Lead Poisoning in Children Intoxicacion Plomo Ninos Envenenamiento
Intoxicacion plomo ninos envenenamiento is a serious concern, affecting the health and development of young children. This comprehensive guide explores the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of lead poisoning in children. We’ll delve into the various routes of exposure, the potential long-term health consequences, and the crucial role of early detection in mitigating harm.
Understanding the different sources of lead in the environment is key to preventing this preventable health crisis. From old paint to contaminated soil, lead exposure can have devastating effects on a child’s developing body and mind. This guide offers practical information and resources for families, healthcare providers, and policymakers to work together towards a healthier future for children.
Introduction to Lead Poisoning in Children

Lead poisoning, a serious health concern, occurs when a child’s body absorbs excessive amounts of lead. This absorption can lead to a range of health problems, impacting various bodily functions, especially in the developing brain and nervous system. Understanding the routes of exposure, sources, and symptoms is crucial for early detection and intervention, safeguarding children’s well-being.
Routes of Lead Exposure in Children
Lead can enter a child’s body through various pathways. Ingestion is a common route, often involving contaminated food or water. Inhalation of lead-laden dust or fumes from sources like old paint or certain industrial processes is another significant mode of exposure. Absorption through the skin, although less frequent, is possible, particularly with prolonged contact with contaminated materials.
Common Sources of Lead in the Environment
Lead is a persistent environmental contaminant, found in various sources. Old paint, especially in older homes and buildings, is a significant source. Contaminated soil, dust, and water, potentially from industrial waste or leaded gasoline (which is now largely phased out), can also expose children. Certain imported products, particularly toys or ceramics, might contain lead, posing a risk.
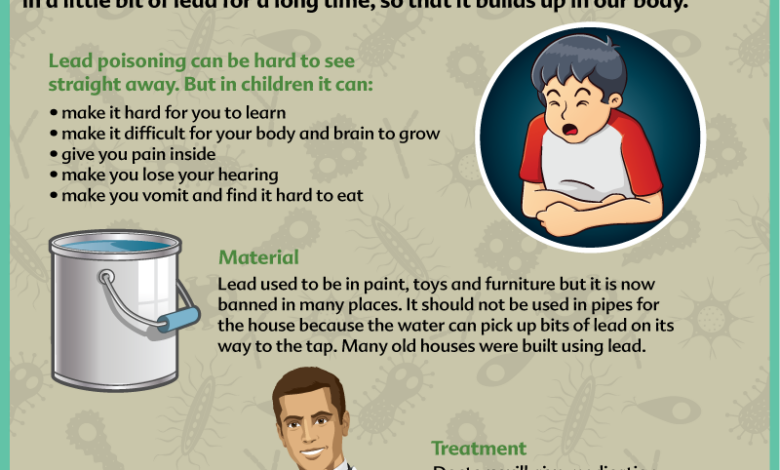
Symptoms and Signs of Lead Poisoning in Children
Lead poisoning in children can manifest with a variety of symptoms, sometimes subtle and easily overlooked. Early signs may include developmental delays, behavioral problems, decreased appetite, and learning difficulties. More severe cases can lead to anemia, abdominal pain, neurological problems, and even coma. The severity of symptoms correlates with the level of lead exposure and the child’s age.
Importance of Early Detection and Intervention
Early detection of lead poisoning is critical. Children who are identified early and receive appropriate treatment have a better chance of avoiding long-term health consequences. Lead poisoning can significantly impact a child’s cognitive development and overall health, making timely intervention paramount.
| Lead Source | Exposure Route | Symptoms | Prevention Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Old paint (in older homes) | Ingestion (eating paint chips), inhalation (breathing dust), skin absorption (contact) | Developmental delays, learning disabilities, behavioral problems, abdominal pain, anemia, neurological problems | Regular home inspections for lead-based paint. Encapsulate or remove lead-based paint if present. Regular cleaning and dust control in homes. Protect children from contact with peeling paint. |
| Contaminated soil/dust | Ingestion (eating contaminated soil), inhalation (breathing dust) | Developmental delays, learning disabilities, anemia, abdominal pain, neurological problems | Avoid playing in contaminated soil. Regular soil testing in potentially contaminated areas. Regular cleaning and dust control. Wash hands thoroughly after playing outdoors. |
| Contaminated water | Ingestion | Lead poisoning may be asymptomatic in some cases; however, it can lead to developmental delays, anemia, and other health issues | Use a water filter that removes lead. Inspect the plumbing system for lead pipes. Avoid drinking water from standing water sources, as these may contain lead. |
| Certain imported products (toys, ceramics) | Ingestion (eating or chewing on contaminated toys or ceramics) | Developmental delays, learning disabilities, abdominal pain, anemia | Avoid use of imported products without a certification stating the product is lead-free. Inspect imported products carefully before use. |
Health Impacts and Consequences
Lead poisoning in children is a serious threat to their overall development, impacting various aspects of their health, from cognitive function to physical growth. Early detection and intervention are crucial to mitigate the long-term consequences and promote optimal health outcomes. The effects of lead exposure can be subtle, making it important to be aware of the potential risks and symptoms.Lead, a heavy metal, interferes with the normal functioning of various body systems.
