
How to Cut Food Waste A Guide
How to cut food waste is a critical issue facing households and the environment. This guide dives deep into practical strategies, from understanding the causes of food waste to implementing innovative solutions. We’ll explore various aspects of food preservation, creative repurposing of leftovers, and the power of meal planning to minimize your environmental impact and save money. Get ready to embark on a journey to reduce your food waste and make a positive change!
Food waste isn’t just about discarding excess food; it encompasses a complex interplay of factors, from our shopping habits to the way we store and prepare meals. This comprehensive guide will help you understand the root causes and provide actionable steps to make a tangible difference in your daily life.
Understanding Food Waste
Food waste is a pervasive problem, impacting our environment, our wallets, and our food security. It’s not just about the discarded food itself; it’s about the resources used to produce, transport, and store that food that are also lost. This section delves into the multifaceted nature of food waste, exploring its various forms, underlying causes, and the far-reaching consequences.Food waste manifests in a variety of forms within households.
Spoiled fruits and vegetables, uneaten leftovers, expired packaged goods, and even perfectly good produce deemed ‘ugly’ or ‘imperfect’ contribute to the problem. This encompasses everything from a single wilted lettuce leaf to a whole batch of bread gone stale. Miscalculations in portion sizes, lack of proper storage, and inconsistent meal planning are often the culprits.
Forms of Household Food Waste
A significant portion of food waste originates from households. This waste encompasses a wide range of items, from readily visible, like uneaten meals, to less apparent, like improperly stored produce. Understanding the types of food waste in our homes is the first step toward effective reduction strategies.
- Fresh Produce: Fruits and vegetables are particularly susceptible to spoilage, often due to improper storage or inadequate handling. Examples include wilted greens, overripe fruits, and vegetables that have developed blemishes or soft spots.
- Cooked Meals: Leftovers not properly stored or reheated lead to significant waste. This includes both cooked dishes and prepared ingredients that are discarded before they are used.
- Dairy and Refrigerated Items: Milk, yogurt, cheese, and other perishable items can quickly spoil if not stored correctly or used within their expiration dates. This category includes items that may appear fine visually but have passed their optimal consumption time.
- Baked Goods and Grains: Bread, pastries, and other baked goods often become stale or moldy before they are consumed. Similarly, grains like rice and pasta can spoil if not stored properly.
- Prepared Foods and Packaged Goods: Pre-portioned meals, sauces, and other prepared foods can be wasted if not consumed before their expiration date. Often, a single serving isn’t enough for a whole meal, leading to food being discarded.
Causes of Food Waste in the Food Supply Chain
Food waste is not confined to the household; it’s a problem across the entire supply chain. From farm to table, various factors contribute to significant losses.
- Post-Harvest Losses: Damage during harvesting, transportation, and storage, as well as inadequate handling and preservation techniques, can result in considerable losses of produce. For example, fruits and vegetables can be damaged during transit or if not stored at the correct temperature.
- Processing and Packaging Issues: Food processing and packaging procedures can also contribute to waste. Imperfect shapes, sizes, or appearances can lead to products being rejected, leading to significant quantities of food being discarded.
- Retail Practices: Supermarkets and grocery stores often discard produce that doesn’t meet their aesthetic standards, even if perfectly edible. This practice, driven by consumer preferences for ‘perfect’ produce, leads to substantial losses. Supermarkets often have strict ‘sell-by’ and ‘use-by’ dates that lead to excess waste if the product is not sold within the timeframe.
- Consumer Preferences: Consumer expectations for perfect produce and the tendency to overbuy can lead to waste. For instance, a family purchasing more groceries than they need often leads to spoilage or expiration of items.
Environmental and Economic Consequences of Food Waste
The environmental and economic consequences of food waste are substantial.
- Environmental Impact: Food production consumes vast resources, including land, water, and energy. Wasted food represents a significant loss of these resources. Moreover, the decomposition of food in landfills generates greenhouse gases, contributing to climate change. A substantial amount of water and land are used in food production, which is wasted when food is discarded.
- Economic Impact: Food waste represents a significant economic loss for consumers, businesses, and governments. The resources invested in producing, transporting, and storing wasted food are lost. Businesses lose revenue due to spoiled or unsold products, while consumers waste money on food they cannot consume.
