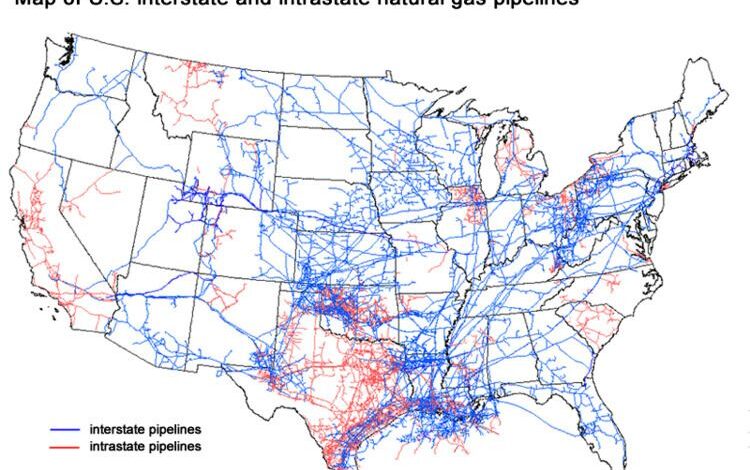
US LNG Natural Gas Leader A Deep Dive
US LNG natural gas leader: The US has emerged as a dominant force in the global natural gas market, leveraging its abundant resources and innovative technologies. This in-depth exploration delves into the factors driving this leadership, from the economic benefits and geopolitical implications to the environmental considerations and future outlook.
This analysis examines the multifaceted aspects of US LNG natural gas leadership, including the pivotal role of technological advancements, the impact on global energy markets, and the intricate interplay of economic, geopolitical, and environmental considerations. We’ll uncover the secrets behind America’s rise to prominence in this critical energy sector.
Overview of US Natural Gas Leadership

The United States stands as a global leader in natural gas production, a position solidified by a confluence of factors. Its robust infrastructure, coupled with innovative technologies, has driven unprecedented output. This dominance has significant implications for the global energy landscape and impacts domestic energy security.The US’s ascendancy in natural gas production is rooted in a multifaceted approach encompassing geological abundance, technological innovation, and supportive regulatory frameworks.
These factors have created an environment conducive to both large-scale exploration and efficient extraction, making the US a significant player in the global natural gas market.
Key Factors Contributing to US Dominance
Several key factors have propelled the US to its leading position in natural gas production. These include the availability of abundant shale gas reserves, advancements in hydraulic fracturing (fracking) technology, and a supportive regulatory environment.
- Abundant Shale Gas Reserves: The US possesses substantial reserves of shale gas, a type of natural gas found within shale formations. These reserves are often located in areas with relatively high accessibility and low production costs, compared to conventional gas fields.
- Technological Advancements in Hydraulic Fracturing (Fracking): Hydraulic fracturing, or fracking, has revolutionized natural gas extraction. This process involves injecting high-pressure fluids into shale formations to fracture the rock and release trapped gas. Significant improvements in fracking technology have dramatically increased the efficiency and profitability of natural gas extraction, enabling access to previously uneconomical reserves.
- Supportive Regulatory Environment: A regulatory environment that balances environmental concerns with economic incentives has facilitated the growth of the US natural gas industry. The policies in place have encouraged exploration and development while mitigating some potential environmental impacts.
Historical Data on US Natural Gas Production Growth
The growth of US natural gas production over the past few decades has been remarkable. The data reveals a clear upward trend, driven largely by the factors mentioned earlier.
- Significant Growth: Between [specific start year] and [specific end year], US natural gas production experienced a dramatic increase, exceeding [specific production figure]. This growth underscores the impact of technological advancements and the availability of shale gas reserves.
Impact of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements have played a critical role in boosting US natural gas production. The efficiency gains from these advancements have significantly lowered production costs and enabled the exploitation of previously inaccessible resources.
- Efficiency Gains: Advancements in drilling techniques, horizontal drilling, and fracking procedures have led to substantial efficiency gains in natural gas extraction. These improvements have reduced the cost of producing a unit of natural gas, making it more competitive in the global market.
