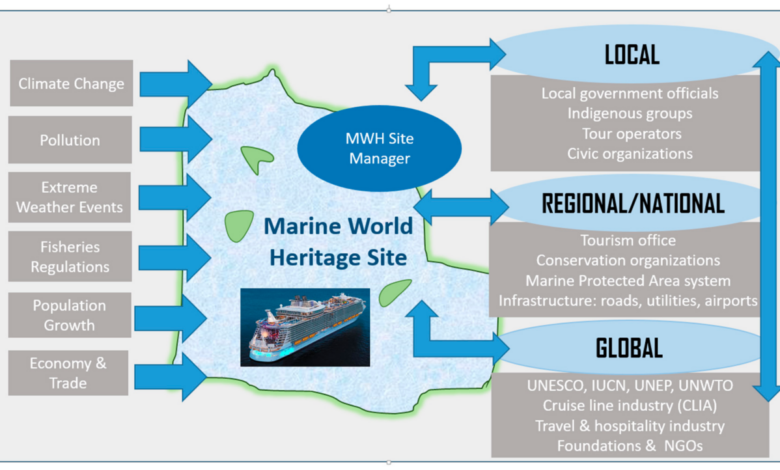
Icon of the Seas Cruise Sustainability
Icon of the Seas cruise ship sustainability is a critical issue, demanding careful consideration. This exploration delves into the environmental, social, and economic impacts of the ship’s operations, examining initiatives, technologies, and case studies to illuminate the path towards a more responsible cruise industry. The voyage towards sustainable travel is complex, but this overview aims to provide a clear picture of the challenges and potential solutions.
The Icon of the Seas, a massive cruise vessel, presents unique challenges for sustainability. From reducing its environmental footprint through innovative technologies to ensuring positive social impacts on crew, passengers, and local communities, this analysis will assess the current state and future trajectory of sustainable cruise practices. The economic aspects of sustainable operations, comparing them to traditional models, are also crucial elements in this examination.
Defining Cruise Ship Sustainability
Cruise ship sustainability is more than just a buzzword; it’s a crucial aspect of responsible tourism. It encompasses a holistic approach to minimizing the environmental footprint, ensuring fair labor practices, and fostering economic benefits for local communities while maintaining a thriving cruise industry. This commitment is essential for the long-term viability of the sector and its positive impact on destinations worldwide.Cruise ship sustainability involves carefully balancing the economic needs of the cruise lines with the environmental protection of the oceans and the social well-being of local communities.
It’s a complex interplay of responsible practices across all aspects of the cruise operation, from fuel efficiency and waste management to fair wages and community engagement.
Defining Cruise Ship Sustainability
Cruise ship sustainability is a multifaceted concept encompassing environmental, social, and economic dimensions. Environmental sustainability focuses on reducing the ship’s ecological impact, minimizing pollution, and conserving marine resources. Social sustainability prioritizes fair labor practices, community engagement, and cultural preservation. Economic sustainability ensures that cruise tourism benefits local economies, creates jobs, and supports the livelihoods of local communities. These three pillars are interconnected, and their successful integration is crucial for long-term cruise industry success.
The Icon of the Seas cruise ship’s sustainability efforts are definitely interesting, but the recent legal victory for Thailand’s Pita Limjaroenrat in the court case, which you can read about here , raises some intriguing questions about the future of environmental regulations in the region. Ultimately, the focus on sustainable practices for cruise ships like the Icon of the Seas needs to keep pace with these evolving legal and environmental landscapes.
Key Aspects of Environmental, Social, and Economic Sustainability
Environmental sustainability in cruise tourism involves reducing greenhouse gas emissions, minimizing waste generation, and promoting responsible use of marine resources. Social sustainability ensures fair wages and working conditions for crew members, and promotes respectful interactions with local communities, respecting their customs and traditions. Economic sustainability involves ensuring that cruise tourism generates positive economic benefits for local communities, creating jobs and supporting local businesses.
Sustainability Certifications and Standards, Icon of the seas cruise ship sustainability
Numerous sustainability certifications and standards exist for cruise lines, each with its own criteria and focus. These certifications act as benchmarks for measuring and promoting responsible practices. Some examples include the Global Sustainable Tourism Council (GSTC) and various environmental standards for fuel efficiency and waste management. The criteria vary, reflecting the diverse aspects of sustainability and the different priorities of different certification bodies.
