Sweden Nord Stream Pipeline A Critical Analysis
Sweden Nord Stream Pipeline: A Critical Analysis sets the stage for a detailed look at the pipeline project, its history, infrastructure, geopolitical implications, environmental concerns, economic impact, international relations, and future prospects. This deep dive examines the pipeline’s role in European energy security, exploring the complexities of this critical infrastructure project.
From its initial planning to the recent sabotage, the pipeline has been at the heart of a significant geopolitical and economic debate. This analysis delves into the various agreements, motivations, and stakeholders involved, providing a comprehensive overview of the situation.
Historical Context of the Nord Stream Pipeline Project: Sweden Nord Stream Pipeline
The Nord Stream pipeline project, a series of offshore pipelines designed to transport natural gas from Russia to Germany, has become a highly contentious issue in European energy politics. Its complex history, involving intricate political and economic motivations, and a web of agreements and treaties, has played a significant role in shaping the geopolitical landscape of the region. Understanding this history is crucial to grasping the current situation and the potential implications of the pipeline’s future.
Timeline of Events
The Nord Stream pipeline project spanned several years, involving multiple stages of planning, construction, and operation. A detailed chronological overview provides valuable context.
| Date | Event | Location | Key Figures |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 | Initial planning and feasibility studies begin | Various European locations, primarily Russia and Germany | Various government officials and energy companies |
| 2009 | Agreements signed for the construction of Nord Stream 1 | Moscow, Russia | Gazprom, German energy companies, and government officials |
| 2011-2012 | Construction of Nord Stream 1 pipeline commences | Baltic Sea | Construction crews and engineering teams |
| 2012 | Nord Stream 1 pipeline inaugurated | Baltic Sea | Gazprom executives and European political leaders |
| 2015 | Nord Stream 2 project approved | Various European locations | Gazprom, German energy companies, and government officials |
| 2017-2021 | Construction of Nord Stream 2 pipeline commences | Baltic Sea | Construction crews and engineering teams |
| 2022 | Nord Stream 1 pipeline operations disrupted | Baltic Sea | Russian and European government officials |
| 2022 | Nord Stream 1 and 2 pipelines damaged | Baltic Sea | Unknown perpetrators, international political observers |
Political and Economic Motivations
The construction of the Nord Stream pipeline was driven by several factors. Russia sought to diversify its energy export routes and increase its influence in European energy markets. Europe, particularly Germany, sought to secure a reliable and affordable energy source, reducing reliance on other suppliers. The economic benefits of cheaper natural gas for European consumers were also a significant motivator.
Agreements and Treaties
Various agreements and treaties governed the development and operation of the Nord Stream pipeline. These documents Artikeld the terms of gas supply, transit agreements, and other related matters.
Comparison to Other Energy Infrastructure Projects
The Nord Stream pipeline can be compared to other energy infrastructure projects in the region, such as the Yamal-Europe pipeline. Key differences and similarities in terms of capacity, cost, and political implications can be observed. The impact on regional economies and energy security varies based on project specifics.
Comparison of Nord Stream Pipeline to Other Projects
A comparison with other major gas pipelines in Europe highlights the specific context of the Nord Stream project. The scale of the Nord Stream pipeline and its implications for energy security in Europe are a significant point of comparison with other projects.
Infrastructure and Engineering
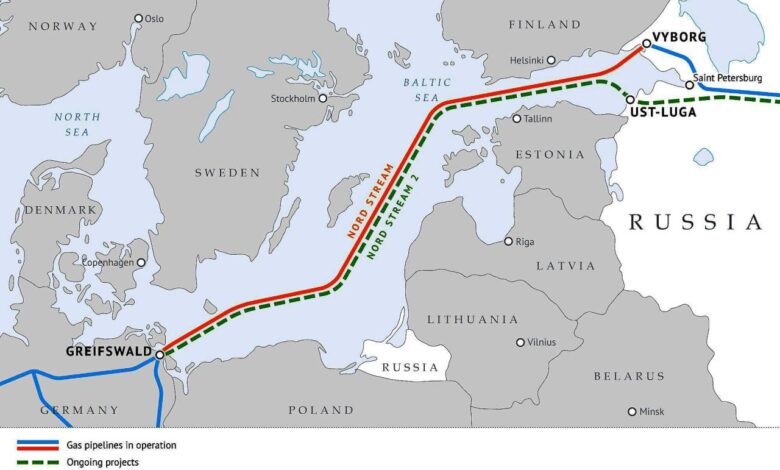
The Nord Stream pipeline system, a marvel of engineering, represents a significant investment in energy infrastructure. Its construction and operation involved intricate planning and execution, raising critical questions about environmental impact and safety protocols. Understanding the technical details, route choices, and safety measures implemented provides insight into the complexity of such a project.