Comparison of US Natural Gas Production with Other Major Producing Nations
A comparative analysis of US natural gas production with other leading nations highlights the US’s significant position.
| Country | 2022 Production (Trillion Cubic Feet) |
|---|---|
| United States | 35.2 |
| Russia | 67.2 |
| Iran | 20.2 |
| Canada | 13.2 |
| Australia | 10.5 |
Note: Data for 2022 is for illustrative purposes only. Actual figures may vary slightly depending on the source.
Economic Impact of US Natural Gas Leadership
US natural gas production has profoundly impacted the domestic economy, driving job creation, bolstering energy independence, and fostering innovation. The nation’s leadership in natural gas has far-reaching effects, influencing global energy markets and shaping the economic landscape of numerous industries. This examination delves into the multifaceted economic benefits arising from US natural gas dominance.The economic impact of US natural gas leadership extends beyond simple cost savings.
It encompasses job creation across the supply chain, from extraction and processing to distribution and end-use applications. The industry’s competitiveness fuels technological advancement and drives investment in related sectors. This article explores the detailed economic ramifications of this crucial energy source.
Economic Benefits for the Domestic Economy
US natural gas production has generated significant economic benefits for the domestic economy. The industry’s infrastructure development and expansion have spurred significant investments, creating a robust supply chain. This has, in turn, stimulated related sectors like construction, equipment manufacturing, and transportation.
US LNG natural gas is a significant player in the global energy market, but even industry leaders face challenges. The recent passing of Sloane Crosley, as highlighted in the article “grief is for people sloane crosley” grief is for people sloane crosley , reminds us that human life, and its inevitable loss, often overshadows the cold, hard realities of the energy industry.
Ultimately, the US LNG natural gas sector will continue to navigate complex global dynamics, and the enduring impact of loss.
- Job Creation: The natural gas industry is a major employer, providing jobs in extraction, processing, transportation, distribution, and retail. Thousands of jobs are supported directly and indirectly by the sector, from skilled labor in drilling and engineering to administrative and support roles.
- Infrastructure Development: Natural gas infrastructure projects, including pipelines, processing plants, and storage facilities, have fostered economic growth in local communities and stimulated regional economies.
- Energy Independence: Domestic natural gas production reduces reliance on foreign energy sources, strengthening energy security and mitigating economic vulnerabilities associated with fluctuating global energy prices.
- Lower Energy Costs: Abundant and affordable natural gas has lowered energy costs for consumers and businesses, positively impacting various sectors like manufacturing, agriculture, and transportation.
Effects of US Natural Gas Exports on Global Energy Markets
US natural gas exports have significantly altered global energy markets, impacting energy security and pricing dynamics. These exports often fill gaps in global supply, allowing for increased energy access and competition.
The US is a major player in the LNG natural gas market, and this has a surprising connection to the housing market near NYC. Recent shifts in the cost of building materials, potentially influenced by LNG availability, are impacting the price of new homes and renovations in the area. This ultimately affects the long-term viability of the US LNG natural gas leader position, as housing demand and affordability directly correlate with the economic stability of the nation.
housing market near nyc is a good resource for details on these factors.
- Increased Global Energy Access: US natural gas exports have broadened access to reliable energy resources for numerous countries, particularly those facing energy shortages or relying on less stable sources.
- Competition and Price Fluctuations: Increased global supply has introduced competition into the global energy market, leading to fluctuations in prices and impacting energy strategies for various nations.
- Geopolitical Implications: US natural gas exports have geopolitical implications, shaping relationships between countries and influencing energy security strategies globally.
Role of Natural Gas in Various Industries Within the US
Natural gas plays a crucial role in diverse sectors across the US economy. Its versatility as a fuel source and its cost-effectiveness make it a prominent energy source.
The US is a leading producer of LNG natural gas, a crucial energy source. While the specifics of Oregon daylight saving time might not directly impact this, the complex interplay of energy markets and local regulations shows the interconnectedness of these seemingly disparate issues. Ultimately, the US’s position as an LNG natural gas leader remains strong, regardless of these regional variations.