It accumulates in the body over time, particularly in the bones and soft tissues, gradually causing damage. Children are particularly vulnerable because their bodies are still developing, making them more susceptible to the toxic effects of lead.
Long-Term Developmental Effects
Lead exposure during childhood can have profound and lasting effects on a child’s development. The brain is particularly susceptible to damage, potentially leading to long-term cognitive impairments. These impairments can affect a child’s ability to learn, reason, and perform in school.
Neurological Effects, Including Cognitive Impairment
Lead’s toxicity significantly impacts the developing nervous system. It can disrupt the communication pathways within the brain, leading to a range of neurological problems. Cognitive impairment is a common outcome, manifesting as difficulties with attention, memory, and learning. Children exposed to lead may struggle in school, exhibit behavioral problems, and have difficulty with social interactions. For example, a child with lead poisoning may have difficulty following instructions or understanding complex concepts, which could impact their academic performance and future opportunities.
Lead poisoning in children is a serious concern, impacting their development and well-being. While global events like the recent Biden-Israel-Hamas cease fire dominate headlines, we shouldn’t lose sight of the critical need for preventative measures against lead poisoning, which can have long-lasting negative effects. Protecting our children from this preventable hazard remains a top priority.
Impact on Behavioral Development
Lead exposure can also disrupt a child’s behavioral development. Children exposed to lead may exhibit hyperactivity, aggression, and impulsivity. These behavioral issues can affect their ability to interact with others and their overall well-being. Difficulties with emotional regulation and social skills can also be observed in lead-exposed children.
Impact on Physical Growth
Lead’s impact on physical growth is also significant. It can hinder the development of bones and teeth, potentially leading to stunted growth and weakened skeletal structures. A child with lead poisoning might experience delays in reaching developmental milestones related to height and weight.
Impact on Kidney Function
Lead exposure can severely affect kidney function. The kidneys are responsible for filtering waste products from the blood. Lead can damage the kidneys, potentially leading to kidney failure. Chronic kidney disease is a serious complication of lead exposure, requiring ongoing medical attention.
Summary Table of Impacts
| Body System | Impact of Lead | Severity of Impact | Preventive Measures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nervous System | Cognitive impairment, attention deficits, learning disabilities, behavioral problems | High | Regular health check-ups, minimizing exposure to lead sources |
| Behavioral Development | Hyperactivity, aggression, impulsivity, emotional problems | High | Lead testing for children at risk, removal of lead hazards |
| Physical Growth | Stunted growth, weakened skeletal structures | Moderate to High | Lead testing for children at risk, removal of lead hazards |
| Kidney | Kidney damage, chronic kidney disease, kidney failure | High | Lead testing for children at risk, removal of lead hazards |
Diagnosis and Assessment: Intoxicacion Plomo Ninos Envenenamiento
Diagnosing lead poisoning in children requires a multifaceted approach, combining various tests and assessments. Early detection is crucial to mitigating the long-term health impacts of lead exposure. Accurate diagnosis hinges on meticulous collection of medical history, a thorough physical examination, and appropriate laboratory testing. The severity of lead poisoning can vary significantly, impacting different organ systems and leading to a range of symptoms.
Common Diagnostic Procedures, Intoxicacion plomo ninos envenenamiento
A comprehensive evaluation for lead poisoning involves a systematic approach. This includes a detailed history of potential lead exposure, considering factors like environmental conditions, diet, and household materials. A physical examination helps identify any existing symptoms or signs that might indicate lead toxicity. Crucially, laboratory tests are essential for quantifying lead levels in the body.
Sadly, lead poisoning in children is a serious concern, and preventing it is crucial. While the focus is often on environmental factors, it’s interesting to consider how the professional sports world, like Anthony Kim’s LIV Golf Return A Detailed Look, Anthony Kims LIV Golf Return A Detailed Look might be seemingly unrelated yet potentially impact public health priorities.