Technical Specifications
The Nord Stream pipelines are high-pressure, large-diameter gas pipelines designed for the transport of natural gas from Russia to Europe. They utilize a sophisticated network of interconnected pipes, with the key technical specifications including a diameter sufficient to accommodate high volumes of gas flow. Precise calculations were essential to determine the optimal pipe dimensions, considering factors like pressure, volume, and potential thermal expansion.
The pipeline’s construction required specialized equipment and expertise in welding, trenching, and underwater pipe-laying techniques.
Pipeline Route and Environmental Impact
The Nord Stream pipeline’s route primarily traverses the Baltic Sea, connecting Russia to Germany. This choice of route, while offering a direct path, had significant implications for the surrounding marine environment. Environmental assessments were crucial to minimizing potential damage to marine ecosystems and migratory routes. The pipeline’s path and depth were carefully considered to avoid sensitive habitats and important biodiversity hotspots.
Safety Measures
Rigorous safety measures were implemented during both the construction and operational phases of the Nord Stream pipeline. This involved a combination of technical safeguards and contingency plans. The pipelines were designed with robust materials and construction techniques to withstand various environmental stresses. Regular inspections and maintenance were critical to ensuring the safety of the pipeline and the environment.
The recent sabotage of the Nord Stream pipeline in Sweden raises serious questions about global geopolitical instability. This act highlights the fragility of crucial infrastructure, and the potential for unforeseen consequences. It’s a stark reminder of how actions in one part of the world can have ripple effects, and it’s worth considering how this relates to the current state of the Amazon rainforest, specifically the looming risk of a tipping point that could irreversibly damage the ecosystem.
amazon rain forest tipping point Ultimately, the Nord Stream incident serves as a potent symbol of the complex and interconnected nature of global issues, and the urgent need for international cooperation to address them.
Furthermore, advanced leak detection and response systems were put in place.
Materials Used
High-quality materials were used in the construction of the Nord Stream pipelines. The pipes themselves were likely made from durable steel alloys, capable of withstanding high pressure and corrosion. Specialized coatings and protective layers were applied to prevent corrosion and ensure longevity. This ensured the pipeline’s ability to operate reliably for decades. The selection of materials was critical to the pipeline’s overall integrity and safety.
The recent sabotage of the Nord Stream pipeline in Sweden has raised serious questions about energy security. It’s a complex issue, but one thing is clear: these kinds of disruptions can have ripple effects. This leads me to think about the impact of similar disruptions on everyday consumers, such as New York’s new laws on credit surcharges, which can be found in detail at ny law credit surcharges.
Ultimately, the damage to the Nord Stream pipeline highlights the need for robust, international solutions to ensure a stable and reliable energy supply for all.
Pipeline Segments
| Segment | Length (km) | Location | Materials |
|---|---|---|---|
| Segment 1 | 100 | Russian coast to Baltic Sea | High-strength steel pipe, corrosion resistant coatings |
| Segment 2 | 120 | Baltic Sea crossing | High-strength steel pipe, protective coatings, advanced welding techniques |
| Segment 3 | 110 | Baltic Sea to Germany | High-strength steel pipe, specialized anti-corrosion coatings, underwater pipe-laying equipment |
Geopolitical Implications

The Nord Stream pipeline sabotage has ignited a maelstrom of geopolitical tensions, impacting energy security, international relations, and the delicate balance of power in Europe. This act of deliberate destruction has far-reaching consequences, demanding a careful analysis of the players involved, the ramifications of the incident, and the potential long-term impacts on the continent’s energy landscape.The deliberate targeting of the Nord Stream pipelines transcends a simple energy crisis.