Categorization of Food Waste
| Category | Examples |
|---|---|
| Fruits and Vegetables | Bananas, apples, lettuce, tomatoes |
| Dairy and Refrigerated Items | Milk, yogurt, cheese, meat |
| Grains and Baked Goods | Bread, pasta, rice, cookies |
| Leftovers | Cooked meals, soups, stews |
| Processed Foods | Sauces, condiments, pre-packaged meals |
Planning for Food Preservation
Preventing food waste isn’t just about buying less; it’s also about knowing how to keep what you buy fresh for longer. Proper food storage is a crucial element in minimizing spoilage and maximizing the lifespan of your groceries. By implementing effective strategies, you can significantly reduce the amount of food that ends up in the trash.
This section delves into various methods of food preservation, from the simple act of organizing your refrigerator to more involved techniques like freezing and canning. Understanding these methods allows you to extend the shelf life of your produce, ensuring that you use every item before it goes bad. This ultimately contributes to a more sustainable and economical approach to food management.
Reducing food waste is super important, and it’s surprisingly easy to do! Planning your meals ahead, using leftovers creatively, and storing food properly are all great ways to minimize what ends up in the bin. Plus, checking out deals at the subway weekend jose lasalle, like the ones happening this weekend, subway weekend jose lasalle , can help you get the most out of your grocery budget while also reducing your food waste.
So, get creative with leftovers and make sure to properly store everything for the best results!
Effective Strategies for Storing Food
Proper storage conditions are paramount in preventing food spoilage. Temperature, humidity, and light exposure all play a significant role in the freshness and longevity of your food. Understanding these factors enables you to select the appropriate storage method and location for each item, maximizing its usable lifespan.
- Temperature Control: Refrigeration is essential for perishable items like dairy products, meats, and many vegetables. Freezer storage is ideal for long-term preservation of fruits, vegetables, and leftovers.
- Humidity Management: Fruits and vegetables with high moisture content, like leafy greens and berries, need to be stored in containers or bags that maintain appropriate humidity levels. Avoid storing them in airtight containers, as this can cause them to spoil faster.
- Light Exclusion: Light exposure accelerates the ripening and deterioration process in many fruits and vegetables. Storing these items in dark, cool locations will significantly increase their shelf life.
Methods of Food Preservation, How to cut food waste
Various techniques can extend the lifespan of food beyond its typical shelf life. Understanding these methods allows you to choose the best approach for different types of food and your specific needs.
- Freezing: Freezing is a popular method for preserving fruits, vegetables, and leftovers. Properly freezing food ensures its quality and safety for months or even years. Freezing is best for preserving the flavor and nutritional value of the food.
- Canning: Canning involves preserving food in sealed jars. This method allows for long-term storage, especially for high-acid foods like fruits and vegetables. Canning requires specific procedures to ensure safety and prevent contamination. It’s a great method for preserving seasonal produce.
- Drying: Drying is a method of food preservation that involves removing moisture from the food item. This can be done naturally or using a dehydrator. Dried foods have a longer shelf life than fresh foods. It’s particularly effective for preserving herbs, fruits, and vegetables.
Storing Fruits and Vegetables
Specific storage requirements vary for different fruits and vegetables. Proper handling and storage prevent spoilage and maintain the quality of your produce.
| Food Item | Storage Method | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Apples | Cool, dark place | Store in a single layer in a ventilated container or basket. Avoid placing them near bananas or other fruits that produce ethylene gas. |
| Leafy Greens | Refrigeration | Store in a perforated plastic bag or container in the crisper drawer. Keep them dry and away from moisture-rich foods. |
| Bananas | Room temperature | Bananas should be kept at room temperature and away from direct sunlight. Avoid placing them near other fruits. |
| Potatoes | Cool, dark, and dry place | Store in a cool, dark, and dry place, like a pantry or cellar. Avoid storing them in the refrigerator. |
Organizing Your Refrigerator
A well-organized refrigerator minimizes food waste and maximizes space. A planned approach to storing food reduces the risk of spoilage and allows you to easily locate items.