Understanding the nuances of each certification is crucial for consumers seeking to support genuinely sustainable cruise operations.
Comparison of Cruise Ship Sustainability Initiatives
| Initiative | Environmental Impact | Social Impact | Economic Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Green Charter | Reduced emissions through fuel efficiency technologies, waste reduction strategies. | Fair wages and working conditions for crew members, cultural sensitivity training for staff. | Support for local businesses through procurement policies, investment in community projects. |
| Sustainable Destinations Program | Minimized environmental impact through reduced emissions, waste management, and responsible resource use. | Community engagement, partnerships with local organizations, and promotion of local culture. | Increased economic benefits for local communities through investment in infrastructure and job creation. |
| OceanWise | Reduced waste and pollution, promoting responsible fishing practices. | Fair labor practices, crew well-being, and respectful interactions with local communities. | Support for local economies, and responsible use of resources. |
This table provides a glimpse into the diverse sustainability initiatives undertaken by various cruise lines. Each initiative tackles different aspects of sustainability, emphasizing the varied nature of the challenge and the different strategies adopted.
The Icon of the Seas cruise ship’s sustainability efforts are impressive, but the recent news about Arthur Smith being hired as the Steelers offensive coordinator arthur smith hired steelers offensive coordinator makes me wonder if there’s a connection. Maybe this hiring will inspire the cruise line to further innovate in their green initiatives. Still, the Icon of the Seas’s commitment to eco-friendly practices is a step in the right direction for the industry.
Environmental Impact of Cruise Ships
Cruise ships, while offering glamorous vacations, carry a significant environmental footprint. Their sheer size and constant operation contribute to various forms of pollution, waste generation, and energy consumption, impacting delicate marine ecosystems. Understanding this impact is crucial for developing sustainable practices within the cruise industry.The environmental impact of cruise ships is multifaceted and substantial. From the exhaust fumes belching into the atmosphere to the waste discharged into the ocean, the consequences ripple through marine life and the wider environment.
Addressing these challenges requires a holistic approach, encompassing technological advancements, operational changes, and industry-wide collaboration.
Pollution Sources
Cruise ships are major contributors to air, water, and noise pollution. Their powerful engines release harmful emissions, including particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and sulfur oxides, contributing to air quality issues in coastal areas and impacting human health. These emissions also contribute to climate change. Water pollution stems from various sources, including sewage discharge, gray water from sinks and showers, and chemical cleaning agents.
Noise pollution from ship engines and activities on deck can disrupt marine animal communication and behavior, affecting their feeding, breeding, and overall well-being.
Waste Generation
Cruise ships generate substantial amounts of waste, including food scraps, garbage, and various types of industrial waste. Proper waste management is a significant challenge, especially in remote locations. Disposal practices often involve dumping waste directly into the ocean, causing harm to marine ecosystems and contributing to the accumulation of marine debris.
Energy Consumption
Cruise ships require substantial amounts of energy for propulsion, operations, and passenger amenities. The high energy demand contributes to carbon emissions and increases the overall environmental impact. Energy efficiency measures are crucial to mitigate this impact, from engine optimization to alternative energy sources.
Impact on Marine Ecosystems
Emissions, whether air, water, or noise, play a critical role in disrupting marine ecosystems. Air pollutants can lead to acid rain and affect the health of marine organisms. Water pollutants can cause eutrophication, harming coral reefs and other sensitive ecosystems. Noise pollution disrupts marine animal communication, navigation, and foraging patterns.
Methods to Reduce Impact
Reducing the environmental impact of cruise ships requires a multi-pronged strategy involving technological advancements, operational changes, and industry-wide collaboration. Implementing stringent emission standards, investing in more fuel-efficient engines, and promoting alternative propulsion systems are key steps in reducing air pollution. Advanced waste management systems and wastewater treatment facilities are necessary to minimize water pollution. Noise reduction technologies and adjusted operational patterns can minimize disturbance to marine life.
