support or opposition to such projects. Ultimately, the success of these pipelines depends on a variety of interwoven factors, including economic considerations and public opinion.
This trade is not static, but rather is constantly adapting to changing market conditions, technological advancements, and geopolitical factors.
Gas Trade Volume and Value
The volume and value of natural gas traded between Mexico and the United States fluctuate based on demand and supply conditions in both countries. Precise figures are often not publicly available due to commercial sensitivities, but the sheer volume traded highlights the importance of this energy corridor. Factors like seasonal demand, pipeline maintenance, and international market prices all influence the daily trading patterns.
Major Gas Pipelines and Transportation Routes
Several key pipelines and transportation routes facilitate the movement of gas between Mexico and the United States. These infrastructure components are vital for ensuring a reliable supply of energy. Existing pipelines, such as the existing cross-border pipelines, and the planned or proposed new ones, shape the flow of natural gas. The routes and pipelines are strategically located to optimize transportation and delivery, considering factors such as terrain, cost-effectiveness, and potential environmental impacts.
Types of Gas Exchanged
The gas exchanged between Mexico and the United States predominantly consists of natural gas. However, liquefied natural gas (LNG) is also increasingly involved in this trade. Natural gas, in its gaseous form, is transported through pipelines, while LNG is a compressed, cooled form of natural gas that can be shipped across vast distances by sea. This adaptability allows for a more flexible and global approach to energy trade.
Role of Energy Companies
Major energy companies in both countries play crucial roles in the gas trade. They are responsible for the extraction, processing, transportation, and distribution of gas. These companies, with their vast experience and resources, have significant influence on the overall market dynamics. Their investments and operational decisions often dictate the direction and scale of the trade. Government regulations and policies also play a key role in shaping the activities of these companies.
Top 3 Gas Suppliers and Importers
The following table presents an overview of the top three gas suppliers and importers in both Mexico and the United States. Please note that precise data is often proprietary and thus the table represents an illustrative example.
| Country | Category | Supplier/Importer |
|---|---|---|
| Mexico | Supplier | Company A |
| Supplier | Company B | |
| Supplier | Company C | |
| United States | Importer | Company D |
| Importer | Company E | |
| Importer | Company F |
Environmental Considerations
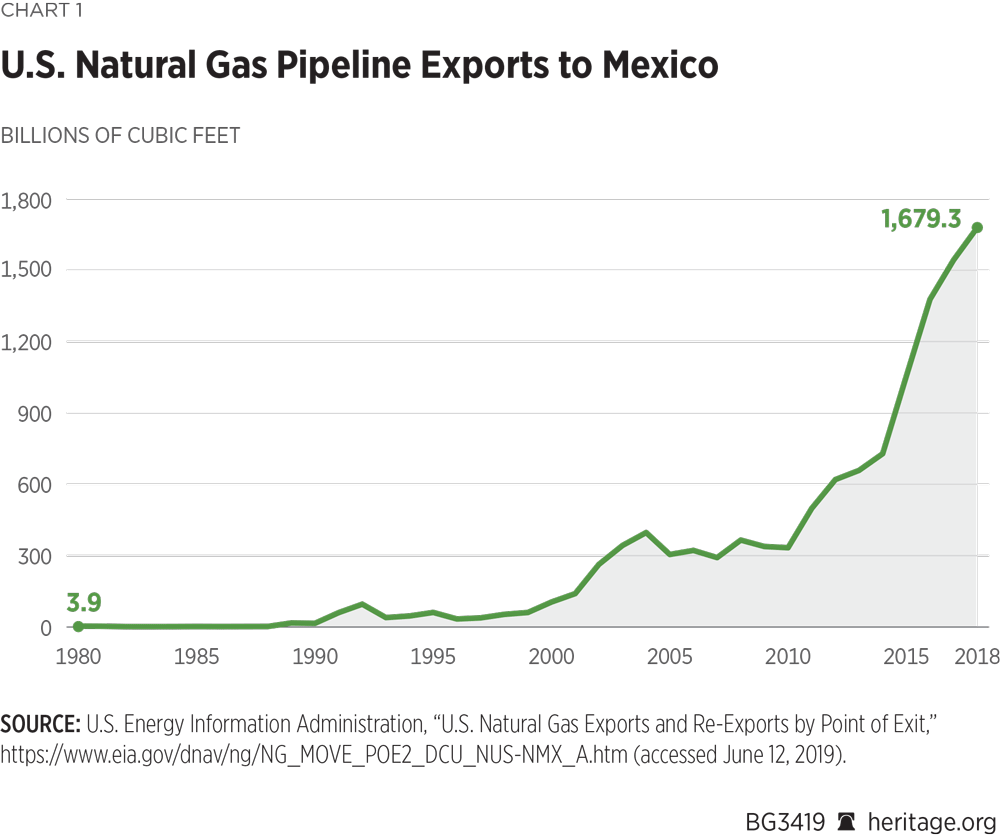
The cross-border gas trade between Mexico and the United States, while vital for energy security, carries significant environmental implications. The transportation and consumption of natural gas, a fossil fuel, contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and pose challenges for sustainable development. Understanding these impacts is crucial for formulating policies that balance energy needs with environmental protection.