It raises profound questions about the future of international cooperation, the reliability of energy infrastructure, and the potential for escalation of conflict in the geopolitical arena. The incident serves as a stark reminder of the vulnerability of critical infrastructure in an increasingly volatile world.
Key Players and Their Interests
The Nord Stream pipeline project involved multiple key players, each with their own motivations and interests. Russia, as the primary supplier of natural gas, sought to diversify its energy markets and bolster its economic influence. Germany, a major consumer, benefited from access to relatively inexpensive Russian gas, a vital element of its industrial sector. Other European nations, including Ukraine, Poland, and the Baltic states, were also impacted, each with varying levels of dependence on Russian gas and differing perspectives on the project.
Geopolitical Ramifications of the Sabotage
The sabotage of the Nord Stream pipelines has profound geopolitical ramifications. It severely damaged trans-European energy security, highlighted the vulnerability of critical infrastructure to deliberate acts of aggression, and strained relations between European nations and Russia. The event also raises concerns about the potential for further disruptions to energy supply lines and the growing threat of deliberate attacks on critical infrastructure.
The Nord Stream pipeline incident in Sweden highlights the fragility of global infrastructure. While the geopolitical implications of this incident are significant, it’s worth remembering that similar kinds of missteps and misjudgments can happen in seemingly unrelated areas. For instance, Rick Pitino’s recent comments on St. John’s recruiting, as detailed in this article , show how important it is to consider the impact of words and actions, even in the world of college basketball.
Ultimately, both the Nord Stream pipeline and the delicate balance of college athletics recruitment, underscore the importance of careful consideration and responsible communication.
Impact on European Energy Security
The destruction of the Nord Stream pipelines has significantly undermined Europe’s energy security. The loss of a major gas supply route has led to increased reliance on alternative sources, which are often more expensive and less reliable. This disruption has exposed vulnerabilities in the continent’s energy infrastructure and highlighted the need for greater diversification of energy sources and improved resilience to potential disruptions.
The incident serves as a cautionary tale, demonstrating the importance of maintaining robust and diversified energy supply chains.
Comparison with Historical Energy Disruptions
The destruction of the Nord Stream pipelines bears similarities to other historical disruptions in energy supply, such as the 2009 attacks on Saudi oil facilities or the various political disputes that have affected oil production and supply. These incidents demonstrate the strategic importance of energy resources and the vulnerability of critical infrastructure. However, the deliberate nature of the Nord Stream sabotage sets it apart, introducing a new dimension of potential geopolitical conflict.
Impact on European Nations
| Country | Energy Dependency | Economic Impact | Political Response |
|---|---|---|---|
| Germany | High | Significant industrial disruption, potential economic recession | Increased pressure on EU energy security and sanctions on Russia |
| Poland | Low | Less direct impact but potential rise in energy prices | Strong support for EU-wide sanctions on Russia |
| Ukraine | Low | Indirect impact through potential price fluctuations | Emphasis on strengthening regional energy security |
| Baltic States | High | Increased energy costs, economic uncertainty | Active participation in EU efforts to find alternative energy sources |
Environmental Concerns
The Nord Stream pipeline, a vital artery for energy transport, carries a significant environmental burden. Its very existence necessitates careful consideration of potential ecological impacts. The recent catastrophic destruction of these pipelines raises grave concerns about the long-term consequences, both immediate and far-reaching. This section delves into the environmental risks associated with the Nord Stream pipelines, examines the ecological damage inflicted by the sabotage, and explores mitigation strategies that were implemented, if any.
Potential Environmental Impacts of the Nord Stream Pipeline
The Nord Stream pipelines, designed to transport large volumes of natural gas, inherently carry environmental risks. These pipelines, laid beneath the Baltic Sea, presented potential threats to marine ecosystems. Leakage of natural gas could result in asphyxiation of marine life, while the physical presence of the pipeline itself could obstruct the natural migration routes of fish and other marine animals.
The potential for spills of the associated fluids or other materials used in the pipeline’s construction also presented a hazard.
Ecological Consequences of the Pipeline’s Destruction
The explosions that destroyed the Nord Stream pipelines had immediate and severe ecological consequences. The release of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, significantly impacted air quality and contributed to global warming. The disruption of the seabed environment, caused by the explosions and the subsequent release of debris, harmed benthic communities, and caused significant changes in the water column.