Cruise Ship Technologies for Minimizing Environmental Damage
| Technology | Description | Environmental Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Hybrid Propulsion Systems | Combining conventional engines with electric motors to optimize fuel efficiency. | Reduced fuel consumption and emissions, contributing to lower carbon footprint. |
| Alternative Fuels (LNG, Biofuels) | Using liquefied natural gas (LNG) or biofuels as alternative energy sources for ship engines. | Lower emissions of particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and sulfur oxides compared to traditional fuels. |
| Advanced Wastewater Treatment Systems | Treating wastewater before discharge to meet stricter environmental regulations. | Minimizes water pollution from sewage and gray water, protecting marine life. |
| Hull Optimization | Improving the hull design for reduced drag and enhanced fuel efficiency. | Significant fuel savings leading to reduced emissions and lower operational costs. |
| Noise Reduction Technologies | Implementing technologies to minimize engine noise and vibrations. | Reduces disruption to marine animal communication and behavior, promoting healthier marine ecosystems. |
Social and Economic Impacts of Sustainability
Cruise ship sustainability initiatives extend beyond environmental considerations. They ripple through the social fabric of crew lives, passenger experiences, and the local communities visited. These initiatives aim to create a more equitable and responsible tourism model, acknowledging the interconnectedness of the industry’s actions and their impact on all stakeholders.A truly sustainable cruise experience prioritizes social well-being alongside environmental protection.
This means considering the livelihoods of crew members, ensuring ethical labor practices, and fostering respectful interactions with local communities. Sustainable practices often translate into positive economic benefits for both the cruise lines and the destinations they visit.
Social Implications of Sustainability Initiatives
Cruise ship sustainability initiatives impact the crew, passengers, and local communities in diverse ways. Crew members often benefit from improved working conditions, fair wages, and enhanced training opportunities. Sustainable itineraries may prioritize cultural exchange and responsible tourism, offering passengers unique and enriching experiences while minimizing disruption to local communities.
The Icon of the Seas cruise ship’s sustainability efforts are definitely intriguing, but let’s be honest, sometimes a good ol’ hockey game can be more exciting. Just like the recent Oilers’ victory, where Stuart Skinner shut out the Blue Jackets oilers stuart skinner defeat blue jackets , it highlights the dedication to a winning performance. Still, back to the cruise ship, a true commitment to sustainability will help the industry progress towards a greener future.
Positive Social Impacts of Sustainable Practices
Examples of positive social impacts from sustainable practices include:
- Improved Crew Conditions: Increased wages, better accommodations, and enhanced safety measures for crew members. This can improve crew morale and retention rates, contributing to a more stable and skilled workforce. For example, a cruise line implementing a living wage for all crew can significantly improve their quality of life.
- Enhanced Passenger Experiences: Opportunities for cultural exchange, engagement with local communities, and a focus on responsible travel can create a more meaningful and enriching experience for passengers. Sustainable itineraries might feature visits to smaller, less-commercialized locations, allowing for a deeper immersion in local culture.
- Support for Local Communities: Sustainable practices often prioritize local businesses and suppliers, generating economic opportunities for the communities visited. This can include sourcing food and supplies from local vendors, supporting local artisans, and engaging with local organizations for cultural exchange.
Economic Benefits of Sustainable Cruise Ship Operations
Sustainable cruise ship operations can lead to significant economic benefits. These extend beyond just the cruise line itself, affecting local economies and the industry’s long-term viability. Cruise lines adopting sustainable practices can potentially attract a growing segment of environmentally conscious travelers, potentially generating higher revenue.
Economic Viability of Sustainable vs. Traditional Cruise Lines
The economic viability of sustainable cruise lines is increasingly competitive with traditional ones. While initial investment in sustainable technologies and practices might be higher, the long-term benefits can outweigh the short-term costs. These benefits include attracting a growing market of environmentally conscious travelers, reducing operational costs through energy efficiency, and enhancing brand reputation. Ultimately, sustainability can become a key differentiator in the market, potentially leading to higher profitability and increased brand loyalty.