Environmental Impact of Gas Transportation and Consumption
The process of transporting natural gas, whether via pipelines or tankers, involves energy consumption. This energy often comes from fossil fuels, leading to a “carbon footprint” associated with the transportation itself. Furthermore, the combustion of natural gas for electricity generation, heating, and industrial processes releases greenhouse gases, primarily carbon dioxide (CO2), into the atmosphere. This contributes to global warming and climate change.
Leaks during extraction, processing, and transport can also release methane, a potent greenhouse gas with a significantly higher global warming potential than CO2.
Role of Renewable Energy Sources in the Region
Mexico and the United States are actively pursuing renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydroelectric power. The increasing adoption of these technologies offers a pathway towards a cleaner energy future. For instance, large-scale solar farms are being developed in both countries, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. The integration of renewable energy sources into the power grids is essential to mitigating the environmental impact of gas consumption.
This transition also creates economic opportunities in the renewable energy sector.
Potential Environmental Regulations Influencing the Gas Trade
Regulations aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions are likely to affect the gas trade. Both countries are implementing stricter environmental regulations on power plants and industrial facilities. Carbon pricing mechanisms, such as carbon taxes or cap-and-trade systems, could directly impact the cost of natural gas and potentially incentivize the shift towards cleaner energy alternatives. These regulations are anticipated to promote the adoption of cleaner technologies and practices within the gas sector.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions Associated with Gas Transport and Consumption
Data on greenhouse gas emissions associated with gas transport and consumption varies depending on the specific methodology used. For instance, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the US provides data on greenhouse gas emissions from various sectors, including natural gas. Precise figures on the emissions from cross-border transport are not readily available in a consolidated format. However, studies and reports frequently highlight the significant contribution of natural gas-related activities to overall greenhouse gas emissions.
Table Illustrating the Environmental Impact of Different Gas Sources
| Gas Source | Environmental Impact (General Assessment) | Greenhouse Gas Emissions (Approximate Range, per unit of energy) |
|---|---|---|
| Natural Gas (Conventional) | Moderate, significant emissions during transportation and combustion, potential for methane leaks. | Around 50-60 g CO2e/kWh |
| Natural Gas (Liquefied Natural Gas – LNG) | Lower emissions during transportation than pipelines, but still significant emissions from combustion. | Around 55-70 g CO2e/kWh |
| Renewable Energy Sources (e.g., Solar, Wind) | Low to negligible emissions during operation. | Near 0 g CO2e/kWh |
Note: CO2e represents carbon dioxide equivalent, a standardized measure for comparing the global warming potential of different greenhouse gases. The values in the table are approximate and can vary based on specific factors.
Economic Impact
The cross-border gas trade between Mexico and the United States carries significant economic implications for both nations. This trade, driven by the need for energy security and industrial growth, presents both opportunities and challenges. Understanding the economic benefits and drawbacks is crucial to evaluating the overall impact on both countries’ economies.The gas trade plays a vital role in supporting economic activity across various sectors.