- Manufacturing: Natural gas is a critical component in manufacturing processes across various industries, from chemicals and plastics to steel and cement production. Its affordability and availability make it an attractive choice for manufacturing facilities.
- Power Generation: Natural gas is a widely used fuel for electricity generation, contributing to the nation’s energy needs. Its efficiency and relatively low emissions compared to coal make it a favorable option for power plants.
- Residential Heating: Natural gas is a primary heating source for numerous homes and businesses, providing a reliable and cost-effective method for indoor temperature regulation.
- Transportation: Natural gas is emerging as a viable alternative fuel for transportation, powering vehicles and reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
Comparison of US Natural Gas Production Costs with Other Sources of Energy
The cost of producing natural gas in the US often compares favorably with other energy sources, depending on factors like extraction methods and infrastructure.
- Lower Production Costs: Modern natural gas extraction techniques, such as hydraulic fracturing (fracking), have often lowered production costs compared to some traditional energy sources. This has made natural gas a more attractive energy option for various sectors.
- Environmental Considerations: The environmental impact of natural gas production is a complex issue, varying based on specific practices and extraction methods. Different sources of energy present varying degrees of environmental impact.
- Technological Advancements: Continued advancements in natural gas extraction and processing technologies are expected to further reduce costs and enhance efficiency.
Creation of Jobs Associated with the Natural Gas Industry
The natural gas industry supports a substantial workforce across the nation. This sector creates numerous jobs, directly and indirectly, stimulating economic activity.
- Direct Employment: Jobs in drilling, extraction, processing, and transportation of natural gas directly contribute to the economy.
- Indirect Employment: Jobs in supporting industries like construction, equipment manufacturing, and engineering services are indirectly linked to natural gas production.
Geopolitical Implications of US Natural Gas Leadership
The United States’ burgeoning natural gas industry has significant geopolitical implications, impacting global energy security and international partnerships. This leadership position, fueled by technological advancements and abundant domestic resources, has altered the global energy landscape, leading to both opportunities and challenges for nations worldwide.The rise of US natural gas production has profoundly affected global energy markets, offering a critical alternative energy source for many countries.
This shift has not only impacted energy prices but also the geopolitical relationships between nations, altering established patterns of trade and dependence.
Influence on Global Energy Security
US natural gas exports have the potential to enhance global energy security by diversifying energy sources for importing nations. By reducing reliance on specific suppliers, importing nations gain resilience against disruptions in energy supply chains. This diversification can lead to more stable energy prices and mitigate the risks associated with geopolitical instability in regions heavily reliant on a single energy source.
For example, the increasing reliance on Russian gas by Europe prior to the 2022 war in Ukraine underscored the vulnerability associated with concentrated energy sources.
Potential Geopolitical Consequences of US Exports
US natural gas exports can potentially reshape international alliances and rivalries. The availability of US natural gas can influence existing energy partnerships, creating new ones, or potentially altering the balance of power. This can lead to shifts in trade agreements, investment strategies, and diplomatic relations between nations. In some instances, countries might seek to reduce their reliance on established energy suppliers in favor of more reliable and diversified sources, such as US natural gas.
The US is a major player in the global LNG (liquefied natural gas) market, and this position is likely to be strengthened by recent geopolitical events. The recent Biden administration’s efforts regarding the Israel-Hamas conflict, specifically the biden israel hamas cease fire , might indirectly influence global energy demands, potentially boosting the US’s already significant role as an LNG natural gas leader.
This position will be important in the years ahead.
Relationship with International Trade Agreements
US natural gas exports are influenced by various international trade agreements and regulations. The country’s participation in these agreements plays a crucial role in shaping its access to foreign markets and the development of global energy infrastructure. Agreements on gas supply and pipeline development can impact the ease of access to markets, leading to opportunities for increased exports and investment in infrastructure.
Moreover, agreements on environmental standards and regulations can impact the export process.
Impact on International Energy Partnerships
US natural gas exports can foster new international energy partnerships and strengthen existing ones. These partnerships can be crucial in supporting the development of energy infrastructure, enabling smooth energy transitions, and promoting global energy security. For example, agreements between the US and countries in Europe on gas supply could create a more stable energy supply for the continent.