- First In, First Out (FIFO): Place newer items behind older ones to ensure that you use the older items first. This helps prevent food from spoiling before you have a chance to consume it.
- Categorization: Group similar items together to facilitate easy retrieval and reduce the likelihood of overlooking items.
- Proper Container Use: Use appropriate containers to prevent spills and maintain freshness. Use airtight containers for items that need to be kept dry. For produce, use perforated containers or bags to allow air circulation.
Utilizing Leftovers Creatively
Leftovers are a valuable resource, not just a culinary inconvenience. Transforming yesterday’s dinner into a delicious and nutritious meal today is an excellent way to reduce food waste and save money. This section explores creative ways to repurpose leftovers, highlighting the nutritional benefits and economic advantages.
Creative Repurposing Ideas
Repurposing leftovers isn’t just about stretching a meal; it’s about unlocking culinary creativity. Here are five unique and innovative ways to breathe new life into your leftovers:
- Leftover Chicken Stir-Fry into a Noodle Bowl: Combine leftover chicken stir-fry with cooked noodles, a sprinkle of sesame seeds, and a drizzle of soy sauce for a quick and satisfying meal. This repurposes the protein and vegetables, while adding a fresh, flavorful element to the dish.
- Roast Chicken and Vegetable Hash: Shred leftover roasted chicken and vegetables, then sauté with diced potatoes, onions, and peppers for a hearty hash. This offers a hearty and nutritious breakfast or brunch option.
- Pasta Primavera with Leftover Veggies: Transform leftover vegetables from a previous meal into a vibrant pasta primavera. Combine the vegetables with cooked pasta, a light sauce, and fresh herbs for a nutritious and flavorful dish.
- Leftover Curry into a Fried Rice: Leftover curry can be transformed into a delicious fried rice dish. Add cooked rice, vegetables, and protein to the curry, stir-fry until heated through, and enjoy. This offers a complete meal and maximizes the use of curry ingredients.
- Leftover Soup into a Creamy Pasta Sauce: Leftover soup, especially vegetable or lentil soups, can be used as a base for a flavorful pasta sauce. Blend the soup with cream or milk, herbs, and spices for a rich and comforting pasta dish.
Nutritional Value Comparison
The nutritional value of a dish made with leftovers often closely resembles that of a fresh equivalent, especially when the original ingredients were healthy. The key difference usually lies in the freshness and specific preparation methods used.
| Dish | Fresh Ingredients | Leftovers |
|---|---|---|
| Roasted Chicken and Vegetables | Freshly roasted chicken and vegetables with vibrant flavors and nutrients. | Roasted chicken and vegetables, retaining the flavors and nutrients of the previous meal, but possibly with slightly diminished freshness. |
| Chicken Stir-Fry | Fresh vegetables and protein, offering vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants in their peak freshness. | Stir-fried chicken and vegetables from the previous meal, with preserved nutrients but potentially slightly altered textures. |
| Pasta Primavera | Fresh vegetables, rich in vitamins and minerals. | Leftover vegetables, retaining much of their nutritional value, though potentially slightly altered textures. |
| Curry Fried Rice | Fresh rice and vegetables, rich in complex carbohydrates and vitamins. | Leftover curry and rice, maintaining the nutritional value of the curry and rice from the previous meal. |
| Creamy Pasta Sauce | Fresh pasta and vegetables, offering carbohydrates and vitamins. | Leftover soup and vegetables blended with cream, retaining the nutrients of the previous meal but possibly with altered fat content. |
Benefits of Using Leftovers
Utilizing leftovers is a simple yet effective way to reduce food waste and save money. By repurposing leftovers into new meals, you avoid discarding edible food and decrease your reliance on purchasing fresh ingredients for every meal. This approach also minimizes the environmental impact associated with food production and transportation.
Reducing food waste is super important for our planet. Planning meals ahead and using up leftovers are great ways to start. Did you know that some shocking statistics about food waste tie into the recent controversy surrounding Felicia Snoop Pearson and Ed Burns’s wire? felicia snoop pearson ed burns wire highlights the need for better practices in the media, and by extension, in our homes.