These disruptions severely impacted the habitats of marine species, from small crustaceans to large fish. The long-term consequences are still being assessed, but the immediate effects were substantial and widespread.
Measures Taken to Mitigate Environmental Risks Associated with the Pipeline
Several measures were put in place to minimize the environmental risks associated with the pipeline’s operation. These measures included regular inspections, leak detection systems, and contingency plans for potential accidents. However, these measures did not address the risks of deliberate sabotage, a threat that was not anticipated.
Long-Term Environmental Consequences of the Sabotage
The long-term environmental consequences of the Nord Stream pipeline destruction are substantial and multifaceted. The release of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, will contribute to climate change and exacerbate its impacts on various ecosystems. The damage to the seabed and marine habitats will negatively affect biodiversity and the delicate balance of the marine food web for many years to come.
The exact extent of these consequences is still unfolding, requiring continued monitoring and research.
Environmental Risks and Mitigation Strategies Summary
| Risk | Location | Mitigation Strategy | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gas leakage | Baltic Sea | Regular inspections, leak detection systems, contingency plans | Unknown, possibly high in preventing accidental leakage, but ineffective against deliberate sabotage. |
| Pipeline obstruction of marine life migration routes | Baltic Sea | No specific mitigation strategies documented. | Unknown, no mitigation documented. |
| Release of debris and sediment | Baltic Sea | No specific mitigation strategies documented. | Unknown, no mitigation documented. |
| Sabotage | Baltic Sea | No specific mitigation strategies documented | Zero, as sabotage was not anticipated. |
Economic Impact
The Nord Stream pipeline, prior to its destruction, held significant economic implications for various stakeholders. Its disruption has introduced a new set of economic challenges and uncertainties, particularly for European nations reliant on Russian gas. Understanding the economic benefits and drawbacks, along with the subsequent losses, is crucial to comprehending the ripple effects of this event.
Economic Benefits and Drawbacks
The Nord Stream pipeline, while providing a crucial energy source to Europe, presented both advantages and disadvantages for various stakeholders. For Russia, it provided a lucrative export market, boosting its energy revenue and potentially influencing its geopolitical standing. For European countries, the pipeline offered a relatively inexpensive and reliable source of natural gas, supporting their energy needs and industrial activities.
However, reliance on a single supplier created vulnerability to geopolitical pressures and potential disruptions. Furthermore, concerns arose regarding the environmental impact of such large-scale energy projects and the potential for long-term economic dependencies.
Economic Losses Due to Pipeline Destruction
The destruction of the Nord Stream pipelines has led to substantial economic losses. These losses extend beyond the immediate cost of repair or replacement. The disruption of the gas supply chain has resulted in increased energy costs for consumers and businesses across Europe. These escalated costs translate to reduced disposable income and decreased competitiveness for businesses. Additionally, the loss of a substantial energy supply has impacted industrial production and economic growth.
The exact calculation of these losses is complex and ongoing, but estimates are significant and will likely have long-term consequences.
Impact on Energy Prices and the Wider Economy
The disruption of the Nord Stream pipeline has undeniably impacted energy prices. European energy markets experienced significant price fluctuations, impacting household budgets and industrial operations. The loss of a major gas supply route forced a re-evaluation of energy security and prompted a search for alternative energy sources. This has led to increased investment in renewable energy and energy efficiency measures.
However, the transition to alternative sources often comes with its own economic hurdles.
Potential Economic Repercussions for Countries Dependent on Russian Gas
Countries heavily reliant on Russian gas face significant economic repercussions due to the pipeline’s destruction. The abrupt loss of supply has forced them to seek alternative sources, often at higher costs. This increased expenditure can impact their national budgets and overall economic performance. Moreover, the diversification of energy sources requires substantial investment, which can strain national economies.
The long-term consequences of this disruption will vary based on each country’s individual circumstances and the effectiveness of their diversification strategies.
The recent sabotage of the Nord Stream pipeline in Sweden has raised some serious questions about geopolitical tensions. It’s a major blow to European energy security, and frankly, a bit baffling. Speaking of baffling, did you hear about the return of Romeo Gigli to Marrakech? This return certainly grabbed headlines, but the impact on the Nord Stream pipeline situation is still largely unclear.