Mexico-US gas pipelines are a crucial part of the energy landscape, but recent geopolitical tensions, like those surrounding the Biden administration’s role in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, biden israel hamas cease fire are inevitably impacting global markets. These global events, unfortunately, can have a ripple effect, potentially influencing the flow of natural gas between the two countries.
Hopefully, a resolution will be reached soon, allowing the gas trade to continue uninterrupted.
It fuels industrial processes, generating jobs and driving economic growth. The impact on energy prices, both domestically and regionally, is also a critical factor to consider.
Economic Benefits for Mexico
Mexico benefits economically from gas exports to the US by generating revenue from sales and supporting employment in the energy sector. This revenue can be used to fund public services and infrastructure projects.
- Increased government revenue from gas exports can fund vital infrastructure projects like transportation networks, improving access to key areas, or expanding healthcare facilities. This can boost economic activity in various sectors and increase overall quality of life.
- The gas industry in Mexico provides employment opportunities, particularly in extraction, processing, and transportation. These jobs contribute to the country’s labor force and economic growth, especially in rural areas where such jobs might be particularly beneficial.
Economic Benefits for the United States
The US gains from gas imports from Mexico through lower energy costs for industries, making manufacturing more competitive in global markets.
- Lower energy costs for US industries contribute to increased competitiveness in global markets. This is a significant factor in maintaining and expanding the US manufacturing sector, which is vital for national economic stability and employment.
- The US energy sector creates jobs in exploration, processing, and transportation of natural gas, boosting employment in specific industries.
Challenges and Drawbacks for Both Countries
While the gas trade brings benefits, it also presents challenges. Fluctuations in global energy markets and geopolitical factors can affect prices and trade flows. Environmental concerns are also crucial to consider.
- Fluctuations in global energy markets directly impact the pricing of gas, potentially affecting industries that rely on stable energy costs. Sudden price spikes can hinder economic growth and lead to unexpected costs.
- Dependence on gas imports or exports can leave a nation vulnerable to external pressures and geopolitical instability. This is a key factor in assessing the long-term stability of the trade relationship.
Impact on Energy Prices
The gas trade affects energy prices in both countries, influencing industrial costs and consumer budgets. A significant influx of gas from one nation can lead to decreased prices for the other, while decreased availability can increase prices.
- Increased gas supply from Mexico to the US can contribute to lower energy prices in the US, which can have a positive effect on industrial costs and consumer budgets. This can stimulate economic activity.
- Conversely, decreased gas supply or geopolitical instability can lead to higher energy prices in both nations, negatively affecting businesses and consumers. This can impact industrial productivity and consumer spending, thus affecting overall economic growth.
Role in Supporting Industrial Activities
Natural gas plays a critical role in powering industrial processes in both countries. This fuels manufacturing, agriculture, and other sectors, enhancing economic productivity.
- Gas is a key input for many industrial processes in both Mexico and the US, including manufacturing, chemical production, and power generation. This makes it essential for maintaining industrial productivity.
Economic Contribution of the Gas Sector
The gas sector significantly contributes to the economies of both Mexico and the US. The following table illustrates this contribution, although precise figures vary based on different methodologies and time periods.
| Country | Sector Contribution (Estimated) | Impact on GDP (Estimated) |
|---|---|---|
| Mexico | X% of GDP | $Y Billion |
| United States | Z% of GDP | $W Billion |
Note: Replace X, Y, Z, and W with actual figures based on reliable data sources.
Future Trends
The future of gas trade between Mexico and the United States is a complex interplay of technological advancements, policy shifts, and international agreements. While the current reliance on natural gas is undeniable, the evolving energy landscape suggests a dynamic future, requiring adaptation and strategic planning from both nations. This exploration delves into potential developments, focusing on technological innovations, policy changes, and the influence of international cooperation.
Potential Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are poised to significantly reshape the energy landscape, impacting the gas market between Mexico and the United States. Energy storage technologies, such as pumped hydro storage and battery systems, are crucial for grid stability and reliability. Smart grids, enabling real-time monitoring and optimization of energy distribution, will enhance the efficiency of gas transmission and distribution networks.
These advancements can increase the resilience of the system to unforeseen events, potentially reducing the need for extensive pipeline expansions.