Ultimately, smart shopping and mindful meal prepping are key to significantly cutting down on food waste at home.
Meal Planning and Shopping
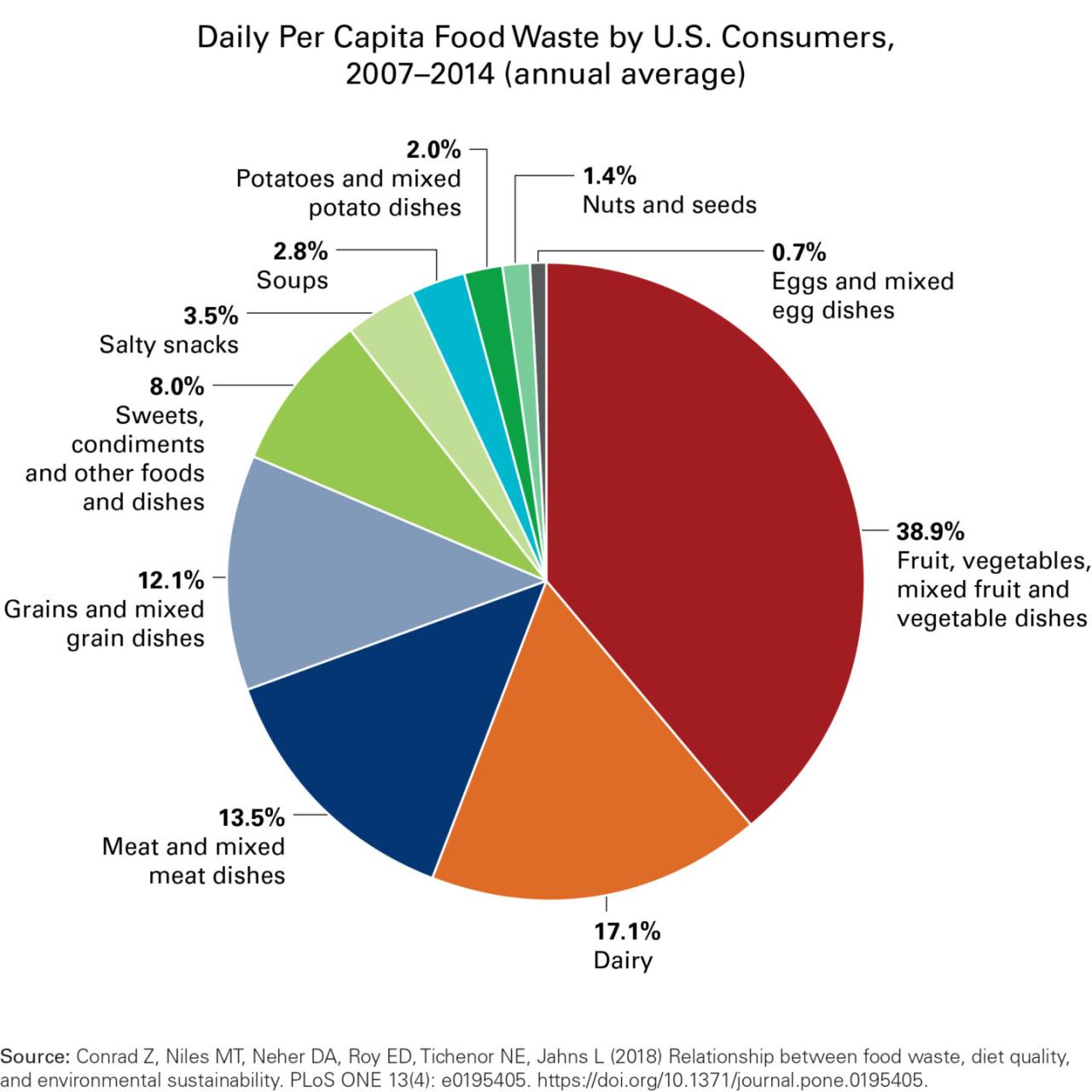
Tackling food waste starts with a strategic approach to meal planning and shopping. Knowing what you’ll eat each week allows you to buy only what’s needed, minimizing the likelihood of perishable items expiring before you can consume them. A well-structured plan also empowers you to creatively use up ingredients, reducing the amount of food that ends up in the bin.