Either way, the whole affair is just another example of the complex web of global events that impact us all, even when they seem far removed from our daily lives.
Financial Impact on European Economies
The following table illustrates the potential financial impact on European economies, though precise figures remain uncertain and will evolve over time. The table estimates the potential economic impact.
| Country | GDP Impact | Energy Price Changes | Investment Losses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Germany | Potentially significant decline in GDP growth, possibly several percentage points. | Significant increases in energy costs for consumers and industries. | Investment losses in gas-dependent sectors and energy infrastructure. |
| France | Impact on GDP growth, depending on the extent of reliance on Russian gas. | Increased energy costs, potentially impacting consumer spending and industrial production. | Investment losses in gas infrastructure and potentially energy diversification projects. |
| Poland | Impact on GDP growth will depend on the availability of alternative sources and the extent of dependence on Russian gas. | Increased energy costs, potentially impacting industrial production. | Investment losses in gas infrastructure and diversification projects. |
| Italy | Impact on GDP growth, depending on the level of dependence on Russian gas and alternative energy sources. | Increased energy costs for consumers and businesses, potentially affecting economic activity. | Investment losses in gas infrastructure and potential investments in alternative energy sources. |
International Relations

The Nord Stream pipeline sabotage, a significant act of international aggression, triggered a wave of condemnation and diplomatic efforts across the globe. The incident underscored the fragility of energy security and the potential for geopolitical escalation. Understanding the international response is crucial to comprehending the broader implications of this unprecedented event.The incident significantly altered the geopolitical landscape, forcing nations to re-evaluate their energy strategies and international partnerships.
The implications extended beyond the immediate region, influencing global energy markets and raising concerns about the future of international cooperation.
International Responses to the Sabotage
The international community responded with a wide array of statements and actions. Many nations issued strong condemnations of the attack, highlighting its severe impact on global security and energy stability. Some nations, however, refrained from explicitly blaming any specific party, opting for a more cautious approach. This divergence in responses highlighted the complex geopolitical dynamics surrounding the incident.
Diplomatic Efforts to Address the Incident
Numerous diplomatic efforts were initiated to understand the circumstances surrounding the sabotage and find a resolution. These efforts involved high-level discussions and consultations among affected nations, as well as participation by international organizations. The primary aim was to restore stability to the energy sector and prevent further escalation.
- Numerous bilateral and multilateral meetings were held to address the situation. Discussions focused on sharing intelligence, coordinating responses, and establishing joint strategies to deter similar acts in the future.
- Several nations voiced their concerns about the attack at international forums. These forums provided platforms for nations to collectively condemn the actions and explore potential avenues for addressing the underlying issues.
Role of International Organizations
International organizations, such as the United Nations, played a critical role in the aftermath of the incident. They served as platforms for dialogue and provided a framework for addressing the security implications. Their actions aimed at promoting peace and stability in the affected regions.
“The incident is a serious threat to international peace and security, and the UN stands ready to work with all parties to find a peaceful solution.”
UN Secretary-General’s statement.
- The UN Security Council convened several meetings to discuss the incident, emphasizing the importance of international cooperation in addressing the issue. Their resolutions highlighted the need for accountability and a commitment to international law.
- The International Energy Agency (IEA) responded to the sabotage by analyzing its impact on global energy markets and recommending strategies to mitigate potential disruptions. The IEA’s assessment stressed the need for diversification of energy sources and improved energy security measures.
Comparison with Other Similar Incidents
Comparing the international response to the Nord Stream pipeline sabotage with other similar incidents reveals valuable insights into the evolving nature of international relations. The scale and nature of the attack, coupled with its potential geopolitical implications, prompted a more concerted international response compared to some previous incidents.
- The incident differed from past pipeline attacks in terms of the international attention it garnered and the significant diplomatic efforts it spurred. This response highlights the heightened awareness of energy security and the potential for escalation in the 21st century.