Ultimately, the need to address lead poisoning in children remains paramount.
Significance of Blood Lead Levels
Blood lead levels (BLLs) are the cornerstone of lead poisoning diagnosis. Elevated BLLs, often exceeding a certain threshold, are strong indicators of lead exposure. Understanding the context of the BLL in relation to the child’s age and potential exposure history is crucial. Interpreting BLLs requires considering the child’s overall health status and the presence of other underlying conditions.
Importance of Proper Testing Procedures and Interpretation
Accurate blood lead testing relies on precise collection and handling of blood samples. Proper laboratory procedures and quality control measures are vital to ensure reliable results. The interpretation of BLLs should consider the child’s age, the potential sources of lead exposure, and any other relevant medical information. The results should be interpreted in consultation with the child’s healthcare provider, who can provide context and guidance on appropriate management strategies.
Role of Medical Professionals
Healthcare professionals play a pivotal role in assessing children for lead poisoning. Pediatricians, family doctors, and other medical personnel should be aware of the signs and symptoms of lead poisoning. Early recognition of potential risks and prompt referral to specialists are crucial for effective management. They should be adept at interpreting test results, advising on necessary interventions, and coordinating care with other specialists as needed.
Types of Tests Used for Lead Detection
Several types of tests can aid in the detection of lead exposure. Each test has specific procedures, expected results, and significance. A crucial aspect of these tests is their accuracy and reliability, enabling clinicians to make informed decisions.
| Test Type | Procedure | Expected Result | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blood Lead Test (BLL) | A blood sample is drawn and analyzed for lead content. | Elevated blood lead levels (above a certain threshold). | Directly indicates the presence and level of lead in the child’s bloodstream. This is the primary diagnostic tool. |
| Urine Lead Test | A urine sample is collected and analyzed for lead content. | Elevated levels of lead in the urine. | Provides a measure of lead excretion and can be helpful in assessing recent exposure. |
| Environmental Assessment | Evaluation of the child’s home and surroundings for potential sources of lead exposure. | Identification of lead-based paint, contaminated dust, or other lead sources. | Identifies the root cause of lead exposure and allows for targeted intervention. |
Prevention and Control Measures

Protecting children from lead poisoning requires a multifaceted approach encompassing individual actions, community efforts, and robust environmental regulations. Early intervention and proactive measures are crucial to minimizing the devastating health impacts of lead exposure. Addressing the root causes of lead contamination and educating families about prevention strategies are essential components of a comprehensive strategy.
Effective Strategies for Preventing Lead Exposure
Preventing lead exposure involves a combination of strategies focusing on reducing exposure in the environment and promoting safer practices within the home and community. A primary focus should be on removing lead sources, especially in older homes. Lead-based paint, often found in older buildings, is a significant source of lead exposure. Regular maintenance and proper handling of these materials are essential to prevent lead dust from contaminating the air and surfaces.
Lead poisoning in children is a serious issue, and the devastating effects on young lives are heartbreaking. It’s easy to see how the pain of such a situation could connect to the profound grief experienced by people, like in the case of Sloane Crosley, as explored in the article “grief is for people sloane crosley” here. Ultimately, though, the focus must return to the crucial need for prevention and awareness surrounding lead poisoning in children.
Children should be educated about the dangers of lead and encouraged to practice good hygiene, like handwashing.
Childhood lead poisoning, or intoxicacion plomo ninos envenenamiento, is a serious concern. It’s heartbreaking to see how environmental factors can affect young lives. This tragic issue unfortunately parallels the recent news surrounding the armorer Alec Baldwin’s involvement in the Rust shooting, a situation that highlights the potential for accidents and negligence to have devastating consequences. The need for preventative measures against lead poisoning remains crucial, emphasizing the importance of safe environments and proper regulations for all.
It’s crucial to prioritize children’s health and safety, just as it’s important to understand the circumstances surrounding tragic events like the armorer alec baldwin rust shooting and take preventative measures.
Role of Environmental Regulations
Environmental regulations play a crucial role in controlling lead contamination. These regulations establish permissible levels of lead in various products and environments. Stringent regulations on lead in gasoline, paint, and other consumer products are critical in reducing lead exposure. Government agencies often work to enforce these regulations through inspections and monitoring. Stricter regulations and increased enforcement help reduce lead exposure across the population, including children.