Inventorying Existing Supplies
Before you head to the grocery store, take stock of your existing food supplies. This crucial step prevents unnecessary purchases and ensures you’re not doubling up on items you already have. A thorough inventory will help you tailor your meal plan to utilize what’s already in your fridge, freezer, and pantry.
Creating a Weekly Meal Plan
A weekly meal plan serves as your roadmap to minimizing food waste. It Artikels the meals you’ll prepare for each day, ensuring you have a clear picture of what you need to purchase and how to use up existing ingredients. This detailed approach promotes mindful consumption, reducing impulse buys and minimizing the likelihood of leftovers going bad.
| Day | Breakfast | Lunch | Dinner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monday | Oatmeal with berries | Leftover lentil soup | Chicken stir-fry with brown rice |
| Tuesday | Yogurt with granola | Tuna salad sandwich on whole-wheat bread | Baked salmon with roasted vegetables |
| Wednesday | Scrambled eggs with toast | Leftover baked salmon and roasted vegetables | Lentil soup |
| Thursday | Whole-wheat pancakes | Leftover chicken stir-fry | Chicken and vegetable curry with brown rice |
| Friday | Smoothie with fruit | Leftover chicken and vegetable curry | Pizza night |
| Saturday | Breakfast burrito | Leftover pizza | Pasta with marinara sauce |
| Sunday | French toast | Leftover pasta | Roast chicken with roasted potatoes and carrots |
Creating a Shopping List
After your meal plan is finalized, create a detailed shopping list. This is crucial for accurate purchasing and prevents overbuying. Prioritize items based on the meal plan and check your inventory against your list to make sure you’re only buying what you need.
- Review your existing pantry, fridge, and freezer. Cross off items from your shopping list that are already present.
- Note quantities needed for each dish. This precise approach ensures you’re purchasing the exact amount required.
- Include items that support multiple recipes. For example, if you’re making both pasta and soup, you can include ingredients that are common to both recipes.
- Prioritize non-perishable items. Having a well-stocked pantry will make your meal planning even easier and reduce waste.
Educating Consumers

Food waste is a global problem with significant environmental and economic consequences. Educating consumers about the issue and empowering them with practical strategies to reduce their own food waste is crucial. By understanding the factors contributing to food waste and adopting sustainable practices, individuals can make a tangible difference.Educating consumers isn’t just about awareness; it’s about equipping them with the tools and knowledge to implement changes in their daily routines.
This includes understanding the science behind food spoilage, recognizing signs of freshness, and implementing effective storage techniques. Effective educational campaigns can lead to profound behavioral shifts, ultimately reducing the amount of edible food that ends up in landfills.
Reducing food waste is crucial, especially when considering the impact on your budget. Thinking about how to efficiently use ingredients and plan meals can help a lot. The housing market near NYC is experiencing some interesting shifts , but regardless of market trends, smart food management remains key. Proper storage, meal prepping, and composting are all great ways to lessen food waste.
Benefits of Educating Individuals
Educating individuals about food waste reduction offers a multitude of benefits, extending beyond environmental impact. Reduced food waste leads to lower grocery bills, less reliance on unsustainable food systems, and a healthier relationship with food. Increased awareness of food safety practices and proper storage can prevent foodborne illnesses.
Impact of Awareness Campaigns
Awareness campaigns have a demonstrable impact on consumer behavior related to food waste. Studies have shown that campaigns highlighting the environmental consequences, such as the link between food waste and greenhouse gas emissions, can motivate consumers to make changes. Targeted campaigns focusing on specific demographics, like families or students, can yield particularly strong results. These campaigns often emphasize practical tips and strategies for reducing food waste, empowering consumers with actionable steps.
Effective Strategies for Educating Children
Children are crucial to fostering long-term change in food waste reduction. Early education instills habits and attitudes that can last a lifetime. Interactive learning experiences, like hands-on activities and games, are more effective than simply presenting facts. Involving children in the process of meal planning, shopping, and preparing meals can cultivate a deeper understanding of food and its value.