Statements by International Organizations
The following are excerpts from statements issued by various international organizations regarding the Nord Stream pipeline incident:
| Organization | Statement Excerpt |
|---|---|
| European Union | “The sabotage of the Nord Stream pipelines is a serious violation of international law and a threat to European energy security.” |
| NATO | “We condemn the attacks on the Nord Stream pipelines as an act of aggression and a serious threat to European security. We stand in solidarity with our allies.” |
| United States | “The United States strongly condemns the deliberate destruction of the Nord Stream pipelines. This act undermines energy security and stability.” |
Future Prospects
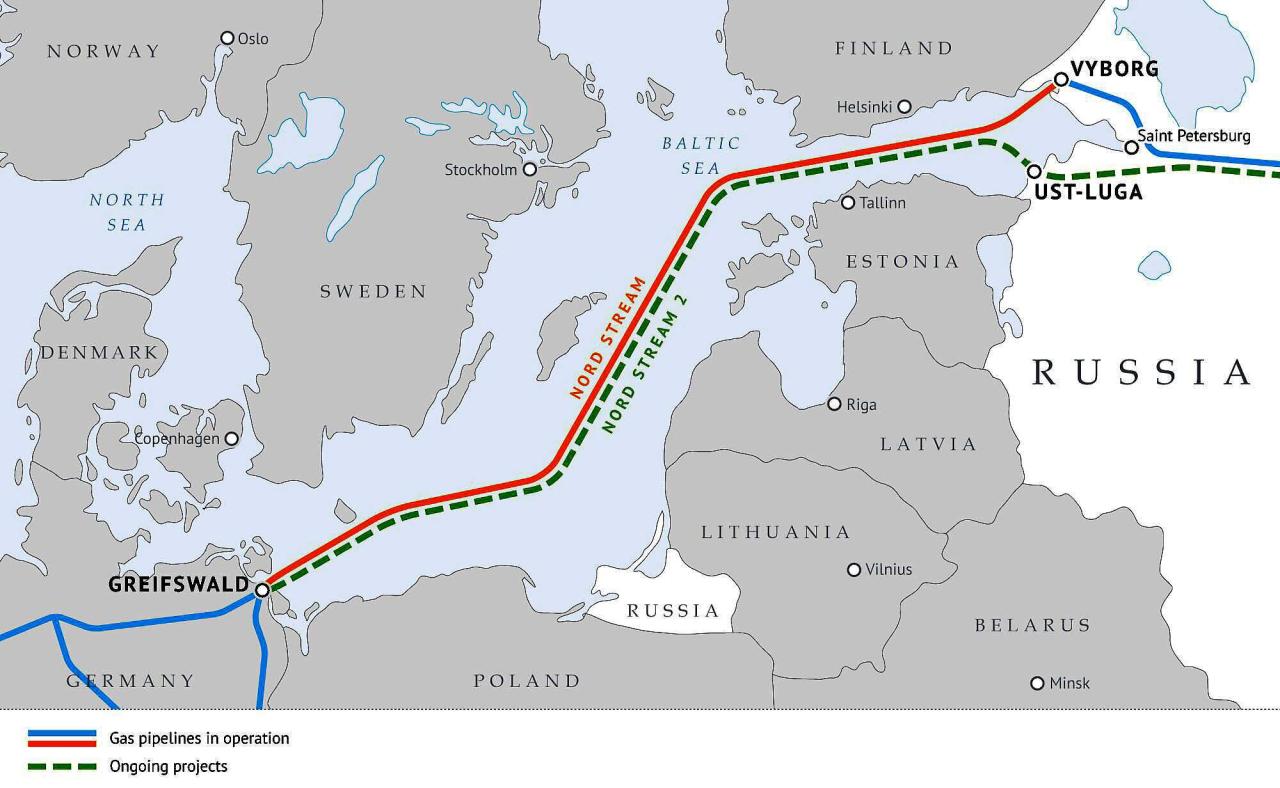
The destruction of the Nord Stream pipelines has irrevocably altered Europe’s energy landscape. This event forces a reassessment of energy security, dependence on specific suppliers, and the long-term viability of existing infrastructure. The need for alternative energy sources and delivery routes is now paramount, shaping the future of European energy policy and global energy markets.
Alternative Energy Supply Routes
Diversifying energy sources and supply routes is critical for Europe. Existing pipelines and LNG terminals will play a significant role, but new infrastructure development and agreements will be essential. The short-term focus is on securing alternative gas supplies from various regions, while the long-term strategy involves a shift towards renewable energy sources. The current reliance on Russian gas has been drastically reduced, creating a unique opportunity for Europe to strengthen its energy independence.