These partnerships often include considerations for environmental sustainability and long-term energy security.
Countries Importing US Natural Gas
| Country | Estimated Import Volume (in millions of cubic feet per day) |
|---|---|
| Europe (various countries) | Varying amounts, dependent on specific agreements |
| Asia (various countries) | Varying amounts, dependent on specific agreements |
| Other countries | Quantities vary depending on market conditions and agreements |
Note: Precise import volumes are not always publicly available due to commercial sensitivities. The table above provides a general overview and is not an exhaustive list.
Environmental Considerations of US Natural Gas Production: Us Lng Natural Gas Leader
The burgeoning US natural gas industry, a cornerstone of energy independence, faces scrutiny regarding its environmental impact. While touted as a cleaner alternative to coal, natural gas production and consumption aren’t without their environmental footprints. This section delves into the environmental implications of this vital energy source.Natural gas, primarily composed of methane, is often presented as a “bridge fuel” to a cleaner energy future.
However, its environmental profile is complex and multifaceted, influenced by extraction, processing, and combustion. Understanding these aspects is critical for a comprehensive evaluation of its role in the transition to a sustainable energy system.
Environmental Impact of Natural Gas Extraction and Processing
Natural gas extraction, often employing hydraulic fracturing (fracking), can have localized environmental consequences. Water contamination from fracking fluids, as well as air pollution from fugitive methane emissions, are significant concerns. Careful regulation and monitoring are essential to mitigate these impacts. Moreover, land use changes associated with well sites and pipeline construction can affect ecosystems.
Role of Natural Gas as a Transition Fuel
Natural gas, with its lower carbon dioxide emissions compared to coal, plays a potential role in the transition to a lower-carbon energy system. Its use can reduce reliance on coal-fired power plants, albeit temporarily. However, the long-term sustainability of natural gas as a transition fuel hinges on the development and deployment of carbon capture and storage technologies.
Comparison of Environmental Footprints, Us lng natural gas leader
Comparing the environmental footprints of natural gas with other fossil fuels is complex, as different factors need consideration. Natural gas has lower carbon dioxide emissions per unit of energy produced compared to coal, but methane leaks throughout the supply chain significantly impact its overall environmental performance. The lifecycle analysis of each fuel is crucial for accurate comparisons.
Potential of Carbon Capture and Storage Technologies
Carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies show promise for reducing the carbon footprint of natural gas. By capturing CO2 emissions from power plants fueled by natural gas, these technologies can significantly reduce their contribution to climate change. The development and deployment of CCS are still in their early stages but hold considerable potential.
Environmental Regulations Impacting US Natural Gas Production
Environmental regulations are crucial in shaping the environmental impact of US natural gas production. Compliance with these regulations is essential for minimizing environmental damage and ensuring responsible energy development.
| Regulation Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Water Quality | Regulations address the potential contamination of water sources from fracking fluids and other operations. Standards dictate the composition and disposal of these fluids, aiming to prevent groundwater pollution. |
| Air Quality | Regulations monitor and control air emissions from natural gas operations, including fugitive methane leaks. Standards set limits on permissible emissions, aiming to minimize air pollution. |
| Land Use and Ecosystem Protection | Regulations address the impact of natural gas infrastructure on land use and ecosystems. They aim to minimize habitat destruction and disruption to wildlife. |
| Waste Management | Regulations control the handling, treatment, and disposal of waste generated during natural gas production and processing. |
Technological Advancements in US Natural Gas Production

The US has emerged as a global leader in natural gas production, driven in large part by innovative technologies that have dramatically enhanced efficiency, safety, and overall operations. These advancements have played a crucial role in making US natural gas a competitive and reliable energy source. From horizontal drilling to hydraulic fracturing, the industry has continuously adapted and improved its techniques.
Key Innovations Enhancing US Natural Gas Production
Technological advancements have been pivotal in boosting the US natural gas industry’s output and efficiency. New techniques have made previously inaccessible reserves economically viable, significantly increasing production capabilities. These innovations include horizontal drilling, hydraulic fracturing (fracking), and sophisticated well completions.