- Visual Learning: Using visual aids like posters, infographics, and videos tailored for children can make complex information easily digestible. For instance, a colorful poster depicting the different stages of fruit ripening and how to store them effectively can be highly engaging.
- Interactive Activities: Organize fun and interactive workshops, competitions, or games focused on food waste reduction. These can include competitions where children design creative ways to use leftovers or scavenger hunts to find ways to reduce food waste in their own homes.
- Role-Playing and Storytelling: Engage children through role-playing scenarios, such as pretending to shop for groceries or prepare meals, emphasizing the importance of reducing food waste at each step.
Comparison of Educational Resources
| Resource Type | Description | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| School Programs | Curriculum-based lessons and workshops integrated into school programs. | Reach a large number of children, often supported by trained educators, aligns with existing educational structure. | May not always be tailored to specific needs of each child, limited time allocated for each topic. |
| Community Workshops | Interactive sessions led by experts, often covering practical skills and demonstrations. | Hands-on experience, opportunity for direct interaction and question-answer sessions. | May have limited reach and may require extra travel and time commitment from participants. |
| Online Resources | Websites, videos, and apps offering educational content on food waste reduction. | Accessible to a wider audience, available 24/7, can be customized to specific learning styles. | Requires self-discipline and motivation to engage with the material, may lack personal interaction. |
| Parent/Guardian Resources | Educational materials distributed to parents or guardians to educate children at home. | Encourages consistent messaging across environments, tailored to specific family situations. | Requires consistent follow-up and support from parents/guardians, may not address all learning styles. |
Innovative Food Waste Solutions
Reducing food waste is no longer just a matter of good habits; it’s a critical component of a sustainable future. Innovative technologies are emerging to tackle this global challenge, offering powerful tools for preventing spoilage and maximizing the utilization of edible food. These solutions not only minimize waste but also enhance efficiency and sustainability in the food supply chain.Technological advancements are revolutionizing how we store, process, and manage food, contributing significantly to the fight against food waste.
From smart refrigerators to online calculators, these tools empower individuals and businesses to make informed decisions, leading to a more sustainable food system.
Reducing food waste is a great way to save money and be eco-friendly. While the extravagant displays at Saint Laurent Dior Paris Fashion Week saint laurent dior paris fashion week might seem worlds apart, both emphasize mindful consumption. Planning meals, using leftovers creatively, and properly storing food are all practical steps to lessen your environmental footprint and your grocery bill.
Innovative Technologies for Reducing Food Waste
Various technologies are being developed to combat food waste at different stages of the supply chain. These include advanced packaging materials that extend shelf life, sensors that monitor food quality, and automated systems for sorting and distributing produce. These technologies help reduce spoilage, optimize storage conditions, and improve food distribution efficiency.
Smart Refrigerators and Food Waste Reduction
Smart refrigerators equipped with sensors and data analytics are becoming increasingly common. These devices monitor food storage conditions, such as temperature and humidity, and alert users to potential spoilage. They track inventory, predict expiration dates based on usage patterns, and even provide recipe suggestions using remaining ingredients. This intelligent approach helps consumers make better decisions about their food purchases and reduces the amount of food that goes uneaten.
For example, a smart fridge might alert you that your milk is approaching its expiration date, encouraging you to use it in a recipe before it spoils.
Reducing food waste is a fantastic way to save money and be more environmentally conscious. One way to think about it is to plan your meals and use up leftovers creatively. Interestingly, the dramatic score of Sweeney Todd, as heard on Broadway cast albums like broadway cast albums sweeney todd , can be a great inspiration for transforming scraps into something delicious.
Ultimately, by planning ahead and getting creative, you can make a real difference in minimizing food waste at home.
Online Food Waste Calculators: Empowering Informed Decisions
Online food waste calculators are valuable tools that help individuals and businesses understand their food waste patterns. These calculators provide estimates of food waste based on user input, such as meal planning, shopping lists, and cooking habits. Using this data, users can identify areas for improvement and adjust their behaviors accordingly. For instance, a calculator might suggest adjusting portion sizes or utilizing leftovers more creatively to minimize food waste.
These calculators are particularly helpful for restaurants, cafeterias, and other large-scale food service operations, enabling them to identify significant waste points and implement solutions to prevent them.