Economic Advantages and Disadvantages of Implementing Sustainability Measures
| Aspect | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | Long-term cost savings from reduced fuel consumption and waste management | Higher upfront costs for new technologies and infrastructure |
| Brand Reputation | Attracting environmentally conscious travelers, increasing brand loyalty | Potential for negative perception from traditional customers who may be unfamiliar with sustainable practices |
| Operational Efficiency | Reduced fuel consumption and waste generation, lower operational costs | Potential for disruption during the transition period to new systems and technologies |
| Community Relations | Strengthening relationships with local communities, fostering positive partnerships | Potentially increased costs associated with sourcing from local suppliers and engaging with local communities |
Case Studies of Sustainable Cruise Lines

Sailing towards a greener future isn’t just a trend; it’s a necessity. Cruise lines are increasingly recognizing the importance of sustainable practices, and several have embarked on significant journeys to reduce their environmental footprint. These case studies offer valuable insights into the challenges and successes of incorporating sustainability into the cruise industry.Implementing sustainable practices in the cruise industry is a multifaceted endeavor.
It involves meticulous planning, substantial investment, and a willingness to adapt existing operational models. Cruise lines must consider environmental impact, social responsibility, and economic viability to achieve true sustainability. This section examines real-world examples to demonstrate the diverse approaches and outcomes of this evolving landscape.
Specific Examples of Sustainable Cruise Lines
Several cruise lines have demonstrated commitment to sustainability through innovative initiatives. Their efforts range from reducing emissions to supporting local communities. Understanding these examples provides crucial insights into practical strategies for the cruise industry.
- MSC Cruises: MSC Cruises has actively pursued a multi-pronged approach to sustainability. They have implemented technologies like scrubbers and alternative fuels to reduce emissions. Their commitment to reducing waste and promoting responsible tourism are further pillars of their sustainability strategy. Success factors include a clear strategic focus and significant investment in research and development for alternative fuel technologies.
Challenges include navigating the complexities of international regulations and achieving widespread adoption of their practices among other cruise lines.
- Viking Ocean Cruises: Viking Ocean Cruises prioritizes the preservation of natural environments. Their commitment to responsible tourism includes partnerships with local communities and environmental organizations. Success factors include strong community engagement, clear ethical guidelines, and a focus on environmental protection. Challenges include balancing tourism with the preservation of fragile ecosystems, especially in sensitive destinations.
- Regent Seven Seas Cruises: Regent Seven Seas Cruises has established a robust environmental management system to minimize their impact on the marine environment. They prioritize responsible waste management and reduce the use of single-use plastics. Their success is driven by comprehensive policy implementation and a culture of sustainability within the organization. Challenges include adapting their practices to meet evolving environmental standards and consumer expectations.
The Icon of the Seas cruise ship’s sustainability efforts are impressive, but what about other sectors? China’s Hefei, a city pushing for an electric vehicle (EV) economy, is a fascinating example of a city-wide shift to greener practices, offering lessons for cruise ship operations. China Hefei’s EV city economy shows how ambitious local government policies can drive a rapid shift to clean energy, which in turn might inspire similar innovative sustainability approaches for the Icon of the Seas and the cruise industry as a whole.
Innovative Approaches Employed
The cruise industry is adopting innovative solutions to address sustainability concerns. These approaches often combine technological advancements, policy changes, and community partnerships.
- Hybrid Propulsion Systems: Some cruise lines are exploring hybrid propulsion systems to reduce reliance on traditional fuels. This involves integrating various power sources to optimize fuel efficiency and minimize emissions. This approach can drastically lower greenhouse gas emissions and improve overall fuel consumption. This is a significant advancement in the cruise industry, potentially offering substantial cost savings and environmental benefits over time.
The Icon of the Seas cruise ship’s sustainability efforts are impressive, but they’re not just about the environment. Think about it – creating a luxurious, high-end cruise experience, while also minimizing impact, is a monumental task. It’s a challenge that mirrors the dedication of chefs like Gordon Ramsay, who pushes culinary boundaries in his Gordon Ramsay next level chef approach.
Ultimately, the Icon of the Seas’ success in sustainability will be measured by its long-term commitment to reducing its footprint.
- Waste Reduction Strategies: Implementing comprehensive waste management plans, including optimized waste segregation and recycling programs, can minimize the environmental impact of cruise operations. This approach reduces landfill waste and conserves resources. Effective waste management is crucial for a cruise line’s environmental footprint, offering tangible improvements in both the operational and environmental aspects of the cruise experience.