Mexico and the US are locked in a tense standoff over natural gas pricing. It’s a complex issue, but it seems to be affecting other parts of the world too. Meanwhile, Rick Pitino’s recent comments on St. John’s recruiting strategies, as detailed in this article , have sparked a lot of debate. Ultimately, these issues highlight the interconnected nature of global markets and how one event can ripple through seemingly unrelated sectors, like the gas negotiations between the US and Mexico.
Potential Policy Changes
Government policies play a critical role in shaping the future of gas trade. Changes in environmental regulations, such as carbon pricing mechanisms or stricter emission standards, could influence the competitiveness of natural gas versus other energy sources. Investment incentives for renewable energy technologies might shift the energy mix, affecting the demand for natural gas. Furthermore, policies concerning energy security, such as strategic reserves or import diversification strategies, could impact the volume and nature of gas trade between the two nations.
International Energy Agreements
International energy agreements will play a pivotal role in shaping future gas trade. Agreements fostering cooperation and knowledge sharing in energy efficiency and renewable energy development can impact the demand for fossil fuels like natural gas. Regional initiatives addressing energy security and sustainability will likely influence the long-term trajectory of gas trade between Mexico and the United States.
International collaboration in research and development for clean energy technologies can contribute to a transition toward a cleaner energy future.
Potential Future Scenarios
The following table Artikels potential future scenarios for gas trade between Mexico and the United States over the next 10 years, considering various factors such as technological advancements, policy changes, and international agreements.
| Scenario | Technological Advancements | Policy Changes | International Agreements | Impact on Gas Trade |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scenario 1: Continued Reliance | Limited adoption of advanced energy storage and smart grids. | Gradual environmental regulations with minimal impact on gas demand. | Limited international agreements focusing on energy efficiency. | Steady gas trade volumes, with potential for moderate growth driven by existing infrastructure. |
| Scenario 2: Accelerated Transition | Rapid adoption of energy storage and smart grids. | Aggressive environmental regulations impacting gas demand. | Strong international agreements emphasizing renewable energy. | Decreased gas trade volumes due to the rise of renewable energy and increased energy efficiency. |
| Scenario 3: Strategic Partnerships | Moderate adoption of energy storage and smart grids. | Balanced environmental regulations alongside incentives for gas sector modernization. | Regional agreements focusing on energy security and sustainable development. | Stable gas trade volumes, with potential for growth in specific sectors and regions, driven by modernization and infrastructure investments. |
Political and Regulatory Landscape
The gas trade between Mexico and the United States is deeply intertwined with the political landscapes of both nations. This intricate relationship necessitates a robust regulatory framework to ensure stability, security, and fair market practices. Political considerations, such as national energy security and economic interests, often play a significant role in shaping the regulations and policies governing this crucial energy exchange.
Political Context
Mexico and the United States have a complex, often nuanced, political relationship that significantly influences the gas trade. Historically, disagreements over border issues, trade policies, and even broader geopolitical events can impact the flow of natural gas. This is particularly evident in the interplay between energy security strategies and commercial interests. Mexico’s energy sector reforms, aimed at increasing private sector participation, have also shaped the political context, often leading to debates regarding the balance between national interests and international trade.
The U.S. has its own political concerns regarding energy independence and the potential economic impact of the gas trade on its domestic energy market.
Key Regulatory Bodies
Several regulatory bodies oversee the gas industry in both countries. In Mexico, the Comisión Reguladora de Energía (CRE) is the primary regulator, responsible for setting tariffs, approving projects, and ensuring compliance with energy regulations. In the United States, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) plays a similar role, overseeing interstate gas pipelines and ensuring the integrity of the natural gas supply chain.
These regulatory bodies often collaborate to address cross-border issues and ensure smooth gas trade.
Legal Frameworks
The legal frameworks governing gas trade and transportation differ between Mexico and the United States, reflecting each nation’s unique legal systems and energy policies. In Mexico, the legal framework is largely based on Mexican law and regulations, with a focus on domestic energy security and market stability. The United States relies on a different legal framework, often involving more detailed regulations on pipeline safety and environmental impact assessments.