Improved Food Preservation and Storage
Technological advancements are constantly improving food preservation and storage methods. Vacuum sealing, modified atmosphere packaging (MAP), and controlled-atmosphere storage are examples of these techniques. These technologies extend the shelf life of food products by reducing exposure to oxygen, moisture, and other factors that contribute to spoilage. For example, vacuum sealing can significantly extend the lifespan of meat and other perishable items, preventing freezer burn and microbial growth.
Food Waste in Specific Food Groups
Reducing food waste isn’t just about saving money; it’s about minimizing our environmental impact. Understanding the specific needs of different food groups allows us to make informed decisions about storage, preparation, and consumption, drastically cutting down on the amount of food destined for the landfill. By tailoring our practices to the unique characteristics of each food group, we can significantly reduce spoilage and maximize the life of our groceries.
Fruit and Vegetable Storage
Proper storage is crucial for preventing fruit and vegetable spoilage. Different produce has different needs. Fruits and vegetables with high water content, like leafy greens and berries, need cool, humid environments to prevent them from wilting or drying out. Conversely, root vegetables, such as carrots and potatoes, thrive in cool, dry conditions. Improper storage can result in significant waste, leading to both financial and environmental consequences.
- Leafy Greens: Store in a perforated plastic bag or container in the crisper drawer of your refrigerator. Avoid washing until ready to use to prevent wilting.
- Berries: Store in an airtight container in the refrigerator. Avoid placing them in a sealed plastic bag, as this can trap moisture and promote spoilage. Separate them from other fruits to prevent bruising and quick deterioration.
- Root Vegetables: Store in a cool, dark, and dry place, like a root cellar or a crisper drawer. Keep them away from fruits that produce ethylene gas, which can accelerate ripening.
- Citrus Fruits: Store at room temperature. Avoid placing them in the refrigerator, as this can cause the fruit to become less flavorful.
- Avocados: Store unripe avocados at room temperature. Once ripe, store in the refrigerator to slow down further ripening.
Bread Waste Reduction
Bread, a staple in many kitchens, is often a significant source of food waste. A simple approach to reducing bread waste is proper storage and creative repurposing. Proper storage can significantly extend the shelf life of bread, reducing the likelihood of it going stale or moldy.
- Proper Storage: Store bread in an airtight container at room temperature or in the freezer. Freezing bread can extend its shelf life significantly. Freezing allows for easy portioning for later use. Consider storing sliced bread in a separate airtight container for ease of use.
- Creative Repurposing: Stale bread can be transformed into delicious and nutritious dishes. Crumble stale bread for use in soups, stews, or stuffing. Bread crumbs can be made from stale bread, providing a versatile ingredient for various dishes.
- Freezing Slices: Freeze bread slices individually on a baking sheet and then transfer them to a freezer bag for convenient use in sandwiches, toast, or other recipes.
Dairy Product Storage
Dairy products are highly perishable and require specific storage conditions to maintain their quality and prevent spoilage. Milk, yogurt, and cheese have varying storage needs. Maintaining the right temperature and humidity levels significantly impacts the lifespan of these items.
- Milk: Store milk in the refrigerator’s coldest section. Avoid storing milk near strong odors or direct sunlight. This can alter the taste and shorten the shelf life.
- Yogurt: Store yogurt in the refrigerator. Proper temperature is crucial to maintain its quality. The shelf life of yogurt is usually determined by the packaging. Keep in mind that opening yogurt can cause spoilage faster, so using it promptly is key.
- Cheese: Store cheese in the refrigerator. Different types of cheese require different storage conditions. Hard cheeses can last longer than soft cheeses.
Food Waste for Specific Dietary Needs
Minimizing food waste for specific dietary needs, such as vegetarian or vegan diets, can present unique challenges. The specific storage requirements for plant-based foods may vary. Careful planning and creative substitutions are key to managing food waste effectively.
- Vegetarian Diets: Vegetarian diets often rely on fresh produce, which requires careful handling and storage. Planning meals around seasonal produce can minimize waste.