Importance of Lead-Safe Housing Practices
Lead-safe housing practices are critical for protecting children from lead exposure. These practices encompass a range of measures to identify and mitigate lead hazards in older homes. Professional inspections can identify lead-based paint and other lead sources, and remediation methods can remove these hazards. Renovation projects should adhere to strict lead-safe practices to avoid reintroducing lead into the environment.
By implementing lead-safe housing practices, families can create a healthier environment for their children.
Significance of Regular Health Checks and Monitoring
Regular health checks and monitoring are essential for identifying lead poisoning in children at an early stage. Blood lead level tests can detect lead exposure, and healthcare providers can provide guidance on prevention and management strategies. Early detection and intervention are crucial in minimizing the long-term health effects of lead exposure. The earlier lead poisoning is identified, the better the chances of mitigating potential health consequences.
Prevention Strategies Table
| Prevention Strategy | Description | Target Population | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lead-Safe Housing Practices | Identifying and removing lead-based paint and other lead hazards in older homes. | Children living in older housing, especially those with pre-1978 construction. | High; can significantly reduce exposure when properly implemented. |
| Environmental Regulations | Setting permissible levels of lead in various products and environments, including gasoline, paint, and plumbing. | Entire population, especially children in communities with potential lead sources. | Moderate to High; depends on the stringency and enforcement of regulations. |
| Regular Health Checks | Blood lead level testing and monitoring to detect lead exposure in children. | Children at risk of lead exposure, particularly those living in older housing or communities with high lead contamination. | High; allows for early detection and intervention. |
| Educational Initiatives | Educating families and communities about the dangers of lead and preventive measures. | Parents, caregivers, and communities with potential lead exposure concerns. | Moderate to High; increases awareness and adoption of preventive measures. |
Treatment and Management
Lead poisoning in children, if left untreated, can have severe and long-lasting consequences. Prompt and effective treatment is crucial to minimizing damage and improving outcomes. Treatment approaches focus on removing lead from the body, managing symptoms, and providing supportive care to address any complications.Effective treatment for lead poisoning involves a multi-faceted approach tailored to the child’s specific situation.
This includes identifying and removing the source of lead exposure, administering chelation therapy, and providing supportive care to manage symptoms and potential complications. Long-term follow-up is essential to monitor the child’s progress and address any ongoing issues.
Chelation Therapy
Chelation therapy is a cornerstone of lead poisoning treatment. It involves administering medications that bind to lead in the blood, allowing it to be excreted from the body. This process, often referred to as chelation, effectively removes lead from the body’s tissues. The most commonly used chelating agents are EDTA, DMSA, and succimer. The choice of chelating agent and specific dosage depends on factors such as the child’s age, the level of lead exposure, and the presence of any other health conditions.
For instance, succimer is often preferred for children under 6 years old due to its safety profile and effectiveness.
Supportive Care
Supportive care plays a vital role in managing lead poisoning. This includes addressing any symptoms the child may be experiencing, such as abdominal pain, fatigue, or neurological problems. Supportive care might involve pain management, nutritional support, and monitoring for complications. Adequate hydration is crucial. The goal is to maintain the child’s overall well-being and address the symptoms while the lead is being removed.
In severe cases, hospitalization might be necessary to monitor the child’s condition closely and provide intensive care.
Potential Complications of Lead Poisoning and Treatment
Lead poisoning can cause a range of complications, impacting various organ systems. Neurological problems, such as developmental delays, learning disabilities, and behavioral issues, are common. Gastrointestinal issues, renal damage, and anemia can also occur. Treatment itself, particularly chelation therapy, can have potential side effects, including nausea, vomiting, headache, and skin rash. In some cases, more serious complications, such as kidney problems or allergic reactions, can arise.
Lead poisoning in children is a serious issue, unfortunately, a tragic one that often goes unnoticed. It’s a sobering reminder of the need for vigilance in protecting our youngest. Interestingly, some parallels can be drawn between the emotional turmoil explored in Taylor Swift’s music, particularly in the “Tortured Poets Department Taylor Swift A Deep Dive” Tortured Poets Department Taylor Swift A Deep Dive analysis, and the devastating impact of environmental factors on child development.
Ultimately, both highlight the importance of recognizing and addressing vulnerabilities, whether in the realm of pop culture or the realm of public health.
Importance of Long-Term Follow-Up
Long-term follow-up is essential to monitor the child’s progress and detect any lingering effects of lead poisoning. Regular medical checkups are crucial to assess the child’s developmental milestones, cognitive function, and overall health. The follow-up period should be tailored to the severity of the lead exposure and the child’s response to treatment. Early intervention and ongoing monitoring can help mitigate long-term complications and ensure the child reaches their full potential.