Examples of New Technologies Impacting Efficiency in Natural Gas Operations
Several technologies have improved efficiency in natural gas operations. For instance, advanced seismic imaging techniques enable more precise identification of potential reservoirs, minimizing drilling time and costs. Optimized well designs and completion strategies, using advanced materials and techniques, maximize gas flow and recovery rates. Moreover, improved production monitoring tools allow real-time adjustments to operations, enhancing efficiency and minimizing downtime.
How These Technologies Have Improved Safety in Natural Gas Extraction
Technological advancements have significantly improved safety in natural gas extraction. Real-time monitoring systems, for example, detect and mitigate potential hazards, such as pressure fluctuations or leaks, in real time, allowing for immediate intervention. Remote-controlled equipment reduces the need for workers to be in potentially hazardous areas, minimizing risks. Enhanced safety protocols and training programs, facilitated by technology, have also been instrumental in reducing accidents and improving workplace safety standards.
The Role of Automation in the Natural Gas Industry
Automation is transforming the natural gas industry, streamlining operations and improving efficiency. Automated drilling rigs, for instance, can operate with greater precision and consistency than manual systems, increasing output and reducing labor costs. Remote monitoring and control systems enhance safety and efficiency, allowing operators to oversee operations from a central location, reducing risks and improving real-time adjustments. Furthermore, automated well maintenance procedures minimize downtime and maximize operational efficiency.
Timeline of Key Technological Advancements in Natural Gas Production
| Year | Technological Advancement | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 1940s | Horizontal Drilling | Increased access to previously inaccessible reserves. |
| 1970s | Hydraulic Fracturing (Fracking) | Significantly expanded the recoverable reserves of shale gas. |
| 1990s | Advanced Seismic Imaging | Improved reservoir identification, minimizing drilling time and costs. |
| 2000s | Automated Drilling Rigs and Remote Monitoring | Enhanced safety, efficiency, and operational control. |
| Present | Enhanced Well Completion Strategies and Production Monitoring Tools | Maximized gas flow and recovery rates, reduced downtime, and improved safety. |
Future Outlook for US Natural Gas Leadership
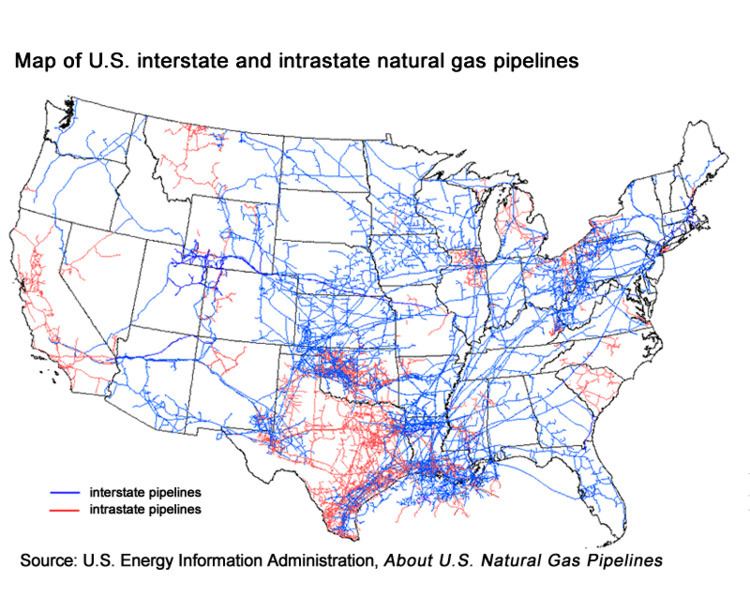
The United States has emerged as a global leader in natural gas production, fueled by technological advancements and favorable economic conditions. This leadership position is likely to endure, but the future of US natural gas hinges on several critical factors, including global demand, technological innovation, the rise of renewable energy, and government policies. The coming decades will see a dynamic interplay of these forces, shaping the future of US natural gas production.The future of US natural gas leadership will be intricately tied to the evolution of global energy markets and the adaptability of the industry to changing circumstances.
Demand projections and technological advancements will play critical roles in determining the US’s continued position.