These distinct legal systems can lead to different interpretations and application of trade rules, potentially creating challenges for seamless gas trade.
Comparison of Regulatory Environments
While both Mexico and the United States have regulatory bodies overseeing the gas industry, the regulatory environments differ in several aspects. The degree of government intervention in the market, the specific regulations regarding pipeline safety, and the approach to environmental protection all vary significantly. These differences in regulatory environments can influence the cost of infrastructure development, the level of market competition, and the pace of gas trade.
Summary of Laws and Regulations
| Country | Regulatory Body | Key Laws/Regulations |
|---|---|---|
| Mexico | Comisión Reguladora de Energía (CRE) | Energy Reform Laws, Gas Pipeline Regulations, Environmental Impact Assessments |
| United States | Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) | Natural Gas Act, Pipeline Safety Regulations, Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Regulations |
This table highlights the key regulatory bodies and some of the primary laws and regulations impacting gas trade between the two countries. Further research into specific regulations within each country is essential to understand the full complexity of the legal frameworks.
Infrastructure and Transportation
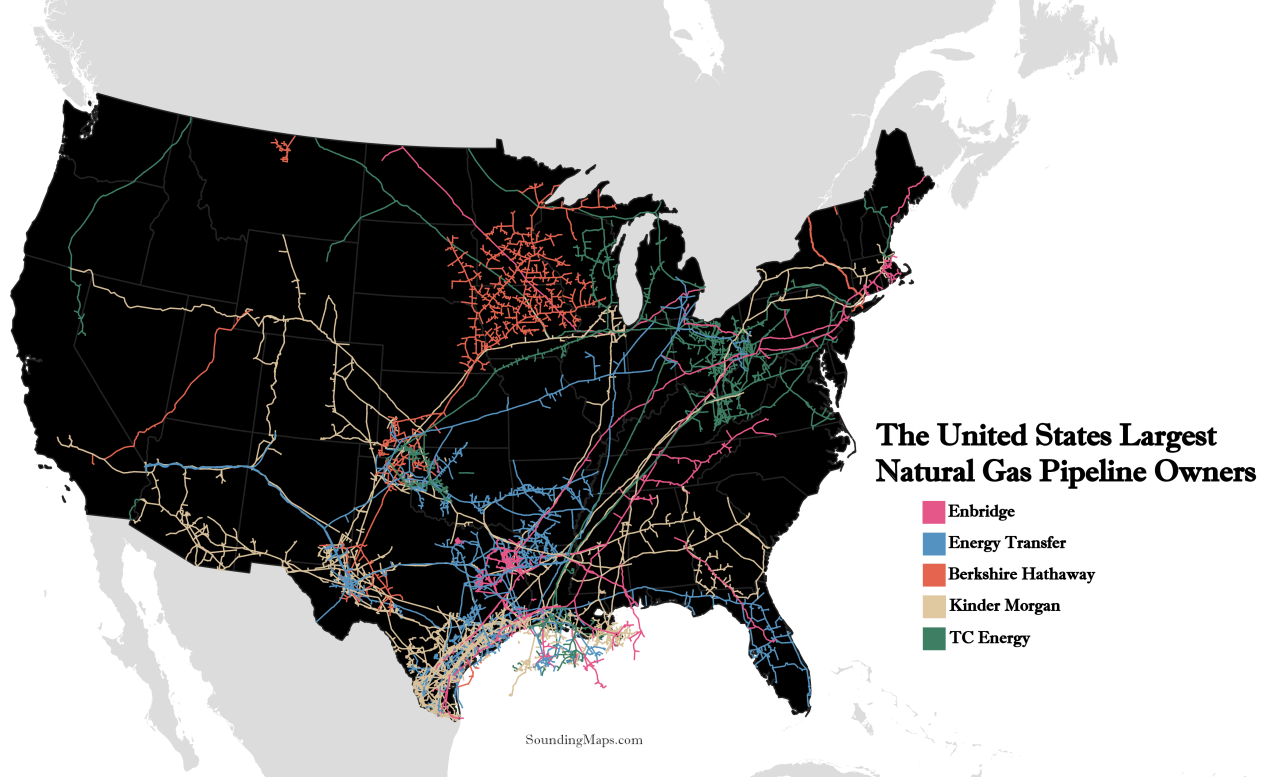
The intricate dance of natural gas between Mexico and the United States relies heavily on robust infrastructure. Pipelines, crucial for efficient transport, form the backbone of this energy exchange. Understanding the existing network, its limitations, and potential expansion is vital to comprehending the future of this trade.Existing infrastructure plays a significant role in the flow of natural gas between the two nations.