Treatment Methods Summary
| Treatment Method | Description | Effectiveness | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chelation Therapy (e.g., EDTA, DMSA, succimer) | Medications that bind to lead in the blood, aiding its excretion. | Generally effective in reducing blood lead levels. Effectiveness varies depending on the specific chelating agent and the level of lead exposure. | Nausea, vomiting, headache, skin rash, potential kidney problems, allergic reactions. |
| Supportive Care | Addressing symptoms, maintaining hydration, nutritional support, and monitoring for complications. | Essential for managing symptoms and overall well-being during and after treatment. | Dependent on the specific supportive care measures implemented, but can potentially include side effects associated with pain management or other medications. |
| Removal of Exposure Source | Identifying and eliminating the source of lead exposure (e.g., old paint, contaminated soil). | Crucial for preventing further lead absorption. | Dependent on the method of lead source removal. If improperly done, can lead to additional risks. |
Case Studies and Examples
Understanding lead poisoning requires examining real-world scenarios. Case studies offer invaluable insights into the symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and long-term effects of lead exposure in children. These examples highlight the importance of early detection and preventative measures to mitigate the devastating consequences of lead poisoning.
A Case Study of Acute Lead Poisoning
Lead poisoning, even in moderate levels, can cause significant health problems in children. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment and management.
A 5-year-old child, living in a house with old lead-based paint, presented with significant developmental delays. The child exhibited behavioral problems, such as irritability and aggression. Physical examination revealed anemia and abdominal pain. Blood tests confirmed elevated lead levels, indicating acute lead poisoning. The child was immediately admitted to the hospital for chelation therapy.
Chelation therapy is a process that removes lead from the body. The treatment involved administering medications to bind and remove lead from the child’s blood. After several weeks of treatment and supportive care, the child’s lead levels decreased, and the symptoms gradually subsided. Regular follow-up visits were scheduled to monitor the child’s progress and ensure the lead levels remained within a safe range.
Long-Term Impacts of Lead Exposure
Children exposed to lead can experience lasting consequences, impacting their cognitive development and overall well-being. A case study illustrating this involves a child with a history of low-level lead exposure during early childhood. The child showed signs of learning difficulties, particularly in math and language arts. They also demonstrated impaired fine motor skills and attention deficits. Despite receiving prompt medical attention and treatment, the long-term impact of lead exposure persisted.
Educational interventions and specialized therapies helped mitigate the effects, but the child still faced challenges in academic performance and social-emotional development compared to their peers.
A Hypothetical Family Case
Imagine a family with a young child living in an older home. The family is unaware of the potential for lead-based paint in their home. The child exhibits developmental delays, fatigue, and persistent abdominal pain. Blood tests reveal elevated lead levels. The family is advised to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate course of action and undergo necessary testing.
The family is educated about lead-safe practices and advised to identify and eliminate potential sources of lead exposure in the home.
Monitoring and Management of Lead Exposure
Regular monitoring of lead levels in a child’s blood is essential, particularly for those at risk. This includes blood tests at appropriate intervals to assess the effectiveness of treatment and prevention strategies. The child’s overall health, development, and behavioral changes are closely monitored, with adjustments to the treatment plan based on these observations. The monitoring process also includes educating the family on lead-safe practices in the home.
Detailed Case Study: Lead Exposure from Contaminated Soil
A 3-year-old boy, residing in a neighborhood with known soil contamination, began exhibiting symptoms of anemia and lethargy. Persistent irritability and difficulty concentrating were also observed. Regular blood tests revealed elevated lead levels. The child’s history indicated frequent outdoor play in the contaminated soil.
- Patient History: The child lived in a house built before 1978, and had been playing frequently in the yard.
- Symptoms: The child exhibited irritability, difficulty concentrating, and lethargy, as well as anemia. He also had abdominal pain.
- Diagnosis: Blood tests revealed elevated lead levels. Environmental investigation identified contaminated soil in the backyard as a source of exposure.
- Treatment: Chelation therapy was initiated to reduce the lead levels in the child’s blood. The family was advised on ways to minimize further exposure, including avoiding contact with the contaminated soil, and the home was assessed for potential lead-based paint hazards. The contaminated soil in the yard was remediated.
Resources and Support Systems
Navigating the complexities of lead poisoning can be overwhelming for families. Understanding available resources and support systems is crucial for effective management and ensuring the best possible outcomes for affected children. This section details the vital organizations and institutions dedicated to providing assistance, information, and support.