The US is a major player in the global LNG (liquefied natural gas) market, but understanding the nuances of red and blue states’ demographics, like those explored in red blue states demographics , could potentially shed light on differing energy consumption patterns. This could ultimately affect the future trajectory of US LNG as a leader in the industry.
Ultimately, factors like population density and economic activity in various regions will continue to influence the demand for LNG.
Projected Future Demand for Natural Gas
Global energy demand is expected to continue to grow, with developing economies driving much of this growth. Natural gas, due to its relatively low carbon emissions compared to coal, is poised to remain a significant energy source in many parts of the world. In the United States, natural gas is expected to remain a crucial component of the energy mix, supporting industrial processes and electricity generation.
Forecasts suggest continued demand for natural gas in both domestic and international markets.
Potential for Further Technological Advancements in Natural Gas Extraction and Processing
Technological innovation is crucial to the continued success of the natural gas industry. Hydraulic fracturing (fracking) and horizontal drilling techniques have already revolutionized natural gas extraction, unlocking vast reserves. Further advancements are likely in areas such as enhanced oil recovery (EOR) techniques that could lead to increased gas production from existing fields. Improving pipeline infrastructure, optimizing processing facilities, and developing advanced gas storage technologies will be vital for efficient delivery and utilization.
The use of AI and machine learning to optimize production and reduce costs will likely become increasingly important.
Potential Impact of Renewable Energy Sources on the Future of Natural Gas
The increasing adoption of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, is a significant factor in the future of energy. While renewable energy is expected to play a growing role, natural gas is likely to remain a crucial bridging fuel. The intermittency of renewable energy sources often necessitates the use of dispatchable power sources like natural gas to ensure a reliable and stable energy grid.
The integration of natural gas with renewable energy systems could lead to a hybrid energy future where both technologies complement each other. This “power-to-gas” technology, for example, converts excess renewable energy into natural gas, addressing intermittency challenges.
Role of Government Policies in Shaping the Future of US Natural Gas Production
Government policies play a significant role in shaping the future of the US natural gas industry. Regulations concerning environmental protection, safety, and pipeline construction will influence production and infrastructure development. Policies related to carbon emissions, renewable energy mandates, and investment incentives will directly affect the competitive landscape for natural gas. Support for research and development of advanced technologies will also play a crucial role.
Possible Scenarios for the US’s Position as a Leader in Natural Gas Production in the Coming Decades
Several scenarios are possible for the US’s position as a leader in natural gas production. A scenario where demand continues to rise globally, coupled with ongoing technological advancements, could see the US maintaining its leadership position. Alternatively, a scenario involving a rapid shift towards renewable energy sources, coupled with stringent environmental regulations, could see the US’s dominance challenged.
The actual trajectory will depend on a complex interplay of factors.
Last Point
In conclusion, US LNG natural gas leadership is a complex phenomenon shaped by a confluence of economic, technological, geopolitical, and environmental factors. The future of this leadership will hinge on continued technological innovation, shrewd policy decisions, and responsible environmental practices. The US’s position as a global natural gas powerhouse is poised for continued evolution and influence in the coming decades.
This exploration provides a comprehensive overview, leaving readers with a clear understanding of the factors that drive this vital sector.
Common Queries
What are the key factors contributing to the US’s dominance in natural gas production?
Technological advancements, such as hydraulic fracturing (fracking), have significantly increased extraction rates, making US natural gas more affordable and accessible. Abundant shale gas reserves also play a major role.
How does US natural gas production impact global energy markets?
US LNG exports have altered global energy dynamics, providing alternative sources for many countries and potentially affecting pricing strategies. The increased supply has also influenced geopolitical relationships.
What are the environmental concerns associated with US natural gas production?
While natural gas is often considered a cleaner-burning fossil fuel than coal, concerns remain regarding methane emissions during extraction and processing. Regulations and advancements in carbon capture technologies are crucial for mitigating these impacts.
What is the projected future demand for natural gas in the coming decades?
Forecasts indicate continued demand for natural gas in various sectors, particularly as a transition fuel in the energy sector. The precise extent of this demand will depend on the adoption of renewable energy sources and the efficiency of natural gas utilization.