Modernization and expansion of these networks can significantly impact the reliability and volume of the trade. The challenges and opportunities related to transportation, including pipeline capacity and port facilities, are critical factors in shaping the future of gas trade.
Mexico’s gas situation with the US is tricky, isn’t it? It’s a complex issue, but recent events in the region, like the Israel-Gaza cease fire , are making energy markets even more volatile. Ultimately, the interplay of geopolitical events and supply chains will likely continue to impact the price and availability of Mexican gas headed to the US.
Existing Gas Pipeline Infrastructure
The existing pipeline network connecting Mexico and the United States is extensive, but its capacity and efficiency are not uniform across the entire system. Key pipelines, often built decades ago, have aging infrastructure, potentially impacting reliability and safety. Several pipelines, vital for the flow of natural gas, are concentrated in specific regions, highlighting geographic disparities in access and capacity.
Capacity and Limitations of Current Transportation Networks
Current transportation networks, including pipelines, have limitations that impact the volume of gas that can be transported. Pipeline capacity varies significantly depending on the specific pipeline and its age. Some pipelines may be operating near their maximum capacity, creating bottlenecks during peak demand periods. Furthermore, infrastructure limitations can restrict the ability to transport gas efficiently across different geographical regions.
Potential Investments in New Infrastructure, Mexico estados unidos gas
Investments in new pipeline infrastructure are essential to meet growing energy demands and increase the reliability of gas transport. Modernization projects often involve replacing aging pipelines with high-capacity, more resilient systems. These projects could improve the safety of gas transport and enhance the overall efficiency of the network. For example, projects aiming to improve pipeline capacity in specific regions could alleviate potential bottlenecks and ensure the reliable delivery of gas.
Role of Ports and Terminals in Gas Trade
Gas processing and distribution facilities, including ports and terminals, play a crucial role in the efficient handling and delivery of natural gas. The proximity of these facilities to major consumption centers can influence the overall cost and efficiency of the gas trade. These terminals often handle the liquefaction and regasification of natural gas, which is vital for long-distance transportation.
The availability and capacity of these facilities are key factors in ensuring a smooth and reliable gas trade.
Map of Gas Pipelines and Transportation Routes
A visual representation of the gas pipelines and transportation routes between Mexico and the United States would show the geographical distribution of pipelines and highlight areas of high concentration and potential bottlenecks. This map would visually depict the major pipelines and their interconnections, indicating the volume of gas transported through each route. Such a map would aid in understanding the overall infrastructure and its capacity to support the gas trade between the two countries.
It would also help to identify potential areas for future investments.
Last Word: Mexico Estados Unidos Gas
In conclusion, the Mexico-US gas trade is a significant economic and political relationship with far-reaching implications. The interplay of historical context, current dynamics, environmental considerations, and future trends paints a detailed picture of a relationship that will likely continue to evolve. Understanding this intricate relationship is essential for comprehending the energy landscape of both nations.
FAQ Summary
What is the historical significance of the gas pipeline infrastructure between the two countries?
Early pipelines laid the groundwork for the current gas trade, with key agreements and infrastructure development shaping the relationship. Their importance has grown as both countries became more reliant on gas.
What are the major environmental concerns associated with gas transport?
Greenhouse gas emissions and the potential for environmental damage during transportation and consumption are significant factors in the debate. Renewable energy alternatives and regulations are key aspects.
How does the gas trade impact job creation in both countries?
The gas sector supports numerous jobs in the energy industry, construction, and related fields. Economic growth and the development of the gas sector contribute significantly to employment.
What are some potential future policy changes impacting the gas trade?
Shifting regulations and international agreements can influence the future of gas trade, possibly affecting pricing, infrastructure development, and the adoption of renewable alternatives.