- Community Partnerships: Cruise lines are engaging with local communities to understand their needs and concerns. This approach can lead to sustainable tourism practices and support local economies. This includes initiatives that create opportunities for local communities to benefit from tourism and protect the environment.
Success and Failure Factors
Factors contributing to the success or failure of sustainable initiatives are multifaceted. Financial investment, regulatory pressures, and operational complexities are crucial elements.
Future of Sustainable Cruise Ship Tourism: Icon Of The Seas Cruise Ship Sustainability
The cruise industry, while experiencing significant growth, faces increasing pressure to adopt sustainable practices. The future of cruise ship tourism hinges on the industry’s ability to balance profitability with environmental and social responsibility. This requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing technological advancements, policy changes, and shifts in consumer preferences. The journey toward a more sustainable future is complex but ultimately crucial for the long-term viability of the cruise industry.
Projected Future of Cruise Ship Sustainability
Cruise lines are increasingly recognizing the necessity of sustainability. This is reflected in their investments in new technologies and strategies designed to reduce their environmental footprint. Expect to see a greater emphasis on alternative fuels, such as liquefied natural gas (LNG), as well as hybrid propulsion systems. These advancements will contribute to a significant reduction in greenhouse gas emissions and other pollutants.
Furthermore, waste management systems are being refined, with a focus on reducing waste generation and implementing advanced recycling techniques. Cruise lines are also striving to minimize their impact on sensitive marine ecosystems through responsible navigation and careful route planning.
Emerging Trends and Technologies
The cruise industry is actively exploring innovative technologies to enhance sustainability. This includes the development of advanced filtration systems for wastewater treatment, reducing the release of harmful pollutants into the ocean. The integration of advanced sensors and monitoring systems will enable real-time tracking of environmental conditions and allow for optimized energy consumption. Furthermore, the use of renewable energy sources, like solar panels and wind turbines, is becoming more common, demonstrating a commitment to reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Role of Government Regulations and Policies
Government regulations play a critical role in shaping the future of cruise ship sustainability. Stringent regulations on emissions, waste disposal, and noise pollution are becoming increasingly common globally. These regulations are driving the development and adoption of cleaner technologies and more sustainable practices within the industry. International collaborations and agreements are also essential for harmonizing standards and ensuring a consistent approach to sustainability across different regions.
For instance, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) plays a key role in setting global standards.
Consumer Preferences and Cruise Travel
Consumer preferences are evolving, and sustainability is becoming a significant factor in travel decisions. Cruise passengers are increasingly seeking eco-conscious options, favoring cruise lines with demonstrable commitments to environmental protection. The demand for transparency and accountability from cruise companies is rising, and consumers are more likely to choose operators with clear sustainability policies and practices. Cruise lines that prioritize sustainability are likely to attract a growing segment of environmentally conscious travelers.
Potential Future Scenarios for Cruise Ship Sustainability
The future of cruise ship sustainability is uncertain, and multiple scenarios are possible. The industry’s ability to adapt to evolving regulations, technologies, and consumer preferences will play a crucial role in shaping these scenarios.