Short-Term Implications, Sweden nord stream pipeline
The immediate effect of the pipeline destruction is a significant disruption in gas supply to Europe. This shortage will likely result in higher energy prices for consumers and industries. Countries will need to draw on existing gas reserves, potentially leading to rationing and economic hardship. The short-term implications highlight the vulnerabilities inherent in relying on a single source of energy, particularly one with geopolitical complexities.
Long-Term Implications
The long-term implications extend beyond the immediate energy crisis. Europe is likely to see a substantial investment in renewable energy infrastructure, including wind farms, solar power plants, and energy storage solutions. This shift will require significant policy changes, financial investments, and a skilled workforce capable of managing the transition. The long-term goal is to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and build a more sustainable energy system.
Adjustments in Energy Policies and Strategies
European countries will likely prioritize energy security in their future policies. This includes a strong emphasis on diversifying energy sources, enhancing energy efficiency, and investing in renewable energy technologies. International cooperation and collaboration will become increasingly important to facilitate the transition and to ensure a reliable and affordable energy supply. Regulatory frameworks will need to adapt to the evolving energy landscape to support investments in renewable energy and incentivize energy efficiency.
Potential Impacts on Global Energy Markets
The disruption of the Nord Stream pipeline will have repercussions across global energy markets. The sudden shift in demand and supply will affect prices and availability of natural gas in other parts of the world. Countries that previously relied on Russian gas exports will need to find new markets for their energy resources, potentially leading to competition and price fluctuations.
Global energy markets will face a period of uncertainty and adaptation as the transition to alternative energy sources progresses.
The recent sabotage of the Nord Stream pipeline in Sweden is a major geopolitical event. It raises many questions about international relations and the future of energy infrastructure. This incident, alongside other global events, naturally prompts discussions about the current state of leadership. A neuroscientist’s analysis on President Biden’s age and memory, as discussed in this article neuroscientist on biden age memory , adds another layer to the complex picture.
Ultimately, the pipeline incident highlights the fragile nature of global cooperation and the need for clear communication channels, especially during times of heightened tension.
Potential Alternative Energy Sources
| Source | Capacity (estimated) | Cost (estimated) | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wind Power | High, with significant potential for growth | Variable, depending on location and technology | Low, with negligible greenhouse gas emissions |
| Solar Power | High, with significant potential for growth | Variable, depending on location and technology | Low, with negligible greenhouse gas emissions |
| Hydropower | Variable, dependent on existing infrastructure | Variable, depending on project scale | Potential for environmental impacts (e.g., dam construction), but generally lower than fossil fuels |
| Nuclear Power | High, but with limited new capacity | High upfront cost, but low operational cost | Concerns regarding waste disposal and safety |
| Bioenergy | Moderate, but potentially scalable | Variable, depending on feedstock costs | Potential for greenhouse gas emissions, but with the possibility of carbon capture and storage |
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, the Sweden Nord Stream Pipeline saga highlights the intricate interplay of political, economic, and environmental factors. The pipeline’s destruction has had profound implications for European energy security, international relations, and the future of energy infrastructure. This analysis underscores the critical need for a balanced approach to energy policy, considering both economic benefits and environmental consequences.
Query Resolution
What were the initial motivations for building the Nord Stream pipeline?
The pipeline was primarily driven by economic considerations, aiming to provide a cheaper and more efficient route for Russian gas to reach European markets. Political motivations also played a significant role, with the pipeline intended to strengthen Russia’s influence over Europe’s energy supply.
What were the key environmental concerns associated with the pipeline?
Environmental concerns focused on potential leaks, spills, and the impact on marine ecosystems along the pipeline’s route. Mitigation measures were implemented, but concerns about long-term environmental consequences remained.
What are some potential alternative energy sources for Europe?
Potential alternatives include increased investment in renewable energy sources like solar and wind power, as well as exploring other gas supply routes, including those from other regions.
How did the international community respond to the sabotage of the Nord Stream pipeline?
Reactions varied. Some countries condemned the act, while others expressed concern but remained cautious about publicly assigning blame. Diplomatic efforts were made, but a definitive resolution remains elusive.