- Vegan Diets: Vegan diets can present unique challenges with regards to food storage, as some vegan alternatives might be more prone to spoilage than other foods. The proper storage and handling of vegan products can significantly reduce waste.
Food Waste and Sustainability
Food waste is a significant global issue with far-reaching consequences, extending beyond the economic realm to impact environmental sustainability and human well-being. Understanding the interconnectedness of food waste and our planet’s health is crucial for developing effective solutions. This section delves into the environmental footprint of food waste, its contribution to greenhouse gas emissions, and the positive impact of reducing it on global food security.Food waste is not merely a matter of wasted resources; it represents a considerable burden on our planet’s capacity to support a growing population.
The environmental impact of this waste is substantial, encompassing issues from greenhouse gas emissions to land use and water depletion. Addressing this issue is essential for creating a more sustainable food system.
Environmental Impact of Food Waste
Food waste contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions throughout the entire food supply chain. From the initial stages of farming and transportation to the final stages of processing and disposal, every stage generates emissions. The decomposition of food waste in landfills releases methane, a potent greenhouse gas, significantly contributing to climate change. The production of food that is ultimately wasted represents a tremendous loss of resources and energy.
Food Waste and Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The process of producing, transporting, and ultimately disposing of wasted food generates significant greenhouse gas emissions. Agricultural activities, such as fertilizer production and livestock farming, require substantial energy inputs, releasing carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Transportation of food items contributes to emissions as well. Ultimately, the decomposition of food waste in landfills releases methane, a potent greenhouse gas with a higher global warming potential than carbon dioxide.
Comparison of Food Waste Reduction Strategies
The following table Artikels the environmental impact of different food waste reduction strategies, focusing on their potential to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions, conserve water resources, and protect biodiversity.
| Strategy | Greenhouse Gas Emission Reduction (Potential) | Water Conservation (Potential) | Biodiversity Protection (Potential) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Improved food storage and handling | Moderate | High | Low |
| Composting of food scraps | High | Moderate | Moderate |
| Donation of surplus food to food banks | Low | Low | Low |
| Improved food packaging and transportation | Moderate | Moderate | Low |
| Consumer education and awareness | Low to Moderate | Low | Low |
Note: The table above provides a general overview. Specific impacts will vary depending on the context and implementation details.
Food Waste Reduction and Global Food Security
Reducing food waste directly contributes to global food security by freeing up resources and improving efficiency within the food system. When less food is wasted, fewer resources are required to produce the same amount of food, potentially enabling resources to be allocated to more vulnerable populations. This approach can help address issues of food insecurity and malnutrition. The surplus food that is currently wasted can be used to feed the hungry, thus creating a more equitable distribution of food.
Epilogue

In conclusion, reducing food waste is a multifaceted challenge that requires a holistic approach. By understanding the causes, implementing effective preservation strategies, and utilizing creative repurposing techniques, you can significantly lessen your impact on the environment and save money. This guide provides the tools and knowledge needed to make informed decisions, and with conscious effort, you can transform your household into a more sustainable and resourceful environment.
Remember, small changes can make a big difference!
FAQs: How To Cut Food Waste
Q: What are some easy ways to prevent fruit and vegetable waste?
A: Store produce properly, separating fruits and vegetables, and using airtight containers can significantly extend their lifespan. Choose the right storage method based on the type of fruit or vegetable. Learn to recognize signs of ripeness and use them promptly.
Q: How can I make the most of leftover cooked food?
A: Turn leftover pasta into a flavorful soup, transform rice into a delicious fried rice dish, or use leftover roasted vegetables as a base for a hearty stew. Be creative! Explore recipes online or experiment with your own variations.
Q: What’s the best way to plan meals for a week?
A: Start by reviewing your current inventory. Create a menu that incorporates ingredients you already have, minimizing the need for unnecessary purchases. Use a template to Artikel your meals and create a detailed shopping list based on your plan. This will help you avoid buying food you don’t need.
Q: How do I store different types of dairy products effectively?
A: Proper storage is key. Wrap individual portions of cheese tightly to maintain freshness. Refrigerate milk and yogurt promptly, using appropriate containers. Different dairy items have specific storage requirements; consult online resources for detailed guidance.