| Scenario | Description | Key Drivers | Potential Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scenario 1: Accelerated Transition | Rapid adoption of sustainable technologies and practices driven by strong consumer demand and stringent regulations. | Strong consumer preference for sustainability, aggressive government regulations, and technological advancements. | Significant reduction in environmental impact, increased profitability for eco-conscious cruise lines, and a shift towards a more sustainable cruise industry. |
| Scenario 2: Delayed Transition | A gradual shift towards sustainability, driven by market forces and evolving consumer expectations. | Moderate consumer interest in sustainability, less stringent government regulations, and slower technological advancements. | A mixed outcome, with some cruise lines adopting sustainable practices while others lag behind. Potential for increased competition and market differentiation. |
| Scenario 3: Regulatory Push | A scenario where strict regulations mandate significant changes in cruise ship operations, forcing a rapid transition. | Strong government commitment to environmental protection and enforcement of strict regulations. | A rapid and possibly costly transition to sustainable practices, potentially impacting the profitability of some cruise lines. |
Last Point
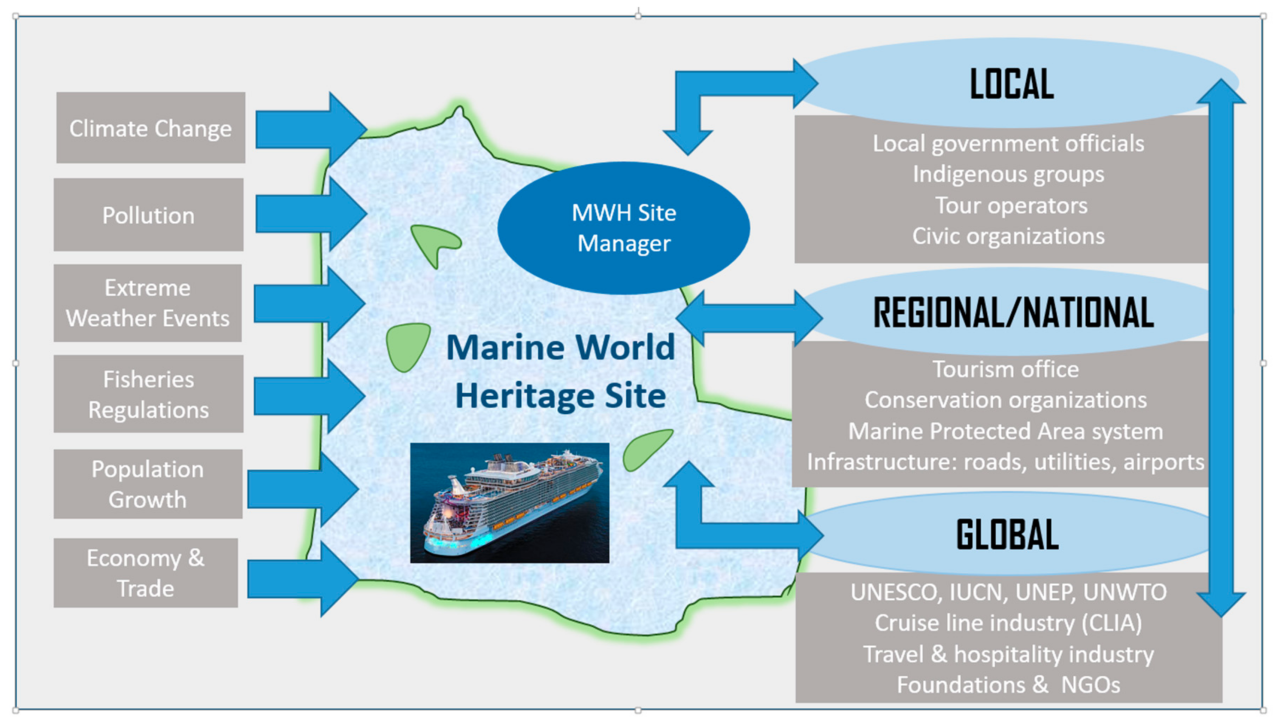
In conclusion, the Icon of the Seas cruise ship sustainability journey is multifaceted. While significant challenges remain, the potential for innovation and positive change is evident. By implementing sustainable technologies, adopting ethical social practices, and understanding the economic benefits, the cruise industry can strive towards a more environmentally conscious and socially responsible future. The future of cruise travel depends on embracing sustainability, and the Icon of the Seas presents a critical case study in this ongoing evolution.
Detailed FAQs
What are some common criticisms of cruise ship sustainability efforts?
Critics often point to the sheer volume of waste generated by cruise ships and the potential for pollution from emissions. They also question the effectiveness of current initiatives and the long-term impact of cruise ship operations on marine ecosystems. Addressing these criticisms requires a multi-faceted approach.
How do government regulations impact cruise ship sustainability?
Government regulations play a vital role in shaping the cruise industry’s sustainability practices. Regulations regarding emissions, waste disposal, and operational procedures can incentivize or hinder the implementation of sustainable technologies and practices.
What are some examples of innovative technologies used to reduce cruise ship environmental impact?
Various technologies are being developed and implemented, including improved hull designs, alternative energy sources, and waste management systems. These are crucial for minimizing the environmental footprint of cruise ships.