Organizations Supporting Families
Numerous organizations and institutions play a critical role in supporting families facing lead poisoning. These groups offer invaluable guidance, resources, and a network of support, helping families navigate the challenges and complexities of this health crisis.
- Public Health Departments: Local and state public health departments are often the first point of contact for families concerned about lead exposure. They provide vital information on lead poisoning prevention, early detection, and treatment options. They can also connect families with relevant specialists and support services within the community. Public health departments are often equipped to conduct community outreach programs to raise awareness and educate residents about lead hazards in their environment.
This proactive approach is crucial for preventing future exposures and protecting vulnerable populations.
- Poison Control Centers: Poison control centers are critical resources for families dealing with suspected lead poisoning. They provide immediate assistance, guidance, and referrals to appropriate healthcare providers and support services. These centers play a vital role in providing prompt intervention, which can be crucial in mitigating the impact of lead exposure.
- Nonprofit Organizations: Numerous nonprofits focus specifically on lead poisoning prevention and treatment. These organizations often conduct community outreach, provide educational materials, and offer financial assistance to families. They also play a significant role in advocacy efforts, working to raise awareness and influence policy changes to reduce lead exposure.
- Medical Professionals: Pediatricians, family doctors, and other medical professionals play a vital role in identifying and managing lead poisoning. They provide diagnosis, treatment, and ongoing monitoring of affected children. They also serve as a crucial link to other resources and support systems.
Local and National Resources
Access to reliable information and support is critical for families affected by lead poisoning. This section Artikels available resources, encompassing local and national organizations.
- Local Public Health Departments: These departments are typically the first point of contact for local resources, offering assistance, support, and referrals. Their role extends to identifying local sources of lead contamination and implementing preventative measures within the community.
- National Lead Information Center: The National Lead Information Center provides a centralized source of information on lead poisoning prevention, treatment, and research. It offers educational materials, fact sheets, and guidance to families and professionals alike.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): The CDC is a national leader in research and prevention of lead poisoning. They offer comprehensive resources, guidelines, and educational materials to assist individuals and communities in reducing exposure to lead.
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): The EPA is responsible for setting and enforcing regulations to protect public health from environmental hazards, including lead. They provide valuable information and resources related to lead-safe practices, and they also oversee lead-based paint programs.
Support Groups
Support groups provide a critical network of understanding and encouragement for families navigating the challenges of lead poisoning. They offer a safe space for sharing experiences, exchanging advice, and receiving emotional support from others facing similar circumstances.
- Online Support Groups: Online forums and social media groups dedicated to lead poisoning can provide a virtual space for families to connect and share experiences. These online communities can offer a sense of belonging and shared understanding, enabling families to feel less isolated.
- Local Support Groups: Some communities have established local support groups specifically for families dealing with lead poisoning. These groups provide an opportunity to meet other families in similar situations and receive support in person.
Organizations Dedicated to Combating Lead Poisoning
A range of organizations actively work to address the issue of lead poisoning. Their efforts encompass prevention, research, and advocacy.
- The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP): The AAP actively promotes the prevention and management of lead poisoning in children, offering guidelines and recommendations for healthcare providers and families.
- The National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH conducts research on lead exposure and its effects on human health. Their research informs strategies for prevention, treatment, and long-term health management.
Closing Notes

In conclusion, lead poisoning in children is a complex issue demanding multifaceted solutions. From proactive prevention strategies to comprehensive treatment plans, a multidisciplinary approach is vital to ensuring the well-being of affected children. By raising awareness, promoting early detection, and supporting families through the process, we can work towards a future where children are protected from the harmful effects of lead exposure.
FAQ Guide
What are the common symptoms of lead poisoning in children?
Symptoms can vary, but some common signs include developmental delays, learning difficulties, behavioral problems, and abdominal pain. In severe cases, anemia and neurological issues can arise.
How can I prevent my child from lead poisoning?
Prevention is key. Regular home inspections, especially in older homes, are crucial. Ensuring proper handling of potential sources, like old paint or contaminated soil, is vital. Lead-safe practices and environmental regulations are also essential.
What types of tests are used to diagnose lead poisoning?
Blood lead level tests are the primary diagnostic tool. Other tests may include urine tests or X-rays, depending on the specific situation.
What resources are available for families dealing with lead poisoning?
Numerous organizations and support groups offer information, guidance, and resources for families. Check with local health departments or contact national organizations dedicated to lead poisoning prevention.

